Facing challenge, support, and indifference shapes your resilience and personal growth in unique ways. Understanding how each response influences your mindset can empower you to navigate obstacles more effectively. Discover how these dynamics impact your life by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
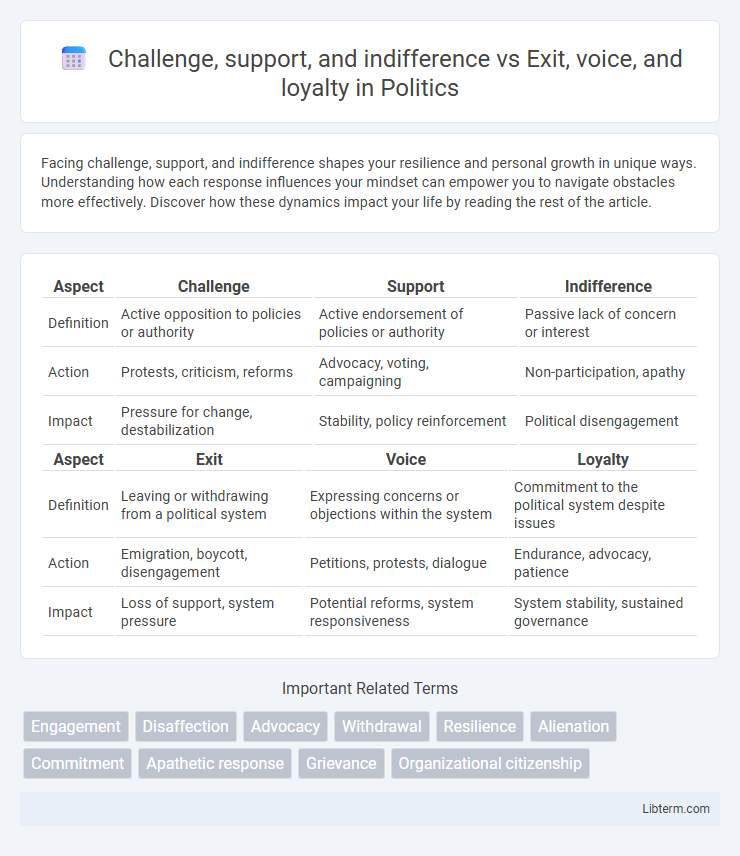
| Aspect | Challenge | Support | Indifference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active opposition to policies or authority | Active endorsement of policies or authority | Passive lack of concern or interest |
| Action | Protests, criticism, reforms | Advocacy, voting, campaigning | Non-participation, apathy |
| Impact | Pressure for change, destabilization | Stability, policy reinforcement | Political disengagement |
| Aspect | Exit | Voice | Loyalty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Leaving or withdrawing from a political system | Expressing concerns or objections within the system | Commitment to the political system despite issues |
| Action | Emigration, boycott, disengagement | Petitions, protests, dialogue | Endurance, advocacy, patience |
| Impact | Loss of support, system pressure | Potential reforms, system responsiveness | System stability, sustained governance |
Understanding Challenge, Support, and Indifference
Challenge, support, and indifference represent distinct stakeholder responses within organizational behavior frameworks, where challenge involves proactive efforts to change or improve conditions, support reflects positive endorsement and reinforcement, and indifference indicates passive disengagement or lack of concern. These reactions influence internal dynamics by shaping communication patterns, decision-making processes, and overall organizational resilience. Understanding these responses is critical for diagnosing organizational health and designing strategies that enhance collaboration, mitigate conflict, and foster adaptive change.
Defining Exit, Voice, and Loyalty
Exit, voice, and loyalty represent key behaviors individuals exhibit when facing dissatisfaction within organizations or relationships. Exit refers to the decision to leave or withdraw from a situation, voice involves actively expressing concerns or seeking change, and loyalty implies commitment and patience despite potential issues. Understanding these responses aids in managing conflict and improving organizational dynamics.
Theoretical Foundations: Comparing the Two Frameworks
Theoretical foundations of Challenge, Support, and Indifference focus on interpersonal dynamics within organizations, emphasizing emotional responses and motivational states as drivers of engagement or withdrawal. Exit, Voice, and Loyalty, developed by Hirschman, categorize individual reactions to dissatisfaction based on behavioral choices and organizational commitment, offering a macro-level perspective on stakeholder responses. Comparing these frameworks reveals complementary insights: Challenge, Support, and Indifference highlight nuanced psychological mechanisms, while Exit, Voice, and Loyalty provide a structural model for understanding decision-making in organizational change.
Behavioral Responses: Challenge vs. Exit
Behavioral responses to dissatisfaction in organizations often manifest as Challenge or Exit, where Challenge involves actively addressing and seeking solutions within the system, demonstrating engagement and commitment. In contrast, Exit represents withdrawal from the organization, reflecting disengagement and rejection of the current conditions. Support and indifference correspond to positive and neutral emotional attitudes, impacting whether individuals employ voice behaviors associated with loyalty or choose disengagement pathways.
The Role of Support and Loyalty in Organizations
Support and loyalty play critical roles in reinforcing organizational stability by encouraging employees to express voice rather than opting for exit. High levels of support foster a sense of belonging, which strengthens loyalty and drives constructive responses to challenges. Indifference weakens this dynamic, increasing the likelihood of exit and diminishing collective resilience.
Indifference and Its Relation to Exit Strategies
Indifference often functions as a subtle precursor to exit strategies, reflecting a lack of engagement or emotional investment that diminishes the incentive to voice concerns or seek support. Unlike challenge or support tactics that involve active participation, indifference signals disengagement, increasing the likelihood of exit as individuals or groups withdraw without resistance. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for predicting when loyalty will erode and exit becomes the dominant response in organizational or social contexts.
Voice as a Form of Constructive Challenge
Voice as a form of constructive challenge empowers individuals to express concerns and propose solutions within an organization, fostering positive change without resorting to exit or exhibiting indifference. This proactive engagement strengthens support mechanisms by encouraging dialogue and collaboration, ultimately enhancing organizational resilience and adaptability. Emphasizing voice nurtures loyalty, as employees feel valued and heard, reducing turnover and promoting a constructive culture of continuous improvement.
Impact on Group Dynamics and Performance
Challenge, support, and indifference shape group dynamics by influencing member engagement and collaboration, directly affecting overall performance and innovation. Exit, voice, and loyalty behaviors determine how conflicts are addressed or avoided, impacting group cohesion and the ability to adapt to change. High levels of voice and loyalty typically enhance trust and accountability, while prevalent exit and indifference can lead to fragmentation and decreased productivity within teams.
Managing Indifference: Retaining Engagement and Loyalty
Managing indifference involves shifting passive disengagement into active loyalty by leveraging targeted support and meaningful challenges that stimulate emotional investment. Retaining engagement requires addressing employee needs through clear communication channels, fostering trust, and providing opportunities for voice to counteract exit tendencies. Effective management balances recognizing indifference with promoting accountability and feedback mechanisms to sustain commitment and reduce turnover risks.
Practical Implications for Leaders and Organizations
Leaders and organizations must balance challenge, support, and indifference with exit, voice, and loyalty to maintain employee engagement and reduce turnover rates. Encouraging voice through open communication channels enhances innovation and problem-solving, while providing support fosters loyalty and mitigates exit risks. Recognizing indifference early allows for targeted interventions that prevent disengagement and preserve organizational performance.
Challenge, support, and indifference Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com