A cartel party operates as a dominant political group that collaborates with other established parties to maintain power and limit competition, often prioritizing stability over ideological purity. This model influences policy-making and electoral strategies by focusing on preserving the status quo and controlling resources within a political system. Discover how a cartel party impacts democratic processes and what it means for Your political engagement in the full article.
Table of Comparison
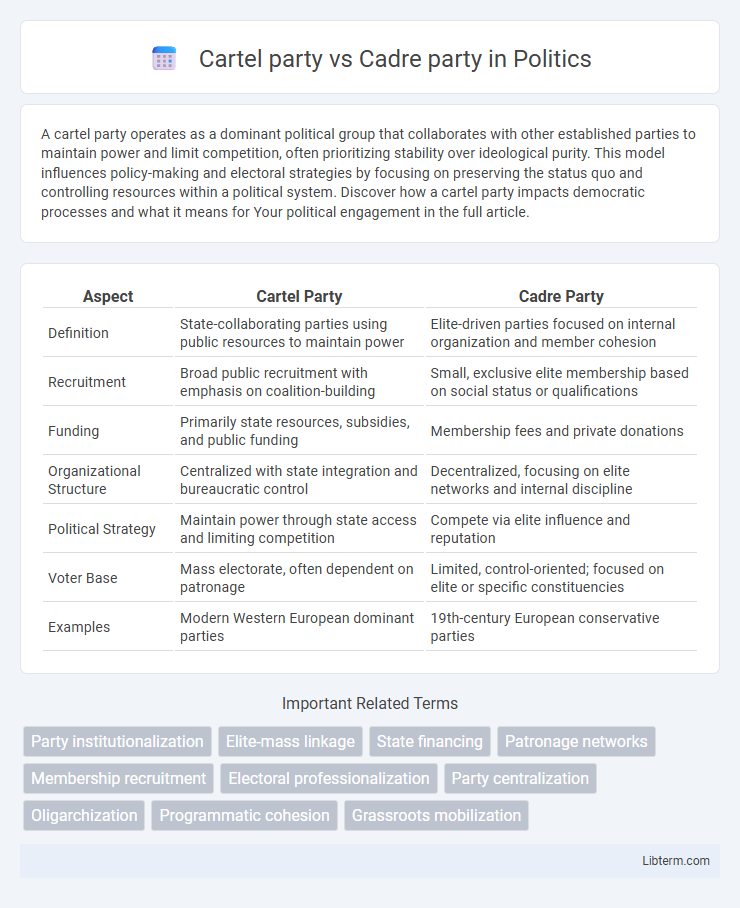
| Aspect | Cartel Party | Cadre Party |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | State-collaborating parties using public resources to maintain power | Elite-driven parties focused on internal organization and member cohesion |
| Recruitment | Broad public recruitment with emphasis on coalition-building | Small, exclusive elite membership based on social status or qualifications |
| Funding | Primarily state resources, subsidies, and public funding | Membership fees and private donations |
| Organizational Structure | Centralized with state integration and bureaucratic control | Decentralized, focusing on elite networks and internal discipline |
| Political Strategy | Maintain power through state access and limiting competition | Compete via elite influence and reputation |
| Voter Base | Mass electorate, often dependent on patronage | Limited, control-oriented; focused on elite or specific constituencies |
| Examples | Modern Western European dominant parties | 19th-century European conservative parties |
Understanding Cartel Parties: Definition and Origins
Cartel parties are political organizations that maintain power by leveraging state resources and limiting competition, rather than relying solely on popular support or ideological appeal, differentiating them from cadre parties, which are built around active membership and elite networks. The concept originated in the 1990s as political scientists observed mainstream parties increasingly collaborating to preserve their dominance through public funding, media access, and institutional advantages. This shift results in reduced party pluralism and a focus on sustaining the party system, impacting democratic engagement and electoral dynamics.
Cadre Parties Explained: Historical Context and Features
Cadre parties emerged in the 19th century as elitist political organizations primarily composed of aristocrats and professionals who aimed to influence government policy through limited mass mobilization. Historically, they featured loose party structures, minimal party membership, and a reliance on patronage and personal networks rather than ideological platforms. This contrasts with cartel parties, which later evolved to dominate political systems through state resources and stronger organizational control.
Key Differences Between Cartel and Cadre Parties
Cartel parties prioritize maintaining power through state resources and institutional advantages, often collaborating with other elite groups to protect their interests, whereas cadre parties emphasize ideological commitment and mobilizing active, dedicated members. Cartel parties rely on public funding and media access to dominate the political landscape, while cadre parties depend on grassroots support and member participation for organizational strength. The core distinction lies in cartel parties' focus on state control and patronage, contrasting with cadre parties' focus on ideological cohesion and internal party networks.
Evolution of Party Structures: From Cadre to Cartel
The evolution from cadre parties to cartel parties reflects a shift in political organization characterized by decreasing reliance on grassroots membership and increasing dependence on state resources and media access. Cadre parties, prominent in the 19th and early 20th centuries, were based on elite networks and active local membership engagement, while cartel parties emerged in the late 20th century, prioritizing inter-party cooperation and state funding to maintain electoral dominance. This transformation underscores changes in party competition, where cartel parties focus on professionalized campaign strategies and institutional advantages rather than mass mobilization.
Funding and Organization: How Cartel and Cadre Parties Operate
Cartel parties rely heavily on state resources and public funding to maintain their organizational structure, reducing dependence on grassroots support and private donors. Their organization is centralized, emphasizing professionalized leadership and close ties with government institutions to secure financial stability. In contrast, cadre parties depend on member contributions and local networks for funding, with decentralized structures that prioritize mobilizing activists and maintaining strong connections to their electoral base.
Party Membership: Recruitment and Engagement Strategies
Cartel parties rely heavily on state resources and professional networks for recruitment, focusing on maintaining elite control and limiting broad member engagement, often prioritizing quality over quantity. Cadre parties emphasize active grassroots participation, recruiting members through local networks and fostering strong ideological commitment to ensure sustained member involvement. Recruitment in cadre parties usually involves more bottom-up engagement strategies, enhancing loyalty and mobilization compared to the top-down, resource-dependent approach characteristic of cartel parties.
Electoral Strategies: Contrasting Approaches of Cartel and Cadre Parties
Cartel parties rely heavily on state resources and public funding to maintain electoral dominance, often emphasizing media campaigns and centralized candidate selection to secure votes. Cadre parties depend on grassroots mobilization and local party elites who build personal networks and loyalty, focusing on direct voter engagement and party organization at the community level. These contrasting strategies reflect cartel parties' top-down control versus cadre parties' bottom-up approach in electoral competition.
The Role of the State in Supporting Cartel Parties
Cartel parties rely heavily on state resources, using public funding, media access, and regulatory advantages to maintain their dominance and reduce dependence on private donations. The state plays a pivotal role by legally institutionalizing financial support, enabling these parties to institutionalize their presence and control electoral competition. This symbiotic relationship blurs the distinction between party and government, cementing cartel parties as gatekeepers in political systems with state-backed privileges.
Impact on Democracy: Cartel versus Cadre Party Systems
Cartel parties centralize power by relying on state resources and limiting competition, which often leads to decreased political pluralism and voter engagement, undermining democratic accountability. Cadre parties, rooted in strong organizational ties and active membership, promote grassroots participation and internal democracy, enhancing representative responsiveness. The shift from cadre to cartel party systems frequently results in party oligopolies that constrain competition and weaken the democratic process.
Contemporary Examples: Cartel and Cadre Parties in Modern Politics
Cartel parties dominate contemporary politics by leveraging state resources to maintain power, as seen in Germany's CDU and SPD, which rely heavily on public funding and media access rather than grassroots mobilization. In contrast, cadre parties like Italy's Lega remain rooted in strong ideological leadership and local organizational networks, emphasizing member-driven decision-making despite financial constraints. These dynamics illustrate how cartel parties prioritize institutional advantages while cadre parties focus on ideological cohesion and active membership engagement.
Cartel party Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com