An open seat in politics refers to an electoral race without an incumbent candidate, often leading to a highly competitive environment that attracts numerous contenders. This situation can significantly alter campaign strategies and voter turnout, providing unique opportunities for new candidates to gain a foothold. Discover how open seats impact elections and what this means for Your voting decisions in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
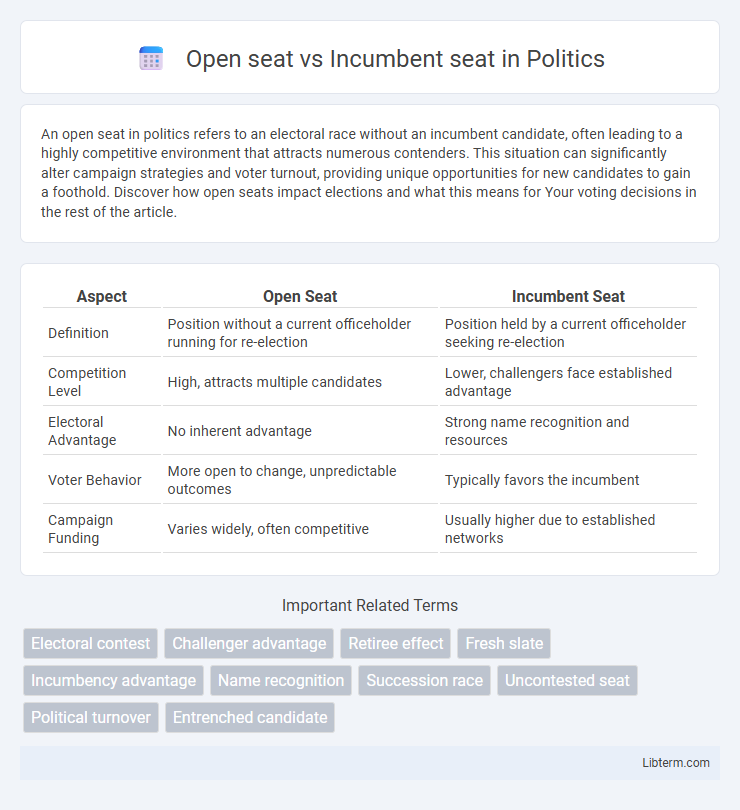
| Aspect | Open Seat | Incumbent Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Position without a current officeholder running for re-election | Position held by a current officeholder seeking re-election |
| Competition Level | High, attracts multiple candidates | Lower, challengers face established advantage |
| Electoral Advantage | No inherent advantage | Strong name recognition and resources |
| Voter Behavior | More open to change, unpredictable outcomes | Typically favors the incumbent |
| Campaign Funding | Varies widely, often competitive | Usually higher due to established networks |
Understanding Open Seats and Incumbent Seats
Open seats refer to electoral districts where no current officeholder is running for re-election, often leading to more competitive races and opportunities for new candidates to emerge. Incumbent seats are held by current officeholders seeking re-election, typically benefiting from name recognition, established voter base, and greater access to campaign resources. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for analyzing election dynamics, campaign strategies, and predicting voter behavior patterns.
Key Differences Between Open Seats and Incumbent Seats
Open seats occur when no current officeholder is running, creating a competitive environment with no established candidate advantage, often leading to higher voter turnout and unpredictable outcomes. Incumbent seats feature sitting officeholders seeking re-election, benefiting from name recognition, existing support networks, and typically higher campaign funding. The key differences between open and incumbent seats significantly impact campaign strategies, voter engagement, and election competitiveness.
Advantages of Running for an Open Seat
Running for an open seat in an election offers significant advantages due to the absence of an incumbent's established voter base and campaign infrastructure. Candidates benefit from a more level playing field, as they avoid facing the challenges of unseating a sitting officeholder with name recognition and fundraising advantages. Open seats often attract more campaign contributions and endorsements since party support is typically stronger for competitive races without an entrenched incumbent.
Challenges Facing Incumbent Candidates
Incumbent candidates face challenges such as voter fatigue, heightened scrutiny over their past performance, and increased competition from well-funded opponents in both primaries and general elections. They must overcome negative perceptions related to policy decisions and respond to calls for change amid shifting political landscapes. Moreover, incumbents often contend with redistricting impacts that can alter their voter base and complicate re-election efforts.
Voter Behavior in Open Seat vs. Incumbent Races
Voter behavior in open seat elections tends to exhibit higher levels of candidate evaluation based on policy proposals and personal qualifications due to the absence of an incumbent's name recognition advantage. In contrast, incumbent races benefit from established voter loyalty, leading to increased support driven by familiarity and perceived experience, often resulting in higher incumbent re-election rates. Shifts in voter turnout and campaign spending patterns also highlight distinct strategic approaches between open seat contests and those involving incumbents.
Impact on Campaign Strategies
Open seats create highly competitive environments due to the absence of an incumbent's advantage, prompting candidates to aggressively build name recognition and secure fundraising early. Incumbent seats benefit from established voter bases and proven campaign infrastructure, allowing more targeted messaging focused on experience and accomplishments. Campaign strategies for open seats emphasize voter outreach and momentum, while incumbent campaigns leverage track records and constituent services to maintain support.
Historical Election Outcomes: Open vs. Incumbent
Historical election outcomes consistently show that open seats tend to be more competitive and have higher turnover rates compared to incumbent seats, where the incumbent advantage often ensures re-election. Incumbents benefit from name recognition, established fundraising networks, and constituent services, which contribute to winning re-election approximately 90% of the time in U.S. congressional elections. Open seat races, lacking these incumbency advantages, generally result in closer margins and present greater opportunities for party flips and fresh candidates to secure office.
Fundraising Differences in Each Race
Fundraising in open seat races typically outpaces incumbent contests due to the absence of an established candidate, prompting higher contributions from donors seeking influence in a competitive field. Incumbents benefit from name recognition and existing donor networks, enabling more consistent and often larger fundraising efforts over time. Campaign expenditures in open seat races tend to be more aggressive and unpredictable, reflecting the increased uncertainty and stakes of winning a vacant position.
Media Coverage and Public Perception
Open seats typically attract more intense media coverage due to the absence of an established candidate, generating increased public interest and speculation about potential contenders. Media outlets often highlight the uncertainty and competitiveness of open seat races, contrasting with incumbent seats where coverage frequently centers on the incumbent's track record and policy positions. Public perception tends to view open seats as opportunities for change, while incumbent seats may be seen as either stable or vulnerable depending on the incumbent's performance and media portrayal.
Implications for Political Parties
Open seats, where no incumbent is running, often lead to more competitive elections, increasing opportunities for political parties to gain control and showcase fresh candidates. Incumbent seats typically provide advantages such as name recognition and established voter bases, making them crucial for parties to maintain stability and continuity in legislative agendas. Strategic allocation of resources by parties focuses heavily on defending incumbent seats while targeting open seats for potential gains, shaping overall election outcomes and party dynamics.
Open seat Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com