Smart power combines the strategic use of both hard power, such as military force, and soft power, like diplomacy and cultural influence, to achieve national or organizational goals effectively. It emphasizes adaptability and understanding the context to tailor responses that maximize impact while minimizing conflict. Discover how smart power can transform your approach to global challenges in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
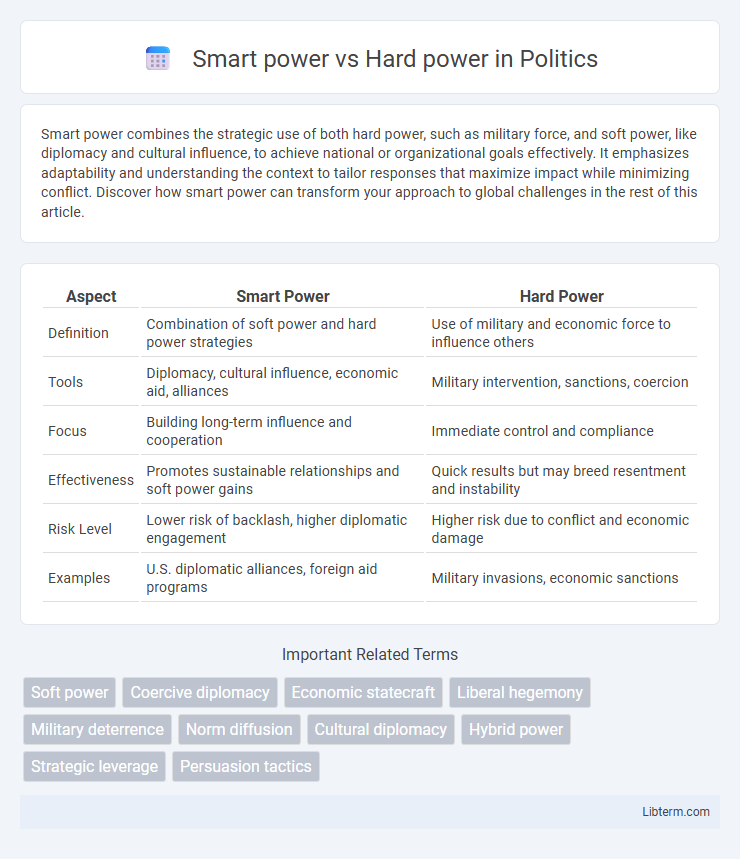
| Aspect | Smart Power | Hard Power |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combination of soft power and hard power strategies | Use of military and economic force to influence others |
| Tools | Diplomacy, cultural influence, economic aid, alliances | Military intervention, sanctions, coercion |
| Focus | Building long-term influence and cooperation | Immediate control and compliance |
| Effectiveness | Promotes sustainable relationships and soft power gains | Quick results but may breed resentment and instability |
| Risk Level | Lower risk of backlash, higher diplomatic engagement | Higher risk due to conflict and economic damage |
| Examples | U.S. diplomatic alliances, foreign aid programs | Military invasions, economic sanctions |
Understanding Smart Power and Hard Power
Smart power combines the strategic use of both hard power, involving military force and economic sanctions, and soft power, which leverages cultural influence and diplomacy to achieve foreign policy goals. Hard power emphasizes coercion and tangible resources like armed forces and economic leverage to compel action, while smart power prioritizes a balanced approach that maximizes the strengths of both methods for effective international relations. Understanding smart power requires recognizing how integrating military capabilities with persuasive diplomatic efforts creates a more adaptable and sustainable form of influence.
Defining the Concepts: What Is Hard Power?
Hard power refers to a country's ability to influence others through military force or economic coercion, often involving direct threats, sanctions, or the use of armed forces. It emphasizes tangible resources such as military capabilities, economic leverage, and physical coercion to achieve strategic objectives. This form of power contrasts with soft power by relying primarily on compulsion rather than attraction or persuasion.
The Essence of Smart Power in Modern Diplomacy
Smart power in modern diplomacy combines the strategic use of both soft power, such as cultural influence and diplomacy, and hard power, including military and economic pressure, to achieve foreign policy goals effectively. This approach leverages communication, alliances, and economic incentives alongside coercion, creating flexible and adaptive responses to global challenges. Emphasizing collaboration and credibility, smart power enhances a nation's ability to navigate complex international relations and secure sustainable outcomes.
Historical Examples of Hard Power in Action
Historical examples of hard power in action include the Roman Empire's military conquests, demonstrating dominance through force and territorial expansion. The United States' use of hard power is evident in the Iraq War (2003), where military intervention aimed to overthrow Saddam Hussein's regime. Similarly, the Soviet Union's invasion of Afghanistan (1979) showcases the application of hard power to influence geopolitical outcomes through direct military engagement.
How Smart Power Shapes Global Influence
Smart power integrates diplomatic strategies, cultural influence, and economic partnerships to enhance a nation's global presence without relying solely on military force. By combining soft power elements like public diplomacy and development aid with selective hard power tactics, countries can build sustainable alliances and shape international norms more effectively. This balanced approach enables states to project influence, resolve conflicts peacefully, and secure long-term geopolitical advantages in a complex global landscape.
Key Differences Between Smart Power and Hard Power
Smart power integrates both soft power and hard power strategies, emphasizing diplomacy, cultural influence, and economic incentives alongside military force. Hard power relies predominantly on coercive measures such as military intervention and economic sanctions to achieve geopolitical objectives. The key difference lies in smart power's strategic blend of attraction and pressure, whereas hard power focuses mainly on direct compulsion and control.
Strategic Advantages of Combining Smart and Hard Power
Combining smart power and hard power leverages the strategic advantage of integrating diplomatic influence, economic incentives, and military strength to achieve comprehensive foreign policy goals. This hybrid approach enhances a nation's ability to shape global outcomes by aligning persuasive tactics with credible force, thereby increasing deterrence and effective conflict resolution. The fusion of soft power's appeal and hard power's coercion creates a balanced strategy that maximizes international influence while minimizing prolonged military engagements.
Case Studies: Smart Power vs Hard Power in International Relations
The case study of U.S. involvement in Iraq highlights the limitations of hard power, where military intervention failed to secure long-term stability, contrasting with smart power approaches that combined diplomacy, economic aid, and cultural engagement in post-apartheid South Africa to foster reconciliation and sustainable development. In Afghanistan, reliance on hard power through extensive military operations showed limited success, whereas smart power strategies, integrating local governance support and coalition-building with regional partners, achieved more nuanced outcomes. China's Belt and Road Initiative exemplifies smart power by leveraging economic influence and infrastructure investments to expand geopolitical reach without direct military confrontation.
Challenges and Critiques of Hard Power Strategies
Hard power strategies often face criticism for provoking resistance and undermining long-term diplomatic relations, as reliance on military force or economic sanctions can escalate conflicts rather than resolve them. Such approaches risk collateral damage, costly military engagements, and humanitarian crises, which can erode international legitimacy and fuel anti-hegemonic sentiments. Furthermore, hard power's inflexibility and emphasis on coercion often ignore the complexities of global interdependence, limiting sustainable influence compared to smart power's integration of soft power elements.
The Future of Global Leadership: Toward Smart Power Approaches
The future of global leadership hinges on integrating smart power strategies, combining the strategic use of soft power--such as cultural influence, diplomacy, and economic partnerships--with hard power capabilities like military strength and sanctions. Nations adopting smart power approaches enhance their global influence by tailoring responses to complex international challenges, leveraging technological innovation and multilateral cooperation. This balanced application promotes sustainable leadership, enabling countries to navigate geopolitical tensions while fostering international stability and economic growth.
Smart power Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com