Parliament serves as the cornerstone of democratic governance, responsible for creating, debating, and enacting laws that shape society's future. Its structure and functions vary across countries but consistently aim to represent the people's interests and hold the executive accountable. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your parliament influences nation-building and citizen participation.
Table of Comparison
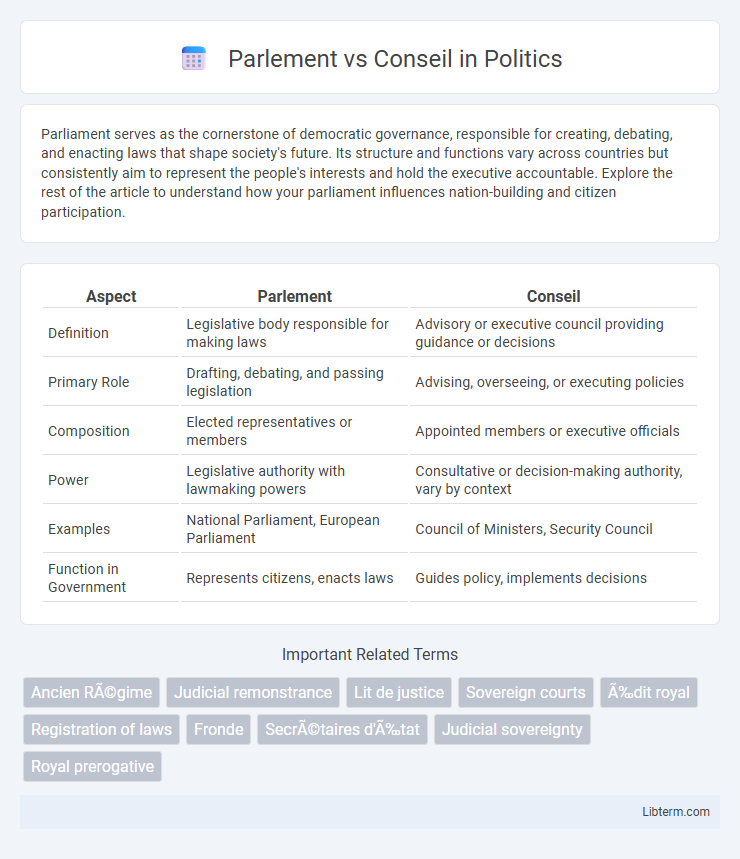
| Aspect | Parlement | Conseil |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legislative body responsible for making laws | Advisory or executive council providing guidance or decisions |
| Primary Role | Drafting, debating, and passing legislation | Advising, overseeing, or executing policies |
| Composition | Elected representatives or members | Appointed members or executive officials |
| Power | Legislative authority with lawmaking powers | Consultative or decision-making authority, vary by context |
| Examples | National Parliament, European Parliament | Council of Ministers, Security Council |
| Function in Government | Represents citizens, enacts laws | Guides policy, implements decisions |
Introduction to Parlement and Conseil
The Parlement and Conseil are key institutions in the French administrative and judicial system, each serving distinct roles. The Parlement primarily functions as a judicial authority, acting as a high court of appeal with powers to review and interpret laws. The Conseil, particularly the Conseil d'Etat and Conseil Constitutionnel, serves as an advisory body on legislative matters and oversees the constitutionality of laws and administrative actions.
Historical Background of Parlement and Conseil
The Parlement originated in the medieval period as sovereign courts of justice in France, evolving from the king's council and serving as appellate courts with legislative advisory roles. The Conseil, or Council, historically functioned as the king's administrative and advisory body, managing executive decisions and governance without judicial authority. Over time, the Parlement became emblematic of judicial review and limited royal power, while the Conseil emphasized centralized royal administration and policy enforcement.
Definitions: What is Parlement?
Parlement refers to a legislative body responsible for making, amending, and repealing laws within a political system. It typically represents the electorate, debates policies, and exercises oversight over the executive branch. The structure and powers of a Parlement vary by country but generally include elected representatives who embody democratic governance.
Definitions: What is Conseil?
Conseil refers to the Council of the European Union, an essential EU institution representing member states' governments to coordinate policies and adopt legislation. It functions alongside the European Parliament, jointly shaping EU laws, budgets, and international agreements. The Conseil's role emphasizes intergovernmental decision-making, balancing national interests within the EU legislative process.
Key Differences between Parlement and Conseil
The Parlement and Conseil differ primarily in their roles and functions within the French government structure; the Parlement serves as the legislative body responsible for making laws, while the Conseil, particularly the Conseil d'Etat, acts as the highest administrative court and legal adviser to the executive. Parlement debates and votes on legislation, representing the people's will, whereas the Conseil provides rulings on administrative disputes and ensures the legality of government decisions. Structurally, the Parlement is divided into two chambers, the National Assembly and the Senate, whereas the Conseil is a singular body composed of legal experts and government advisors.
Structures and Functions
The European Parliament functions as the directly elected legislative body responsible for debating and passing EU laws, representing citizens across member states, while the Council of the European Union, also known as the Council of Ministers, comprises government ministers from each member state and negotiates legislation alongside the Parliament. The Parliament's structure includes 705 Members of the European Parliament (MEPs) organized into political groups and committees, whereas the Council's configuration changes based on policy area, hosting different ministerial formations such as agriculture or finance. Both institutions collaborate within the ordinary legislative procedure, with the Parliament primarily focusing on democratic representation and legislative approval, and the Council emphasizing intergovernmental coordination and policy consensus.
Roles in Governance
The Parlement represents the legislative authority responsible for drafting, debating, and enacting laws within the political system. The Conseil functions as an advisory or judicial council, overseeing legal compliance, providing expert opinions, and ensuring the implementation of governance frameworks. Together, they balance law-making and regulatory enforcement to maintain effective governmental operations.
Decision-Making Processes
The European Parliament participates directly in the legislative process by debating and adopting laws through the ordinary legislative procedure alongside the Council of the European Union, which represents member states' governments. The Council plays a decisive role in shaping policies and finalizing legislation, often negotiating amendments proposed by the Parliament to reach consensus. Both institutions work collaboratively to balance supranational and intergovernmental interests in decision-making, ensuring democratic legitimacy and efficient governance across the EU.
Impact on Legislation and Policy
The European Parliament directly influences legislation by debating, amending, and approving laws proposed by the European Commission, ensuring democratic representation in policymaking. The Council of the European Union, representing member states, negotiates legislation and coordinates policies, balancing national interests with EU objectives. Their collaboration shapes comprehensive policies and legal frameworks, impacting economic, social, and environmental sectors across the EU.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Parlement and Conseil
Choosing between Parlement and Conseil depends on the specific needs of legislative efficiency versus advisory expertise. Parlement typically handles legislative decision-making with a focus on political representation and law-making authority. Conseil serves as an advisory body, offering specialized guidance and strategic recommendations, making it ideal for policy consultation rather than direct legislation.
Parlement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com