Lane and Ersson's typology categorizes political parties based on their societal functions, organizational structures, and ideological orientations, offering a comprehensive framework for understanding party systems. This typology helps analyze how parties mobilize support, maintain internal cohesion, and link citizens to the state through various mechanisms. Explore the rest of the article to discover how this classification impacts current political analysis and your understanding of party dynamics.
Table of Comparison
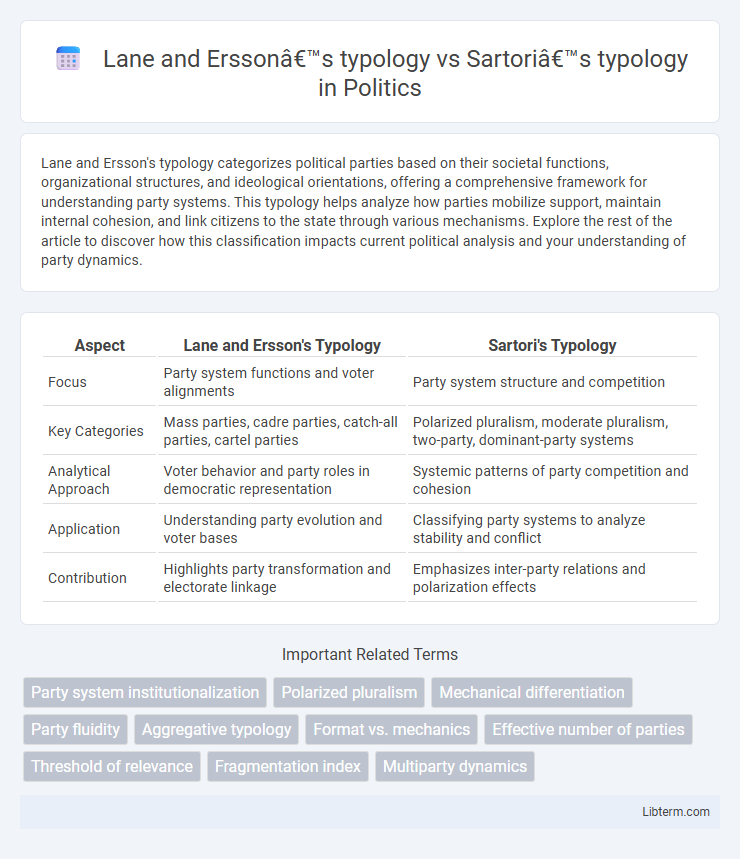
| Aspect | Lane and Ersson's Typology | Sartori's Typology |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Party system functions and voter alignments | Party system structure and competition |
| Key Categories | Mass parties, cadre parties, catch-all parties, cartel parties | Polarized pluralism, moderate pluralism, two-party, dominant-party systems |
| Analytical Approach | Voter behavior and party roles in democratic representation | Systemic patterns of party competition and cohesion |
| Application | Understanding party evolution and voter bases | Classifying party systems to analyze stability and conflict |
| Contribution | Highlights party transformation and electorate linkage | Emphasizes inter-party relations and polarization effects |
Introduction to Typologies in Political Science
Lane and Ersson's typology emphasizes empirical classification based on observable political behaviors and institutional patterns, contrasting with Sartori's typology which is grounded in conceptual frameworks aimed at identifying ideal types within political systems. Sartori's approach prioritizes theoretical rigor and the development of clear, analytical categories, whereas Lane and Ersson integrate comparative empirical data to refine typological distinctions. Both contribute significantly to the introduction of typologies in political science by balancing conceptual clarity with empirical applicability in understanding political phenomena.
Overview of Lane and Ersson’s Typology
Lane and Ersson's typology focuses on categorizing political parties based on ideological dimensions and organizational structures, emphasizing the role of party systems in shaping political behavior. Their framework contrasts with Sartori's typology by incorporating factors such as party integration and the dynamics of electoral competition. This approach highlights the interaction between parties and voter alignments, providing a nuanced understanding of party systems beyond Sartori's emphasis on party system fragmentation and polarization.
Overview of Sartori’s Typology
Sartori's typology categorizes political parties based on their ideological orientation, organizational structure, and levels of competition, distinguishing between mass parties, cadre parties, and catch-all parties. This framework emphasizes the historical development and strategic adaptations of parties within electoral systems, highlighting the shift from elite-driven cadre parties to broader-based catch-all parties. Lane and Ersson's typology, while also analyzing party systems, focuses more on voter behavior and alignment, offering a complementary perspective to Sartori's structural approach.
Conceptual Foundations of Both Typologies
Lane and Ersson's typology is grounded in a behavioral approach emphasizing patterns of political participation and voter alignment, categorizing party systems based on social cleavages and voter loyalty. Sartori's typology centers on the structural and functional relationships between parties, focusing on competition, polarization, and fragmentation to define party system types. Conceptually, Lane and Ersson prioritize sociopolitical cohesion and voter behavior, whereas Sartori emphasizes interaction dynamics and institutional stability within party systems.
Criteria and Dimensions Used by Lane and Ersson
Lane and Ersson's typology emphasizes political systems' structural and functional criteria, analyzing dimensions such as authority distribution, institutional integration, and policy coordination. Their framework categorizes regimes based on how power is allocated between central and regional governments, the strength of party systems, and the capacity for collective decision-making. In contrast, Sartori's typology focuses primarily on party systems and electoral competition, using party number and ideological distance as key dimensions.
Sartori’s Approach to Classification
Sartori's approach to classification emphasizes the importance of clear and precise definitions to create mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive categories, enhancing analytical clarity in political science. Unlike Lane and Ersson's typology, which often focuses on empirical distinctions and descriptive categories, Sartori insists on the systematic conceptual differentiation that allows for clearer comparison and theoretical generalization. This method prioritizes the logical structuring of concepts to avoid overlapping categories, thereby improving the rigor and replicability of typological analysis.
Comparative Strengths and Weaknesses
Lane and Ersson's typology excels in capturing the dynamic interaction between political actors and institutions, offering a flexible framework suited for mixed political systems, while Sartori's typology provides a more structured and clear-cut classification of party systems grounded in regular patterns of competition. Sartori's approach is stronger in its theoretical rigor and ability to generate testable hypotheses about party system fragmentation, but it can be rigid and less adaptable to emerging or hybrid political landscapes. Lane and Ersson's model better accommodates political complexity and variability but may sacrifice some analytical precision and comparability across cases.
Application in Political System Analysis
Lane and Ersson's typology emphasizes empirical categorization of political systems based on observable institutional dynamics and citizen participation, facilitating comparative analysis in diverse governance contexts. Sartori's typology offers a more normative framework centered on party systems, particularly effective in analyzing electoral competition and party behavior within democratic regimes. Applying both typologies enriches political system analysis by integrating institutional structures with party system configurations, enhancing the depth of political behavior and regime stability studies.
Influence on Political Science Research
Lane and Ersson's typology emphasizes the functional differentiation of political institutions, influencing political science research by providing nuanced frameworks for analyzing institutional roles and interactions within complex systems. Sartori's typology, centered on the conceptual clarity of party systems and political processes, has shaped research by offering precise criteria for classification and comparison, fostering empirical rigor. Together, these typologies have enriched political science by balancing institutional analysis with conceptual precision, advancing both theoretical development and empirical investigation.
Conclusion: Relevance and Future Directions
Lane and Ersson's typology refines Sartori's foundational framework by incorporating contemporary political complexities and emphasizing contextual variability across democratic regimes. Their approach enhances the applicability of typological analysis in comparative politics by integrating multidimensional criteria such as institutional design, party systems, and voter behavior. Future research should prioritize empirical testing of these expanded categories to improve predictive accuracy and adapt to evolving political landscapes.
Lane and Ersson’s typology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com