The concept of the silent majority refers to a large group of people who hold opinions privately but do not express them publicly or participate actively in political debates. This demographic can significantly influence election outcomes and social trends despite their low visibility in media and public discourse. Discover how understanding the silent majority can reshape your perspective on current events in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
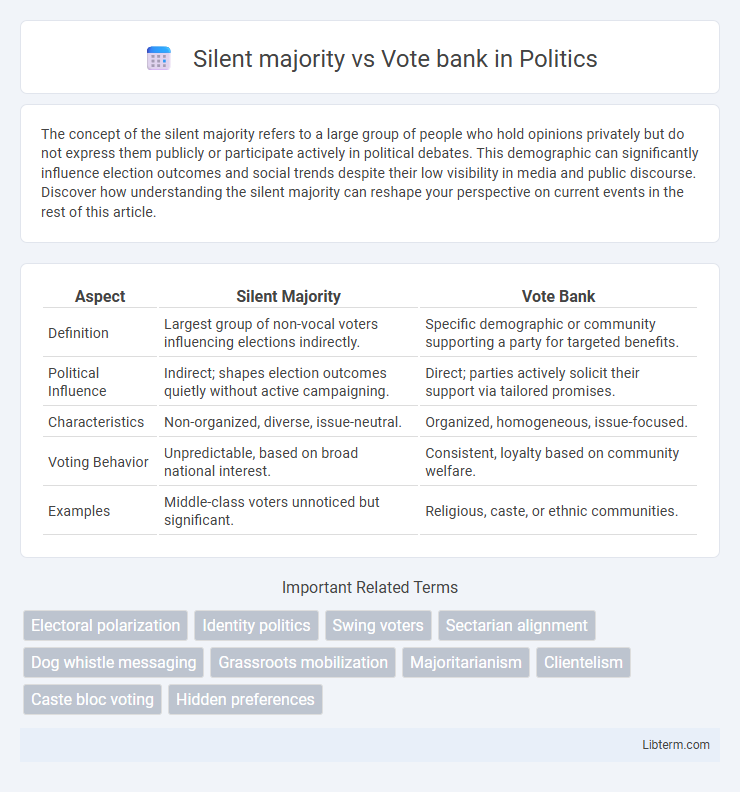
| Aspect | Silent Majority | Vote Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Largest group of non-vocal voters influencing elections indirectly. | Specific demographic or community supporting a party for targeted benefits. |
| Political Influence | Indirect; shapes election outcomes quietly without active campaigning. | Direct; parties actively solicit their support via tailored promises. |
| Characteristics | Non-organized, diverse, issue-neutral. | Organized, homogeneous, issue-focused. |
| Voting Behavior | Unpredictable, based on broad national interest. | Consistent, loyalty based on community welfare. |
| Examples | Middle-class voters unnoticed but significant. | Religious, caste, or ethnic communities. |
Understanding the Silent Majority: Who Are They?
The silent majority refers to a large group of people who do not openly express their opinions publicly but significantly influence election outcomes through their votes. Unlike vote banks, which are composed of specific communities or interest groups consistently supporting particular parties for targeted benefits, the silent majority includes diverse individuals unified by shared values or concerns yet lacking vocal representation. Understanding this demographic is crucial for political strategists aiming to gauge true public sentiment and mobilize latent electoral power effectively.
Defining the Vote Bank: Characteristics and Influence
Vote banks are specific demographic groups that consistently support a political party or candidate based on shared interests, identity, or socioeconomic factors, often influenced by ethnicity, religion, caste, or economic status. These groups exhibit predictable voting patterns, which parties strategically target through tailored policies and promises to secure electoral loyalty. The influence of vote banks is significant in shaping electoral outcomes, as their collective support can sway tightly contested elections and impact political stability.
Historical Context: Origins of Both Concepts
The concept of the silent majority gained prominence during the 1960s in the United States, describing a large group of people who do not express their opinions publicly but hold significant political influence. In contrast, the vote bank emerged in Indian political discourse to represent a stable bloc of voters aligned by caste, religion, or ethnicity, influencing electoral outcomes since the mid-20th century. Both concepts highlight different facets of voter behavior and political mobilization shaped by their distinct historical and cultural contexts.
Political Strategies: Appealing to the Silent Majority
Political strategies targeting the silent majority focus on addressing the moderate, non-vocal voters whose preferences often drive election outcomes, contrasting with the vote bank approach that caters to specific, loyal demographic groups. Campaigns appealing to the silent majority emphasize broad-based policies and inclusive rhetoric to capture widespread support, rather than relying on identity-based or interest-specific promises typical of vote bank politics. Understanding voter behavior analytics and public sentiment helps politicians craft messages that resonate with the silent majority, aiming for decisive electoral victories beyond fragmented vote banks.
Vote Bank Politics: Methods and Implications
Vote bank politics relies on securing electoral support from specific social, ethnic, or religious groups by promising targeted benefits, often through patronage, identity appeals, and welfare schemes. This method fosters political polarization and perpetuates clientelism, weakening broader democratic engagement and policy discussions focused on collective welfare. The implications include reduced accountability of politicians, increased social divisions, and distortion of governance priorities to favor narrow interest groups over inclusive development.
Media’s Role in Shaping Perceptions
Media plays a pivotal role in shaping public perceptions of the silent majority and vote bank dynamics by selectively highlighting certain voices and issues while marginalizing others. The framing of political narratives often amplifies vote bank politics, focusing on identity-based voting patterns, whereas the silent majority's preferences may remain underreported or misrepresented. This bias influences electoral discourse and voter behavior, underscoring the media's power in constructing political realities.
Societal Impact: Division or Unity?
The silent majority often represents a large, unvoiced group whose opinions can influence societal norms without direct confrontation, fostering unity by stabilizing political discourse. In contrast, vote banks are characterized by segmented groups voting based on specific interests, which can deepen societal divisions by prioritizing narrow agendas over collective welfare. The tension between these dynamics shapes political strategies and impacts social cohesion, highlighting the importance of inclusive dialogue to bridge divides.
Silent Majority vs Vote Bank: Key Differences
The silent majority refers to a large group of people who refrain from expressing their political opinions publicly but hold significant sway in elections through their votes, whereas a vote bank is a specific, often loyal, segment of the electorate consistently supporting a particular party or candidate based on shared identity factors like caste, religion, or ethnicity. Silent majority influences electoral outcomes through quiet consensus without overt mobilization, while vote banks are actively courted and mobilized by political parties through targeted policies and appeals. The key difference lies in the silent majority's preference for discretion and non-participation in public discourse versus the vote bank's organized, visible backing rooted in social identities.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples and Outcomes
In the 2016 Brexit referendum, the silent majority expressed skepticism about the European Union but did not actively campaign, ultimately tipping the vote in favor of leaving. In contrast, India's vote bank politics during the 2019 general elections saw targeted appeals to specific caste and religious groups, solidifying party strongholds but also polarizing the electorate. These cases demonstrate how silent majorities may sway pivotal decisions quietly, while vote banks mobilize through active, identity-based engagement to influence electoral outcomes.
Future Trends: Evolving Dynamics in Democratic Elections
The future of democratic elections will witness the silent majority increasingly influencing outcomes through digital platforms and social media, bypassing traditional vote banks reliant on caste, religion, or regional loyalties. Emerging data analytics and AI-powered voter behavior predictions are reshaping campaign strategies to engage this less vocal but decisive segment. Political parties must adapt to these evolving dynamics, focusing on issues that resonate with the silent majority's aspirations rather than static vote bank politics.
Silent majority Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com