Candidate voting plays a crucial role in democratic elections by allowing voters to choose individuals who best represent their interests and values. This process influences policy decisions and shapes the future leadership of communities and nations. Discover how understanding candidate voting can empower Your decision-making in upcoming elections by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
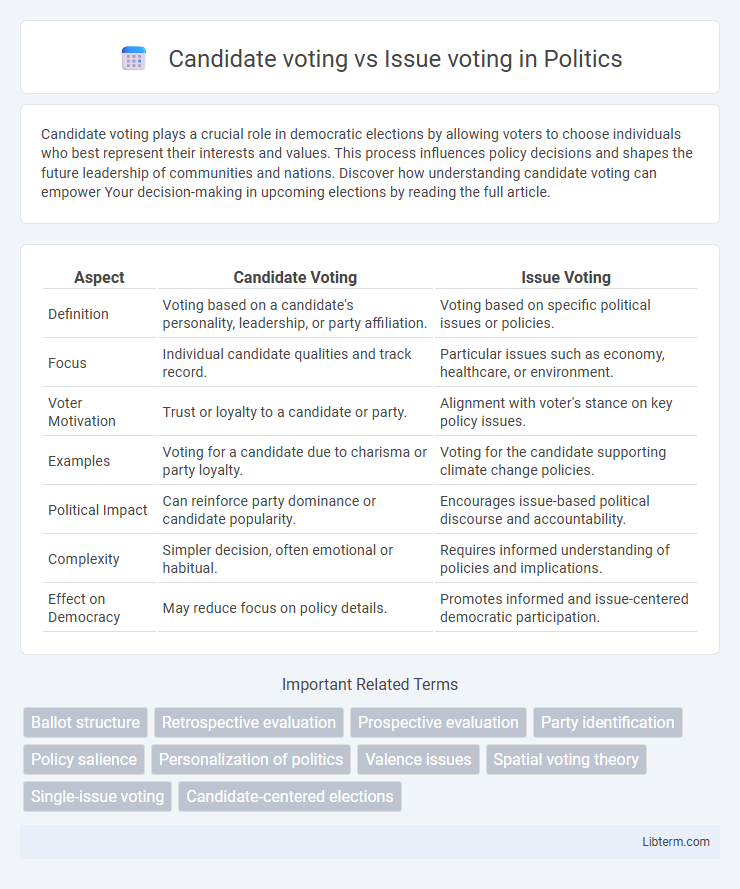
| Aspect | Candidate Voting | Issue Voting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voting based on a candidate's personality, leadership, or party affiliation. | Voting based on specific political issues or policies. |
| Focus | Individual candidate qualities and track record. | Particular issues such as economy, healthcare, or environment. |
| Voter Motivation | Trust or loyalty to a candidate or party. | Alignment with voter's stance on key policy issues. |
| Examples | Voting for a candidate due to charisma or party loyalty. | Voting for the candidate supporting climate change policies. |
| Political Impact | Can reinforce party dominance or candidate popularity. | Encourages issue-based political discourse and accountability. |
| Complexity | Simpler decision, often emotional or habitual. | Requires informed understanding of policies and implications. |
| Effect on Democracy | May reduce focus on policy details. | Promotes informed and issue-centered democratic participation. |
Understanding Candidate Voting: Definition and Dynamics
Candidate voting centers on voters making decisions based on the characteristics, policies, and personal qualities of individual candidates rather than specific issues. This approach emphasizes factors such as experience, leadership style, party affiliation, and perceived integrity, shaping voter preferences beyond policy stances. The dynamics of candidate voting involve emotional connections, media influence, and candidate debates, reflecting how personal attributes influence electoral choices more than issue-based evaluations.
The Fundamentals of Issue Voting Explained
Issue voting centers on assessing candidates based on their positions on specific policy issues rather than personal traits or party affiliation. Voters prioritize topics like healthcare, the economy, or climate change, aligning their choices with candidates whose policy proposals best match their preferences. This approach promotes informed decision-making by emphasizing substantive policy analysis over partisan loyalty or personality-driven campaigns.
Historical Trends in Candidate vs. Issue Voting
Historical trends in candidate voting reveal a shift in voter alignment from personality-driven choices to issue-based preferences, particularly since the 1960s civil rights movement. Analysis of electoral data shows increased polarization, with voters increasingly motivated by specific policy issues such as economic inequality and social justice rather than party loyalty. Studies from the American National Election Studies (ANES) highlight this transition, documenting the rise in issue voting as ideological polarization intensifies.
Factors Influencing Voter Decisions: Persona vs. Policy
Candidate voting emphasizes personal traits such as charisma, trustworthiness, and experience, which heavily influence voter preferences based on identity and perceived relatability. Issue voting prioritizes specific policy positions on topics like healthcare, economy, and education, guiding voters who assess candidates primarily through policy alignment. Voter decisions often balance persona-driven appeal and substantive policy issues, with context and individual priorities shaping the dominant factor.
The Role of Media in Shaping Voting Behavior
Media plays a critical role in shaping voter behavior by framing candidate qualities and issue salience, influencing how voters prioritize information. Coverage intensity and tone affect candidate evaluations and issue awareness, often guiding voters toward candidate-centric or issue-based decisions. Social media platforms amplify targeted messaging, reinforcing partisan beliefs and shaping the cognitive shortcuts voters use in elections.
Psychological Drivers: Identity, Loyalty, and Values
Candidate voting is often influenced by psychological drivers such as identity, where voters see themselves reflected in a candidate's personal traits and background, fostering loyalty through shared group membership. Issue voting centers on values, compelling voters to support policies that align with their core beliefs and moral priorities. These psychological factors interplay, with identity and loyalty strengthening candidate preferences, while deeply held values motivate issue-based decisions.
Impact of Electoral Systems on Voting Patterns
Electoral systems significantly shape candidate voting and issue voting patterns by influencing strategic voter behavior and party dynamics. Proportional representation systems tend to encourage issue voting by allowing smaller parties to gain representation focused on specific policies, while majoritarian systems often promote candidate voting due to the winner-takes-all nature that emphasizes individual personalities and party dominance. This divergence impacts voter engagement and policy responsiveness, affecting the overall political landscape and democratic accountability.
Case Studies: Candidate-Centric vs. Issue-Centric Campaigns
Case studies of candidate-centric campaigns, such as Barack Obama's 2008 presidential run, emphasize personal charisma and leadership qualities, driving voter support through candidate appeal. In contrast, issue-centric campaigns like Elizabeth Warren's 2020 bid focus on policy positions, mobilizing voters around specific agendas like economic reform and healthcare. Research comparing these approaches highlights that candidate-centric campaigns excel in broad-based voter mobilization, while issue-centric efforts strengthen engagement among ideologically motivated electorates.
Implications for Democracy and Political Representation
Candidate voting emphasizes individual qualities and party affiliation, potentially enhancing accountability by fostering direct voter-candidate connections. Issue voting, centered on specific policy preferences, promotes substantive representation by aligning elected officials with voter priorities on matters like healthcare or climate change. Both approaches significantly impact democratic responsiveness and the quality of political representation, shaping how effectively citizens' interests are reflected in governance.
Future Trends: The Evolving Landscape of Voter Choice
Future trends in candidate voting show increased reliance on personalized data analytics and social media engagement, enhancing voter-candidate connections. Issue voting is gaining prominence as voters prioritize policy impacts on climate change, social justice, and economic inequality over partisan loyalty. Emerging technologies and digital platforms are reshaping voter choice by enabling real-time issue tracking and more informed decision-making processes.
Candidate voting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com