A referendum allows citizens to directly vote on important legislative or constitutional issues, ensuring public participation in the democratic process. It empowers Your voice to influence government decisions on crucial matters, from policy changes to national reforms. Explore the rest of the article to understand how referendums impact governance and your role in shaping the future.
Table of Comparison
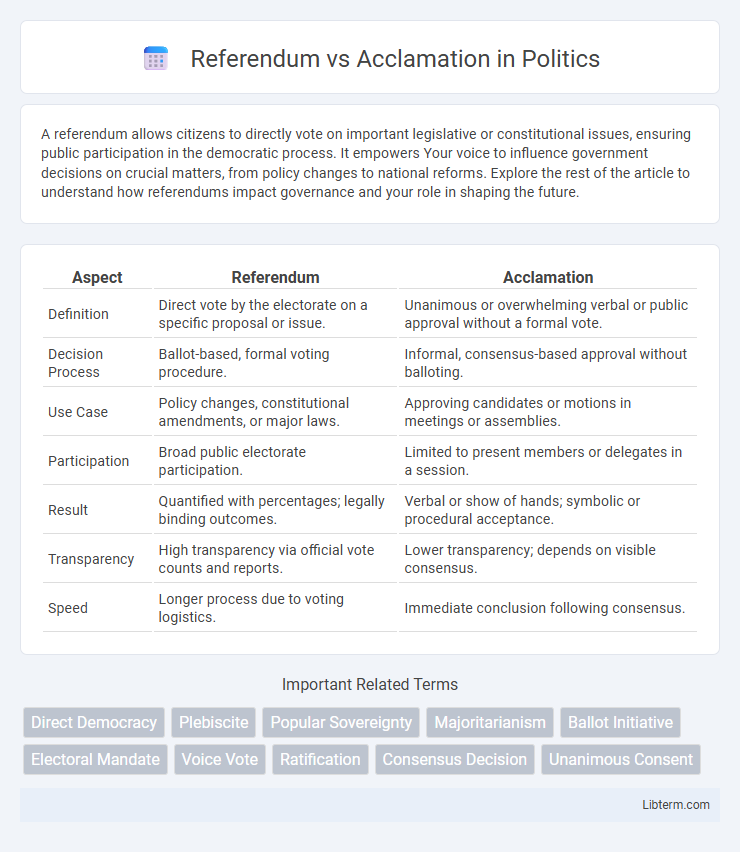
| Aspect | Referendum | Acclamation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct vote by the electorate on a specific proposal or issue. | Unanimous or overwhelming verbal or public approval without a formal vote. |
| Decision Process | Ballot-based, formal voting procedure. | Informal, consensus-based approval without balloting. |
| Use Case | Policy changes, constitutional amendments, or major laws. | Approving candidates or motions in meetings or assemblies. |
| Participation | Broad public electorate participation. | Limited to present members or delegates in a session. |
| Result | Quantified with percentages; legally binding outcomes. | Verbal or show of hands; symbolic or procedural acceptance. |
| Transparency | High transparency via official vote counts and reports. | Lower transparency; depends on visible consensus. |
| Speed | Longer process due to voting logistics. | Immediate conclusion following consensus. |
Understanding Referendum: Definition and Process
A referendum is a direct voting process where citizens approve or reject specific legislative proposals or constitutional amendments, providing a fundamental form of democratic participation. The process involves submitting a question to the electorate, followed by a formal vote, often requiring precise legal frameworks governing eligibility, timing, and vote counting. Understanding the referendum process clarifies its role in enhancing public influence on critical political decisions compared to indirect representation mechanisms.
What is Acclamation? Key Concepts Explained
Acclamation is a decision-making process where a proposal is approved unanimously or without opposition, often expressed through vocal or show-of-hands agreement rather than a formal vote. Unlike a referendum, which involves a broad, often secret ballot among eligible voters to decide on a specific issue, acclamation relies on collective consensus within smaller groups or assemblies. This method is commonly used in parliamentary procedures, meetings, or elections where consensus is clear and formal polling is unnecessary.
Historical Origins of Referendum and Acclamation
Referendums originated in ancient Roman times as a method for citizens to vote directly on legislation, embodying early democratic practices. Acclamation dates back to ancient assemblies where collective vocal approval was used to endorse decisions without formal ballots. The historical roots of referendum emphasize direct popular sovereignty, while acclamation reflects communal consensus through immediate public expression.
Mechanisms: How Does a Referendum Work?
A referendum works by submitting a specific legislative proposal or constitutional question directly to the electorate for a vote, requiring governments to organize a formal ballot process where eligible voters cast their decision. The outcome is typically binding, leading to the adoption or rejection of the proposed measure based on majority or supermajority votes, depending on legal frameworks. This direct democracy mechanism contrasts with acclamation, where decisions are made through unanimous consent or without formal voting procedures, often in smaller or less formal settings.
The Acclamation Procedure: Steps and Examples
The acclamation procedure involves unanimous or near-unanimous approval without a formal vote, streamlining decision-making in assemblies or boards. Key steps include proposing the motion, soliciting verbal or non-verbal agreement from all present members, and confirming the absence of objections before declaring the motion passed by acclamation. Examples include approving routine procedural motions, honoring a member's achievements, or swiftly endorsing non-controversial business items where consensus is evident.
Comparative Analysis: Referendum vs Acclamation
Referendum and acclamation represent two distinct democratic decision-making processes with differing mechanisms and implications. Referendum involves a formal vote by the electorate on specific issues or policies, ensuring direct public participation and legal legitimacy, whereas acclamation is an informal show of consensus without a formal vote, often used in parliamentary procedures or elections when candidates run unopposed. The key comparative aspect lies in the level of public engagement and procedural formality, with referendums providing quantifiable results and broader voter inclusion compared to the symbolic affirmation inherent in acclamation.
Advantages of Referendum in Modern Democracies
Referendums enhance direct democracy by allowing citizens to vote directly on key policy issues, increasing political participation and legitimacy. They provide a clear mandate for governments, reducing ambiguity and strengthening accountability in decision-making. This process also fosters greater public awareness and engagement on critical matters, promoting transparency and trust in modern democratic systems.
Risks and Limitations of Acclamation
Acclamation, while efficient for decision-making, carries risks such as lack of transparency, potential suppression of dissenting opinions, and limited voter engagement, which can undermine legitimacy. The absence of a formal voting process increases vulnerability to manipulation or unrepresentative outcomes. These limitations highlight the importance of careful consideration before opting for acclamation in governance or organizational contexts.
Global Case Studies: Referendum and Acclamation in Practice
Referendum and acclamation serve as distinct democratic tools for decision-making, with referendums exemplified by Switzerland's frequent use of nationwide votes to address constitutional changes, while acclamation is notably seen in smaller indigenous communities where consensus replaces formal voting. In global case studies, referendums provide a direct mechanism for citizen participation on specific policies, as demonstrated by the Brexit referendum in the UK, contrasting with acclamation's reliance on unanimous or overwhelming approval without a ballot, common in local tribal governance in Canada. The effectiveness of these approaches depends on the scale and nature of the decision, highlighting the referendum's strength in large-scale democratic engagement and acclamation's role in fostering unity within cohesive groups.
Which Works Best? Choosing Between Referendum and Acclamation
Referendums work best in democratic decision-making processes by allowing voters to directly express their opinions on specific issues, ensuring legitimacy through majority consensus. Acclamation, often used in smaller or less formal settings, is effective when unanimity or near-unanimity is expected, streamlining decisions without the need for ballots. Choosing between referendum and acclamation depends on the scale of participation and the necessity for formal validation of the collective decision.
Referendum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com