Open primaries allow voters to participate in any party's primary election without declaring party affiliation, promoting broader voter engagement. This system can influence candidate selection by encouraging more moderate platforms that appeal to a wider audience. Discover how open primaries may impact your voting experience and the political landscape throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
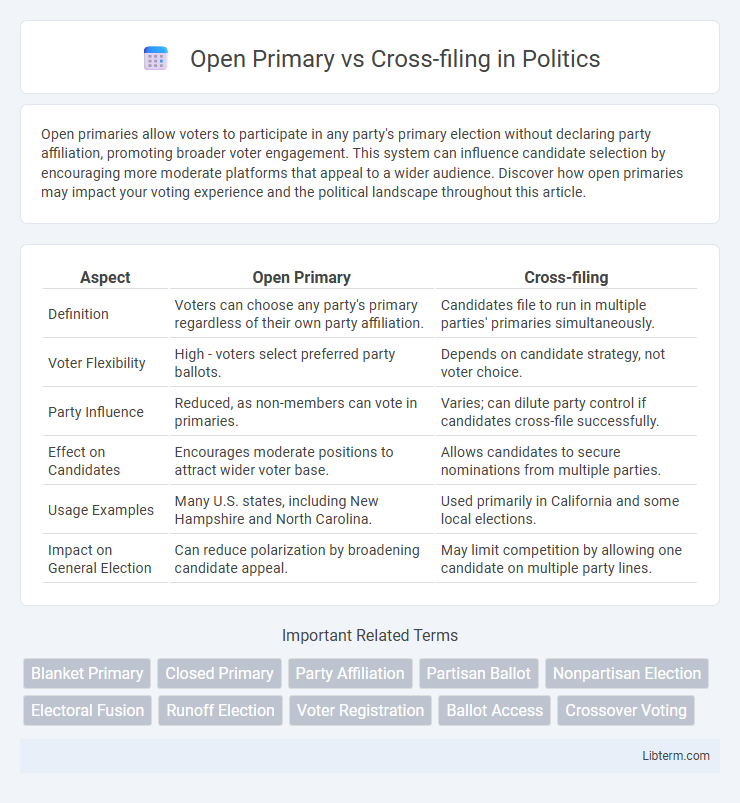
| Aspect | Open Primary | Cross-filing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voters can choose any party's primary regardless of their own party affiliation. | Candidates file to run in multiple parties' primaries simultaneously. |
| Voter Flexibility | High - voters select preferred party ballots. | Depends on candidate strategy, not voter choice. |
| Party Influence | Reduced, as non-members can vote in primaries. | Varies; can dilute party control if candidates cross-file successfully. |
| Effect on Candidates | Encourages moderate positions to attract wider voter base. | Allows candidates to secure nominations from multiple parties. |
| Usage Examples | Many U.S. states, including New Hampshire and North Carolina. | Used primarily in California and some local elections. |
| Impact on General Election | Can reduce polarization by broadening candidate appeal. | May limit competition by allowing one candidate on multiple party lines. |
Introduction to Open Primary and Cross-filing
Open primaries allow all registered voters to participate in choosing a party's candidate regardless of their own party affiliation, promoting broader voter engagement and influence in the candidate selection process. Cross-filing permits candidates to appear on multiple party ballots simultaneously, often used in jurisdictions like California to increase electoral competitiveness and reduce partisan barriers. Understanding these systems highlights their impact on voter choice, candidate strategy, and overall election dynamics.
Historical Background of Primary Election Systems
The historical background of primary election systems reveals that open primaries, first adopted in the early 20th century, emerged to increase voter participation by allowing any registered voter to choose a party's primary regardless of affiliation. Cross-filing, introduced notably in California during the Progressive Era of the 1910s, permitted candidates to run in multiple party primaries simultaneously, aiming to reduce party control and encourage broader candidate appeal. These systems reflect evolving efforts to balance party influence, voter choice, and electoral competitiveness in the American political landscape.
Definition and Key Features of Open Primary
An open primary allows all registered voters to participate regardless of party affiliation, enabling greater voter inclusivity and flexibility in candidate selection. Key features include the absence of party membership restrictions and the potential for voters to influence the nomination of major party candidates. This system contrasts with cross-filing, where candidates can run in multiple party primaries, potentially diluting partisan competition.
Understanding Cross-filing in Elections
Cross-filing in elections allows candidates to run in multiple party primaries simultaneously, often used to maximize ballot access and reduce competition. Unlike open primaries where voters can choose any party's primary regardless of affiliation, cross-filing enables the same candidate to appear on multiple party ballots. This strategy can streamline campaign efforts and influence election outcomes by broadening voter reach.
Advantages of Open Primary Elections
Open primary elections increase voter participation by allowing independents and members of other parties to vote, which leads to more representative candidate selection. This system reduces partisan polarization by encouraging candidates to appeal to a broader electorate rather than just their party base. Open primaries also enhance transparency and competitiveness, providing voters with greater choice in the electoral process.
Drawbacks and Criticisms of Open Primaries
Open primaries often face criticism for enabling strategic voting, where members of opposing parties participate to influence the selection of weaker candidates. They can dilute party ideology by allowing non-members to affect candidate nomination, leading to less party cohesion. Voter confusion and increased administrative costs are additional drawbacks associated with implementing open primary systems.
Pros and Cons of Cross-filing
Cross-filing allows candidates to appear on multiple party primary ballots, increasing their chances of securing nominations across party lines. This strategy can reduce partisan conflict and promote moderate candidates but may also dilute party identity and confuse voters. Critics argue cross-filing undermines party loyalty and leads to less ideologically driven election outcomes.
Impact on Party Dynamics and Voter Choice
Open primaries allow voters to participate in any party's primary regardless of affiliation, encouraging broader voter engagement and often leading to moderate candidate selections that appeal to a wider electorate. Cross-filing permits candidates to appear on multiple party primary ballots simultaneously, which can reduce partisan polarization by incentivizing candidates to seek support across party lines. Both systems significantly influence party dynamics by potentially diminishing strict party control over nominations while expanding voter choice and competitive candidate options.
Case Studies: States Using Open Primary or Cross-filing
California and Washington serve as prominent case studies for open primaries, where all candidates compete on a single ballot irrespective of party affiliation, enhancing voter choice and promoting moderate candidates. In contrast, Pennsylvania's historic use of cross-filing allowed candidates to appear on multiple party ballots, often leading to reduced partisan competition and incumbency advantages. Evaluations show open primaries tend to increase electoral competitiveness, whereas cross-filing may diminish clear party distinctions in state elections.
Future Trends and Reforms in Primary Election Systems
Future trends in primary election systems suggest increased adoption of open primaries to enhance voter inclusivity and boost turnout, allowing any registered voter to participate regardless of party affiliation. Cross-filing, historically used to lessen partisan divides by enabling candidates to run in multiple party primaries, faces declining popularity due to concerns about voter confusion and reduced party cohesion. Emerging reforms prioritize transparency and security, with some states experimenting with ranked-choice voting and digital platforms to modernize the electoral process and improve representativeness.
Open Primary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com