Democracy empowers citizens to participate in decision-making processes, ensuring their voices influence government actions. It promotes transparency, accountability, and protection of individual rights within a society. Explore the rest of the article to understand how democracy shapes your daily life and global governance.
Table of Comparison
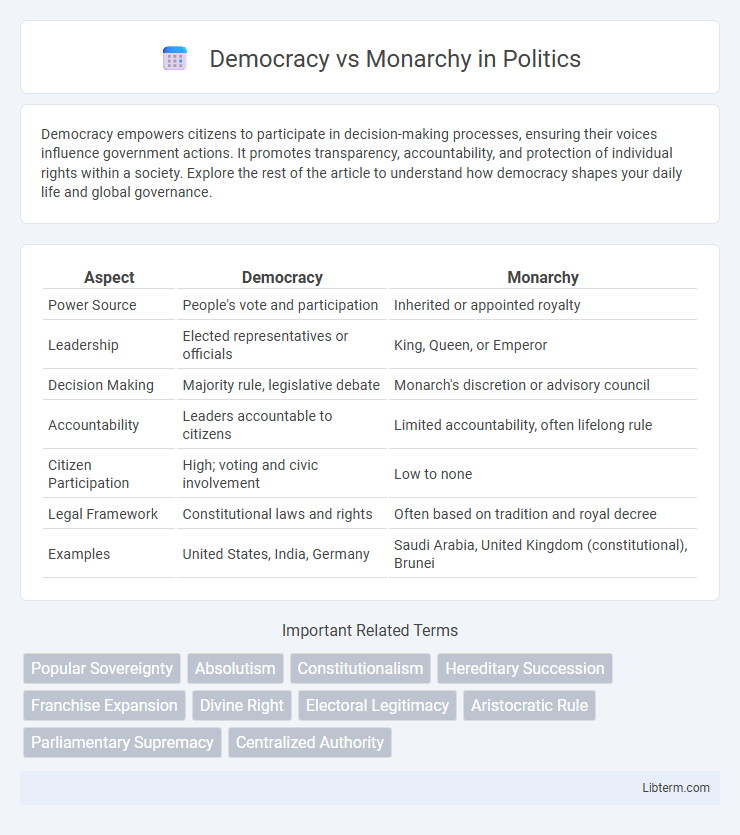
| Aspect | Democracy | Monarchy |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | People's vote and participation | Inherited or appointed royalty |
| Leadership | Elected representatives or officials | King, Queen, or Emperor |
| Decision Making | Majority rule, legislative debate | Monarch's discretion or advisory council |
| Accountability | Leaders accountable to citizens | Limited accountability, often lifelong rule |
| Citizen Participation | High; voting and civic involvement | Low to none |
| Legal Framework | Constitutional laws and rights | Often based on tradition and royal decree |
| Examples | United States, India, Germany | Saudi Arabia, United Kingdom (constitutional), Brunei |
Introduction: Defining Democracy and Monarchy
Democracy is a political system where power is vested in the people, allowing citizens to participate directly or through elected representatives in decision-making processes. Monarchy is a form of governance led by a single ruler, often hereditary, such as a king or queen, holding supreme authority over the state. While democracy emphasizes collective participation and equality, monarchy centers on centralized power and traditional legitimacy.
Historical Evolution of Governance Systems
Democracy emerged as a governance system emphasizing individual rights and collective decision-making, tracing its roots back to ancient Athens, where citizen participation shaped legislative processes. Monarchy, originating in early civilizations such as Egypt and Mesopotamia, centralized authority under hereditary rulers whose power was often justified by divine sanction. The historical evolution shows a gradual shift from absolute monarchies toward constitutional monarchies and representative democracies, reflecting societies' increasing demands for political accountability and citizen involvement.
Core Principles of Democracy
Democracy is founded on the core principles of popular sovereignty, political equality, and individual freedoms, ensuring that power originates from the people and is exercised through fair elections and representative institutions. Accountability and transparency are essential components, enabling citizens to hold elected officials responsible for their governance. This contrasts with monarchy, where authority is typically centralized in a single ruler or royal family, often without the same level of public participation or checks on power.
Key Features of Monarchical Rule
Monarchical rule is characterized by the concentration of power in a single sovereign, often a king or queen, who typically inherits the position through hereditary succession. This system emphasizes centralized authority, where decision-making is often absolute or limited by traditional laws and customs rather than popular consent. Monarchies may maintain stability and continuity, but they often lack the representative political participation seen in democratic systems.
Power Distribution: People vs. Sovereign
In a democracy, power is distributed among the populace through elected representatives, ensuring accountability and collective decision-making. Contrarily, a monarchy centralizes authority in a sovereign, often hereditary, who exercises significant control over governance and laws. This fundamental difference affects the mechanisms of power legitimacy, with democracies emphasizing popular consent and monarchies relying on tradition or divine right.
Decision-Making Processes in Both Systems
Democracy centers decision-making power in the hands of the populace or their elected representatives, emphasizing majority rule and transparent deliberation through legislative bodies. Monarchy concentrates authority within a singular ruler or royal family, allowing decisions to be made swiftly but often without public input or accountability. The democratic process fosters inclusivity and debate, while monarchy relies on centralized control and hierarchical command structures.
Accountability and Transparency in Governance
Democracy ensures high accountability and transparency in governance through regular elections, free press, and mechanisms like checks and balances that empower citizens to hold leaders responsible. In contrast, monarchy centralizes power in a single ruler or royal family, often limiting public oversight and reducing governmental transparency. Democratic systems thus promote openness and citizen participation, while monarchies may lack institutional means for accountability.
Economic and Social Impacts
Democracy fosters economic growth by encouraging innovation, protecting property rights, and ensuring fair competition, leading to increased investment and wealth distribution across society. Monarchies often centralize economic power, which can result in inefficiencies and limited social mobility but may provide political stability that attracts certain types of investment. Socially, democracies promote equality and civil liberties, enabling diverse participation in decision-making, whereas monarchies tend to reinforce hierarchical structures that restrict social freedoms and access to opportunities.
Popular Case Studies: Nations in Focus
The United States exemplifies democracy through its representative government and constitutional framework ensuring citizens' rights and electoral participation. The United Kingdom represents a constitutional monarchy where a hereditary monarch coexists with a parliamentary system, balancing tradition with democratic governance. Contrastingly, Saudi Arabia operates as an absolute monarchy, with political power centralized in the royal family and limited public political engagement.
Conclusion: Future Prospects of Democracy and Monarchy
Democracy offers adaptability and broader citizen participation, making it a resilient system in rapidly changing societies, while monarchy often provides stability and continuity through centralized authority. Emerging global trends suggest that hybrid models, combining democratic processes with monarchical elements, may influence future governance structures. The sustainability of each system will depend on their ability to address modern challenges such as technological advancements, social equity, and political inclusivity.
Democracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com