The conference committee plays a crucial role in organizing and managing the logistics, agenda, and speaker coordination to ensure a successful event. Their responsibilities include selecting relevant topics, facilitating smooth communication among participants, and handling unexpected changes efficiently. Discover how understanding the function of a conference committee can enhance your event planning skills by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
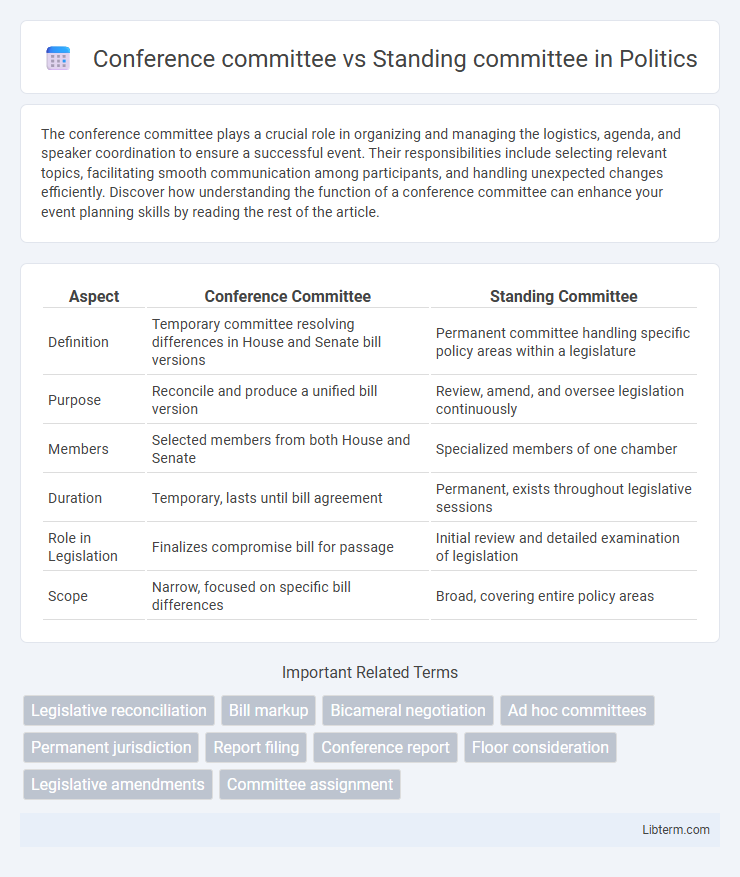
| Aspect | Conference Committee | Standing Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary committee resolving differences in House and Senate bill versions | Permanent committee handling specific policy areas within a legislature |
| Purpose | Reconcile and produce a unified bill version | Review, amend, and oversee legislation continuously |
| Members | Selected members from both House and Senate | Specialized members of one chamber |
| Duration | Temporary, lasts until bill agreement | Permanent, exists throughout legislative sessions |
| Role in Legislation | Finalizes compromise bill for passage | Initial review and detailed examination of legislation |
| Scope | Narrow, focused on specific bill differences | Broad, covering entire policy areas |
Overview of Congressional Committees
Conference committees resolve differences between House and Senate versions of a bill, playing a crucial role in finalizing legislation before it reaches the president. Standing committees are permanent panels in Congress responsible for the detailed review, amendment, and oversight of legislation within specific policy areas like finance, agriculture, or foreign affairs. Together, these committees enable specialized expertise and bipartisan negotiation essential for the legislative process.
Definition of Conference Committee
A Conference Committee is a temporary, joint legislative panel formed to reconcile differences between the House and Senate versions of a bill, ensuring both chambers agree on a single text before the final vote. Unlike Standing Committees, which are permanent and handle specific policy areas, Conference Committees dissolve once their task of resolving bill discrepancies is complete. This committee plays a crucial role in the legislative process by producing compromise legislation that reflects the priorities of both chambers.
Definition of Standing Committee
Standing committees are permanent legislative panels established by rules of a legislative body, tasked with considering bills and issues related to specific subject areas such as finance, health, or education. Conference committees, in contrast, are temporary joint committees formed to reconcile differences between House and Senate versions of a bill. Standing committees play a crucial role in the legislative process by conducting hearings, reviewing legislation, and overseeing government agencies within their jurisdiction.
Purpose and Functions of Conference Committees
Conference committees resolve disagreements between the House and Senate versions of legislation, ensuring a unified bill before final passage, while standing committees handle the ongoing legislative review, oversight, and development within specific policy areas. The primary function of conference committees is to reconcile differences, produce a compromise bill acceptable to both chambers, and facilitate a smooth legislative process. Unlike standing committees that conduct hearings and markup bills, conference committees focus solely on negotiating consensus on conflicting legislative provisions.
Role and Responsibilities of Standing Committees
Standing committees are permanent legislative panels established to review bills, oversee government functions, and conduct investigations within specific policy areas such as finance, health, or education. These committees play a crucial role in shaping legislation by holding hearings, analyzing proposed laws, and making recommendations to the full legislative body. Unlike conference committees, which resolve differences between House and Senate versions of bills temporarily, standing committees maintain ongoing oversight and ensure continuous legislative scrutiny.
Formation and Membership Differences
Conference committees are formed temporarily to reconcile differences between House and Senate versions of a specific bill, consisting of appointed members from both chambers who served on the original committees. Standing committees are permanent panels established by the rules of each chamber, with members assigned based on party ratio and seniority, handling specific areas of legislation continually. Conference committee membership is selective and issue-specific, while standing committee membership is broader, ongoing, and aligned with legislative jurisdictions.
Duration and Lifespan of Each Committee
Conference committees operate temporarily, dissolving after resolving differences between House and Senate bills, typically lasting only a few weeks during a specific legislative session. Standing committees are permanent panels established in each legislative chamber, continuing across multiple sessions with ongoing jurisdiction over particular policy areas. The lifespan of standing committees extends indefinitely, allowing continuous review and refinement of legislation within their specialty fields.
Legislative Process Involvement
Conference committees reconcile differences between House and Senate versions of a bill to produce a unified piece of legislation before final approval. Standing committees conduct detailed evaluation, amendment, and initial approval of bills within their specific legislative jurisdictions, playing a critical role in shaping policy at earlier stages. Both committees are essential for legislative process efficiency, with standing committees focusing on development and conference committees resolving inter-chamber discrepancies.
Key Examples of Conference and Standing Committees
Key examples of conference committees include the House-Senate Conference Committee on the 2020 National Defense Authorization Act, which resolved differences between the House and Senate versions of the bill, and the Tax Conference Committee that reconciles tax legislation discrepancies. Standing committees such as the House Ways and Means Committee and Senate Judiciary Committee are permanent panels responsible for ongoing legislative oversight and lawmaking within specific policy areas. Conference committees are temporary, formed to reconcile legislative differences, while standing committees maintain continuous jurisdiction over particular issues like finance, defense, or judiciary matters.
Impact on Lawmaking Effectiveness
Conference committees reconcile House and Senate bill differences, ensuring unified legislation that advances lawmaking efficiency through compromise. Standing committees conduct detailed policy review, expert hearings, and amendments, shaping the substance and practicality of laws before floor consideration. The interplay between conference committees' final harmonization and standing committees' in-depth analysis enhances overall legislative precision and effectiveness.
Conference committee Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com