A district serves as a defined administrative or geographical area within a city, state, or country, often established for governance, planning, or statistical purposes. Understanding the specific functions and boundaries of your district can enhance community engagement and access to local services. Discover more about how districts impact everyday life and their significance in the complete article.
Table of Comparison
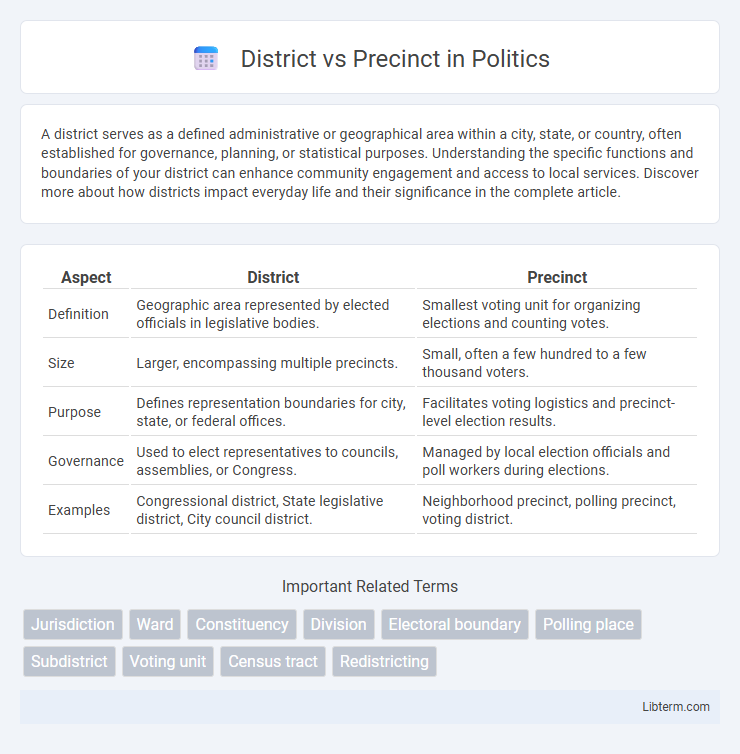
| Aspect | District | Precinct |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Geographic area represented by elected officials in legislative bodies. | Smallest voting unit for organizing elections and counting votes. |
| Size | Larger, encompassing multiple precincts. | Small, often a few hundred to a few thousand voters. |
| Purpose | Defines representation boundaries for city, state, or federal offices. | Facilitates voting logistics and precinct-level election results. |
| Governance | Used to elect representatives to councils, assemblies, or Congress. | Managed by local election officials and poll workers during elections. |
| Examples | Congressional district, State legislative district, City council district. | Neighborhood precinct, polling precinct, voting district. |
Understanding Districts and Precincts
Districts are larger geopolitical areas designed for administrative, legislative, or electoral purposes, often encompassing multiple communities or precincts. Precincts represent smaller subdivisions within districts, serving as the primary units for voting and local organization, typically reflecting neighborhood boundaries. Understanding the hierarchical relationship between districts and precincts is essential for effective governance, resource allocation, and electoral process management.
Definition of a District
A district is a defined geographical area established for administrative, political, or electoral purposes, often encompassing multiple neighborhoods or precincts. It serves as a primary unit for representation in government, such as a congressional or legislative district, where elected officials represent the constituents within its boundaries. Districts vary in size and population but are designed to ensure organized governance and fair representation.
Definition of a Precinct
A precinct is a defined geographic area within a city or district used primarily for administrative, law enforcement, or electoral purposes. It represents the smallest unit of local governance or policing, often serving as the boundary for organizing voting locations and police patrols. Unlike districts, which cover larger regions and multiple precincts, precincts enable precise management and resource allocation at the neighborhood level.
Key Differences Between Districts and Precincts
Districts typically refer to larger geographic areas used for administrative, political, or electoral purposes, encompassing multiple neighborhoods or precincts. Precincts are smaller subdivisions within districts, often serving as fundamental units for voting and local law enforcement jurisdictions. The key difference lies in their scale and function: districts organize broader governance and representation, while precincts facilitate more localized management and electoral processes.
Role of Districts in Elections
Districts serve as fundamental electoral units that define the boundaries for legislative representation, determining which constituents vote for specific elected officials such as state legislators or members of Congress. They enable the organization of elections by grouping voters into geographically defined areas, ensuring equitable representation based on population. Unlike precincts, which are smaller units used primarily for managing polling locations, districts shape the broader political landscape and influence the distribution of political power.
Role of Precincts in Voting Processes
Precincts serve as the foundational units in voting processes, organizing voters into manageable geographic areas to ensure efficient ballot distribution and accurate vote counting. Each precinct operates polling stations where residents cast their votes, facilitating local administration of elections and minimizing logistical challenges. This granular division enhances election integrity by enabling precise voter registration, monitoring turnout, and addressing disputes at a community level.
How Districts Are Formed
Districts are formed through a legal and political process called redistricting, which typically occurs every ten years following the decennial census to reflect population changes and maintain equal representation. State legislatures or independent commissions use demographic data, geographic boundaries, and community interests to draw district lines, ensuring compliance with the Voting Rights Act and preventing gerrymandering. Unlike precincts, which are smaller administrative units for organizing voters during elections, districts determine legislative representation and policy-making jurisdictions.
How Precincts Are Organized
Precincts are the smallest electoral units, typically organized by geographic boundaries such as neighborhoods or voting districts to facilitate local voting and administrative efficiency. Each precinct contains designated polling places and is managed by election officials who oversee voter registration, ballot distribution, and vote counting. These precincts collectively form larger districts that aggregate voting results for county, state, or federal elections.
Impact on Voter Representation
Districts create larger electoral areas representing diverse populations, which can dilute minority voting power but enable broader policy focus. Precincts are smaller, more localized units that allow for more precise voter targeting and can improve accessibility and responsiveness in elections. The choice between districts and precincts directly influences the effectiveness of voter representation and the equity of political influence.
District vs Precinct: Which Matters More?
Districts define larger political or administrative boundaries that influence resource allocation, representation, and policy-making, while precincts are smaller, localized voting units essential for organizing elections and managing voter rolls. Districts matter more in shaping legislative influence and governance outcomes, whereas precincts primarily facilitate the logistical aspects of voting and community-level engagement. Understanding the distinct roles of districts and precincts clarifies their impact on political representation and electoral processes.
District Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com