A whip is a flexible weapon or tool used historically for animal herding, punishment, and performance arts. Its design typically features a long, tapered piece of leather or synthetic material that creates a cracking sound when snapped. Discover more about the history, types, and uses of whips in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
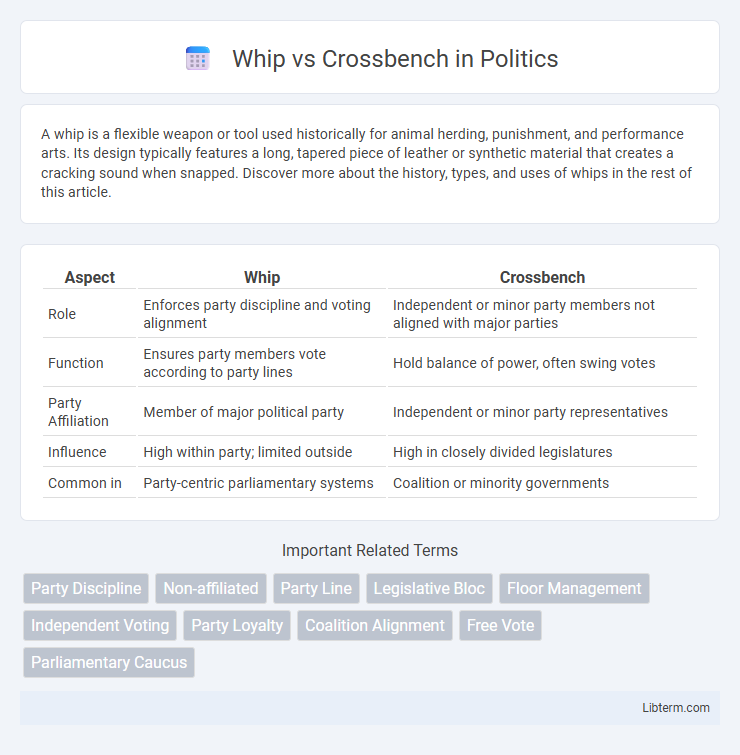
| Aspect | Whip | Crossbench |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Enforces party discipline and voting alignment | Independent or minor party members not aligned with major parties |
| Function | Ensures party members vote according to party lines | Hold balance of power, often swing votes |
| Party Affiliation | Member of major political party | Independent or minor party representatives |
| Influence | High within party; limited outside | High in closely divided legislatures |
| Common in | Party-centric parliamentary systems | Coalition or minority governments |
Understanding the Role of a Whip in Parliament
A whip in parliament plays a critical role in maintaining party discipline by ensuring members attend and vote according to party lines, thus facilitating legislative agendas. Unlike crossbenchers, who are independent or minor party members with flexible voting, whips coordinate party strategies and monitor member compliance to strengthen political cohesion. Effective whip management is essential for passing bills and sustaining government stability in parliamentary systems.
What is the Crossbench?
The Crossbench refers to independent or minor party members in a parliamentary system who do not align strictly with the government or opposition parties, often holding a balance of power in legislative decisions. They provide critical independent scrutiny and debate, influencing policy outcomes by supporting or opposing legislation on a case-by-case basis. Unlike party Whips, who enforce voting discipline within their ranks, Crossbenchers exercise greater voting autonomy, representing diverse interests beyond party lines.
Key Responsibilities: Whip vs Crossbench
Whips are responsible for party discipline, ensuring members attend votes and adhere to party policies, acting as a liaison between party leadership and members. Crossbenchers, as independent or minor party members, focus on representing diverse viewpoints without party constraints, often holding balance of power in legislative decisions. Their key role involves scrutinizing government legislation and influencing outcomes through negotiation rather than enforcing party cohesion.
How Whips Influence Parliamentary Voting
Whips play a crucial role in parliamentary voting by ensuring party discipline and coordinating members to vote according to party lines, thereby maintaining government stability. They use strategies such as issuing voting instructions, monitoring attendance, and negotiating with dissenters to secure majority support for key legislation. Crossbench members, who remain independent of party whips, often act as pivotal votes in closely contested decisions, influencing outcomes through their discretionary support.
The Independence of Crossbench Members
Crossbench members maintain independence by not adhering to party whips, allowing them to vote according to personal judgment or constituency interests. This autonomy facilitates unbiased decision-making, enhancing the diversity of parliamentary debate and scrutiny. Their independent stance often positions them as crucial swing votes on contentious legislation.
Party Loyalty: Whip’s Impact on Discipline
Whips play a crucial role in maintaining party loyalty by enforcing discipline through strategic communication, vote monitoring, and pressure tactics within parliamentary systems. Crossbench members, often independent or from minor parties, experience greater freedom to vote according to personal or constituency interests due to the absence or minimal influence of a whip system. This dynamic highlights how the whip's impact significantly strengthens party cohesion and legislative predictability, contrasting with the crossbench's more autonomous voting behavior.
Crossbench Power in Close Votes
Crossbenchers hold significant sway in close votes within the UK Parliament due to their independent stance outside party whips, enabling them to act as pivotal swing votes. Their power is amplified in hung parliaments or situations with narrow majorities, where government and opposition numbers are almost evenly split. This leverage forces major parties to negotiate and build consensus, underscoring the strategic importance of crossbench votes in legislative outcomes.
Historical Evolution of Whip and Crossbench Roles
The historical evolution of whip and crossbench roles in parliamentary systems reflects the increasing complexity of legislative governance and party discipline. Whips originated as party enforcers responsible for ensuring member attendance and voting alignment, evolving into key figures managing legislative agendas and internal cohesion. Crossbenchers historically emerged as independent or minor party members holding balance of power, their roles evolving from peripheral critics to influential swing votes shaping policy outcomes.
Whip and Crossbench: Case Studies and Examples
In parliamentary systems, a whip ensures party discipline by managing members' voting behavior, exemplified by the UK Conservative Party's strict voting instructions to maintain government stability during Brexit debates. Crossbenchers, typically independent or minor party members in the UK House of Lords, provide crucial swing votes, as seen when Crossbench peers influenced the passage of key amendments on environmental legislation. The interplay between whips maintaining cohesion and crossbenchers exercising independent judgment highlights the balance of power and influence in legislative processes.
The Future of Parliamentary Discipline and Independence
The future of parliamentary discipline hinges on balancing the whip system's enforcement power with the crossbenchers' independence, promoting democratic accountability and diverse representation. Reform efforts aim to reduce excessive party control by whips, ensuring crossbench MPs can vote freely while maintaining parliamentary cohesion. This evolution supports enhanced legislative scrutiny and strengthens the integrity of democratic processes within modern parliaments.
Whip Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com