Liberalism champions individual freedoms, equality, and democratic governance as core principles. It advocates for limited government intervention to ensure personal rights and economic opportunities flourish. Discover how liberalism shapes modern society and influences your personal and political life by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
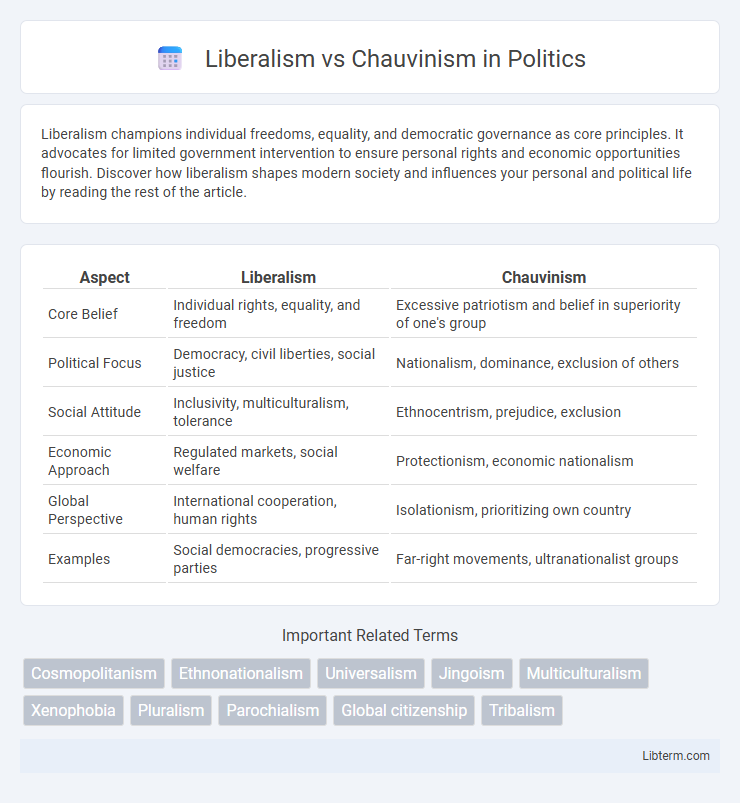
| Aspect | Liberalism | Chauvinism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Belief | Individual rights, equality, and freedom | Excessive patriotism and belief in superiority of one's group |
| Political Focus | Democracy, civil liberties, social justice | Nationalism, dominance, exclusion of others |
| Social Attitude | Inclusivity, multiculturalism, tolerance | Ethnocentrism, prejudice, exclusion |
| Economic Approach | Regulated markets, social welfare | Protectionism, economic nationalism |
| Global Perspective | International cooperation, human rights | Isolationism, prioritizing own country |
| Examples | Social democracies, progressive parties | Far-right movements, ultranationalist groups |
Understanding Liberalism: Core Principles
Liberalism is grounded in core principles such as individual liberty, equality before the law, and the protection of human rights. It advocates for democratic governance, free markets, and the separation of church and state to ensure personal freedoms and social progress. Emphasizing tolerance and pluralism, liberalism counters chauvinism's exclusionary nationalism and promotes inclusive, open societies.
Defining Chauvinism: Origins and Characteristics
Chauvinism traces its origins to the fervent nationalism associated with Nicolas Chauvin, a soldier reputed for extreme patriotism and loyalty to Napoleon. Defined by an exaggerated and aggressive form of bias, chauvinism manifests through an unwavering belief in the superiority of one's group, often leading to discrimination against others. This ideology contrasts sharply with liberalism, which emphasizes individual rights, equality, and openness to diversity.
Historical Contexts of Liberalism and Chauvinism
Liberalism emerged during the Enlightenment as a political philosophy advocating individual freedoms, equality before the law, and democratic governance, influencing revolutions such as the American and French Revolutions in the 18th century. Chauvinism, rooted in extreme nationalism and exaggerated patriotism, often manifested in aggressive militarism and xenophobia, notably evident during the 19th and early 20th centuries, including the lead-up to World War I. The historical contexts of liberalism emphasize progressive social reform and universal rights, while chauvinism aligns with exclusionary, ethnocentric ideologies that have catalyzed conflicts and imperial expansion.
Key Ideological Differences
Liberalism emphasizes individual rights, equality, and justice, advocating for inclusive policies that promote diversity and protect minority groups. Chauvinism centers on aggressive patriotism and a belief in national or group superiority, often leading to exclusionary and discriminatory practices. Key ideological differences lie in liberalism's commitment to universal human rights versus chauvinism's focus on preferential treatment based on race, nationality, or gender.
Social Impact of Liberalism
Liberalism promotes individual freedoms, equality, and social justice, leading to inclusive policies that enhance civil rights, education, and healthcare access. It fosters diverse societies by encouraging pluralism and reducing discrimination against marginalized groups. The social impact of liberalism is evident in improved social mobility and the establishment of democratic institutions that protect personal liberties.
Societal Consequences of Chauvinism
Chauvinism fosters social division by promoting exclusionary attitudes and undermining diversity, leading to heightened discrimination and conflict within communities. It erodes social cohesion, fueling inequality and marginalization of minority groups, which disrupts economic and cultural development. Persistent chauvinistic ideologies contribute to the deterioration of democratic values and social justice, impeding societal progress and human rights advancements.
Liberalism vs Chauvinism in Politics
Liberalism in politics advocates for individual rights, equality, and inclusive governance, emphasizing the protection of civil liberties and democratic principles. Chauvinism reflects an aggressive, often nationalistic bias favoring one group or nation over others, undermining pluralism and minority rights. The tension between liberalism and chauvinism shapes debates on immigration, voting rights, and social policies, influencing whether societies move toward inclusivity or exclusion.
Influence on Cultural and Gender Norms
Liberalism promotes individual rights, equality, and freedom, challenging traditional cultural and gender norms by advocating for gender equality and the dismantling of patriarchal structures. Chauvinism reinforces rigid cultural roles and gender hierarchies, often emphasizing male dominance and exclusion of minorities from social and political power. The influence of liberal values fosters inclusivity and diversity, whereas chauvinistic views maintain discriminatory practices and social stratification.
Modern Manifestations and Debates
Modern manifestations of liberalism emphasize individual rights, equality, and multiculturalism, advocating for inclusive policies and global cooperation. Chauvinism, often seen in nationalistic and ethnocentric rhetoric, resurges in political debates around immigration, identity, and sovereignty, promoting exclusionary and protectionist agendas. Contemporary discourse centers on balancing liberal values of diversity with challenges posed by chauvinistic movements seeking cultural homogeneity.
Pathways Toward Tolerance and Inclusivity
Liberalism emphasizes individual rights, equality, and open dialogue as foundational pathways toward tolerance and inclusivity, promoting policies that protect minority groups and encourage diverse perspectives. Chauvinism, by contrast, fosters exclusivity and prejudiced superiority, obstructing social cohesion and acceptance. Embracing liberal values facilitates education, empathy, and legal frameworks that dismantle discriminatory practices and build inclusive communities.
Liberalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com