Democratic backsliding refers to the gradual decline in the quality and strength of democratic institutions, leading to weakened checks and balances, reduced political freedoms, and erosion of civil liberties. This process often undermines the rule of law and allows authoritarian tendencies to take root within democratically elected governments. Explore the rest of this article to understand how democratic backsliding impacts your rights and global political stability.
Table of Comparison
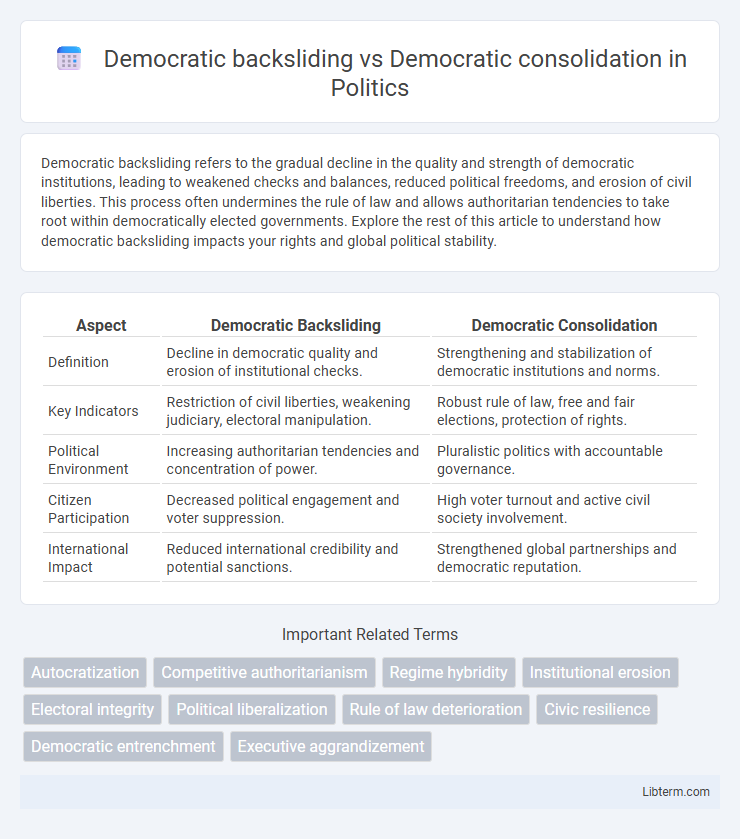
| Aspect | Democratic Backsliding | Democratic Consolidation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decline in democratic quality and erosion of institutional checks. | Strengthening and stabilization of democratic institutions and norms. |
| Key Indicators | Restriction of civil liberties, weakening judiciary, electoral manipulation. | Robust rule of law, free and fair elections, protection of rights. |
| Political Environment | Increasing authoritarian tendencies and concentration of power. | Pluralistic politics with accountable governance. |
| Citizen Participation | Decreased political engagement and voter suppression. | High voter turnout and active civil society involvement. |
| International Impact | Reduced international credibility and potential sanctions. | Strengthened global partnerships and democratic reputation. |
Understanding Democratic Backsliding: Key Concepts
Democratic backsliding involves the gradual erosion of democratic institutions, norms, and civil liberties, often marked by weakening checks and balances, undermined judicial independence, and diminished media freedom. Key concepts include the rise of authoritarian practices within elected governments, erosion of electoral integrity, and declining political pluralism. Understanding these indicators helps distinguish democratic backsliding from democratic consolidation, where institutions are strengthened, political competition is fair, and the rule of law is upheld.
Defining Democratic Consolidation: Core Principles
Democratic consolidation refers to the process by which a democracy matures, becoming stable and enduring through the widespread acceptance of democratic norms, institutions, and practices. Core principles include adherence to the rule of law, protection of individual rights and freedoms, regular free and fair elections, and the effective functioning of checks and balances within government. Successful consolidation also depends on the development of a political culture that supports pluralism, tolerance, and peaceful conflict resolution.
Historical Context: How Democracies Evolve
Democratic backsliding refers to the gradual decline in the quality of democracy through the erosion of institutions, restrictions on civil liberties, and weakening of the rule of law, while democratic consolidation signifies the process by which democracy becomes stable and deeply rooted in political culture and institutions. Historically, democracies evolve through cycles influenced by internal conflicts, economic challenges, and external pressures, shaping their trajectory toward either consolidation or backsliding. Key case studies include the Weimar Republic's collapse into authoritarianism and the post-World War II consolidation of democracy in Western Europe, illustrating how political resilience and institutional safeguards determine democratic outcomes.
Indicators of Democratic Backsliding
Indicators of democratic backsliding include erosion of electoral integrity, suppression of press freedom, and weakening of judicial independence. Persistent violations of civil liberties, such as restricting freedom of assembly and targeting political opponents, also signal backsliding. Declining transparency and increased executive overreach further highlight the regression from democratic consolidation toward authoritarian tendencies.
Challenges to Democratic Consolidation
Democratic consolidation faces challenges such as erosion of rule of law, weak institutional checks and balances, and increased political polarization, which undermine stable governance and citizen trust. Persistent corruption, electoral manipulation, and suppression of civil liberties further inhibit the development of resilient democratic norms. These factors heighten vulnerability to democratic backsliding, where democratic systems regress into authoritarianism or illiberalism.
Comparing Causes: Backsliding vs Consolidation
Democratic backsliding often results from rising authoritarian tendencies, eroding rule of law, weakened checks and balances, and increasing political polarization undermining institutional trust. In contrast, democratic consolidation depends on strong institutions, widespread public support for democratic norms, effective governance, and civil society engagement reinforcing political stability. The divergence between these causes highlights how institutional resilience and societal commitment differentiate democratic stability from erosion.
Impact on Institutions: Governance and Rule of Law
Democratic backsliding erodes the foundations of governance by undermining institutional checks and balances, weakening judicial independence, and facilitating authoritarian practices that compromise rule of law. Democratic consolidation strengthens institutions through increased transparency, accountability, and the entrenchment of legal frameworks that protect civil liberties and ensure fair governance. The impact on institutions determines whether democracies maintain stability and effective governance or descend into authoritarianism and institutional decay.
Case Studies: Global Examples and Trends
Democratic backsliding, characterized by the erosion of political institutions and civil liberties, is evident in countries like Hungary and Turkey, where authoritarian tendencies have undermined electoral integrity and judicial independence. In contrast, democratic consolidation in nations such as South Korea and Chile showcases strengthened rule of law, robust civil society, and adherence to democratic norms, ensuring stability and citizen participation. Global trends reveal that economic development, institutional reforms, and international support play crucial roles in promoting democratic consolidation while weak governance and populist nationalism accelerate backsliding.
Strategies for Preventing Democratic Backsliding
Effective strategies for preventing democratic backsliding include strengthening independent institutions such as the judiciary and electoral bodies to ensure accountability and uphold the rule of law. Promoting civic education and active citizen engagement fosters public awareness and resilience against authoritarian tendencies. International cooperation and monitoring mechanisms help detect early warning signs and support democratically committed governments in maintaining democratic consolidation.
Strengthening Democratic Consolidation: Policy Recommendations
Strengthening democratic consolidation requires robust institutional frameworks that promote transparency, accountability, and inclusive governance. Implementing policies such as judicial independence, free press protections, and civic education enhances citizen trust and political participation. Targeted reforms that address corruption, safeguard electoral integrity, and support civil society organizations are crucial for preventing democratic backsliding and ensuring long-term stability.
Democratic backsliding Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com