Block voting is a voting system in which voters can cast multiple votes, typically equal to the number of available seats in an election, allowing them to vote for several candidates simultaneously. This method can lead to majority groups dominating the election outcome, often reducing minority representation and affecting the fairness of results. Explore the rest of the article to understand how block voting influences electoral systems and impacts democratic processes.
Table of Comparison
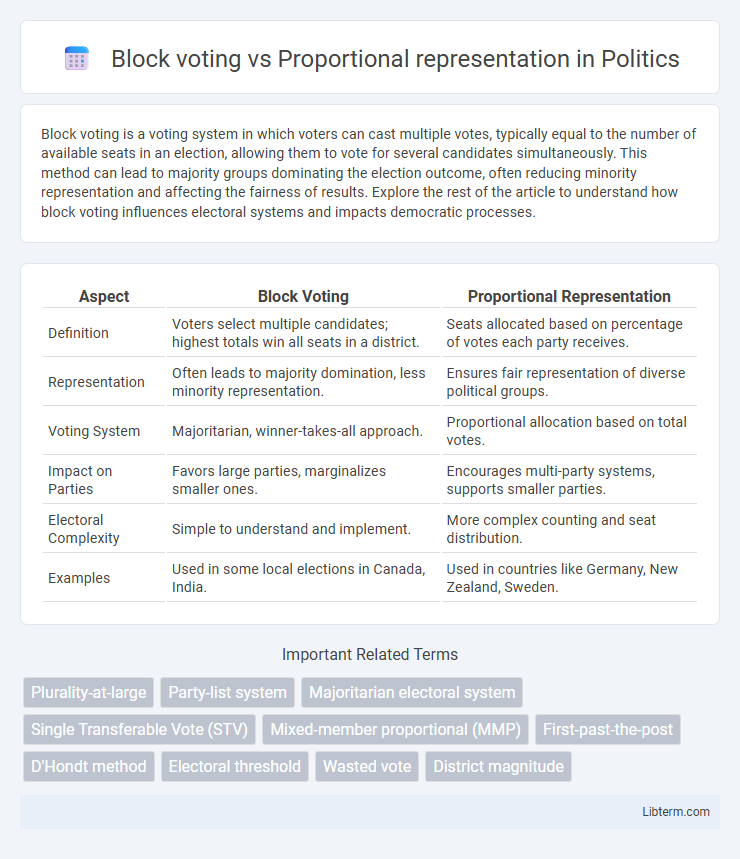
| Aspect | Block Voting | Proportional Representation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voters select multiple candidates; highest totals win all seats in a district. | Seats allocated based on percentage of votes each party receives. |
| Representation | Often leads to majority domination, less minority representation. | Ensures fair representation of diverse political groups. |
| Voting System | Majoritarian, winner-takes-all approach. | Proportional allocation based on total votes. |
| Impact on Parties | Favors large parties, marginalizes smaller ones. | Encourages multi-party systems, supports smaller parties. |
| Electoral Complexity | Simple to understand and implement. | More complex counting and seat distribution. |
| Examples | Used in some local elections in Canada, India. | Used in countries like Germany, New Zealand, Sweden. |
Introduction to Electoral Systems
Block voting allows voters to cast multiple votes for candidates in a multi-member district, often resulting in a winner-takes-all outcome that favors majority groups. Proportional representation allocates seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, promoting a more accurate reflection of voter preferences and minority representation. These contrasting electoral systems influence the political landscape by shaping party dynamics, voter engagement, and legislative diversity.
What is Block Voting?
Block voting is an electoral system where voters can cast multiple votes, usually equal to the number of seats available, often leading to a winner-takes-all outcome. This method tends to favor larger parties or groups, as it allows the majority to elect all representatives in a multi-member district. Block voting contrasts with proportional representation, which allocates seats based on the overall vote share to ensure minority representation.
How Proportional Representation Works
Proportional representation allocates seats in a legislature based on the percentage of votes each party receives, ensuring a more accurate reflection of voter preferences. Voters typically choose a party list or individual candidates within multi-member districts, allowing for diverse political views to gain representation. This system contrasts with block voting, which often favors majority groups and leads to disproportionate outcomes by giving all seats in a district to the winning party.
Key Differences Between Block Voting and Proportional Representation
Block voting typically awards all seats to the majority winner in a district, resulting in a "winner-takes-all" outcome that can marginalize minority voices. Proportional representation allocates seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, ensuring a more accurate reflection of voter preferences and enhancing political diversity. This fundamental difference affects election fairness, minority representation, and the overall composition of legislative bodies.
Advantages of Block Voting
Block voting offers the advantage of simplicity in its straightforward electoral process, where voters select multiple candidates, and those with the highest votes win, leading to clear, decisive outcomes. This system tends to produce stable majorities, which can enhance governmental efficiency by reducing fragmented legislatures and facilitating stronger policy implementation. Furthermore, block voting can strengthen local representation as it often elects candidates with strong community ties, promoting accountability and responsiveness to constituent needs.
Advantages of Proportional Representation
Proportional representation ensures a more accurate reflection of voter preferences by allocating seats according to the percentage of votes each party receives, enhancing fairness in electoral outcomes. It promotes political diversity and inclusivity by allowing smaller parties and minority groups to gain representation, which is often excluded under block voting systems. This voting method reduces the likelihood of disproportionate majorities and fosters coalition-building, leading to more consensus-driven governance.
Disadvantages of Block Voting
Block voting often leads to disproportionate election results, where the majority group can secure all seats, marginalizing minority voices. This system encourages a "winner-takes-all" outcome, reducing political diversity and limiting fair representation for smaller parties or groups. It also risks reinforcing existing power structures and decreasing voter engagement by making elections feel less competitive.
Disadvantages of Proportional Representation
Proportional representation can lead to fragmented legislatures with numerous small parties, complicating coalition-building and causing political instability. The system may also empower extremist groups by granting them parliamentary representation despite low overall support. Furthermore, it often weakens the direct link between voters and their representatives, reducing accountability and decreasing voter engagement.
Impact on Political Diversity and Fairness
Block voting often limits political diversity by favoring majority groups, resulting in less fair representation for minority parties. Proportional representation enhances fairness by allocating seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, promoting a wider range of political perspectives. This system fosters inclusive governance and better reflects the electorate's preferences.
Which System Is Best for Modern Democracies?
Proportional representation better reflects the diverse political preferences of modern democracies by allocating seats according to the percentage of votes each party receives, enhancing fairness and inclusivity. Block voting tends to favor larger parties or coalitions, often marginalizing minority voices and leading to disproportionate majorities in legislatures. Countries seeking to strengthen democratic legitimacy and voter representation increasingly adopt proportional systems to ensure that legislative bodies mirror the electorate's varied interests.
Block voting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com