A sunset provision is a clause within a law or contract that sets an expiration date, after which the policy or agreement automatically terminates unless renewed. This mechanism ensures that laws remain relevant and are periodically reviewed for effectiveness. Discover how sunset provisions impact legal frameworks and what they mean for your rights by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
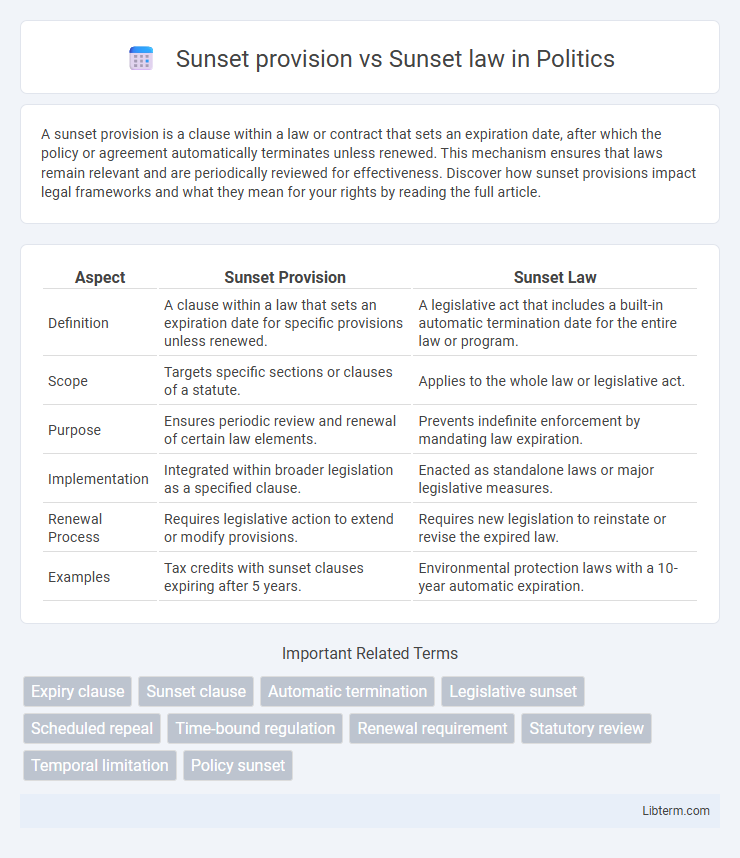
| Aspect | Sunset Provision | Sunset Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A clause within a law that sets an expiration date for specific provisions unless renewed. | A legislative act that includes a built-in automatic termination date for the entire law or program. |
| Scope | Targets specific sections or clauses of a statute. | Applies to the whole law or legislative act. |
| Purpose | Ensures periodic review and renewal of certain law elements. | Prevents indefinite enforcement by mandating law expiration. |
| Implementation | Integrated within broader legislation as a specified clause. | Enacted as standalone laws or major legislative measures. |
| Renewal Process | Requires legislative action to extend or modify provisions. | Requires new legislation to reinstate or revise the expired law. |
| Examples | Tax credits with sunset clauses expiring after 5 years. | Environmental protection laws with a 10-year automatic expiration. |
Understanding Sunset Provisions and Sunset Laws
Sunset provisions are specific clauses inserted into legislation or contracts that set an expiration date, causing the law or regulation to automatically terminate unless renewed by legislative action. Sunset laws refer broadly to statutes that include such provisions, requiring periodic review and reauthorization to ensure they remain relevant and effective. Understanding the distinction helps policymakers design mechanisms for accountability, preventing outdated or unnecessary laws from remaining in force indefinitely.
Defining Sunset Provision
A sunset provision is a clause within a law or contract that sets an automatic expiration date unless further legislative action is taken to extend it. This mechanism ensures that the legislation or agreement is periodically reviewed and reauthorized, promoting accountability and relevance over time. Unlike a sunset law, which is a statute that incorporates sunset provisions across multiple items or laws, a sunset provision specifically refers to the embedded expiration clause within an individual legal or contractual instrument.
Defining Sunset Law
Sunset law refers to legislation that includes a specific expiration date, requiring periodic review and reauthorization to remain effective. This legal mechanism ensures government programs or agencies undergo evaluation, promoting accountability and efficiency by preventing indefinite continuation without oversight. Unlike a general sunset provision, a sunset law is formally enacted legislation mandating automatic termination unless actively renewed by the legislature.
Key Differences Between Sunset Provision and Sunset Law
Sunset provision refers to a specific clause within a legislative act that sets an expiration date for that law or regulation unless renewed, while a sunset law is an entire statute designed to automatically terminate after a certain period. The key difference lies in scope: sunset provisions are embedded within broader laws to limit their duration, whereas sunset laws are standalone laws created with a fixed lifespan. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for lawmakers and legal professionals managing regulatory timelines and renewals.
Purpose and Importance of Sunset Provisions
Sunset provisions are specific clauses within laws or regulations designed to automatically terminate the statute or program after a predetermined period unless renewed by the legislature, ensuring continuous evaluation and relevance. They promote legislative accountability and prevent outdated or ineffective regulations from persisting indefinitely, fostering adaptive governance. Sunset laws, embodying a broader legal framework, institutionalize these provisions across multiple statutes to systematically streamline government functions and enhance policy efficiency.
Role and Impact of Sunset Laws in Legislation
Sunset laws play a critical role in legislative processes by establishing automatic expiration dates for statutes and government agencies, ensuring regular review and evaluation of their effectiveness. The impact of these laws promotes accountability, reduces government waste, and encourages lawmakers to update or repeal outdated policies. In contrast, a sunset provision is a specific clause embedded within a law that triggers its expiration unless renewed, serving as a mechanism to implement sunset laws.
Examples of Sunset Provisions
Sunset provisions are clauses included in legislation that set an automatic expiration date unless further legislative action is taken, commonly seen in tax credits or emergency laws. Examples include the federal estate tax exemption in the United States, which has periodic sunset dates requiring renewal, and state-level renewable energy incentives that expire after a set term unless extended. Sunset laws refer more broadly to statutes designed to expire after a fixed period, but sunset provisions are specific mechanisms within those laws, exemplified by the USA PATRIOT Act's various provisions scheduled for automatic review or expiration.
Notable Cases of Sunset Laws
Sunset provisions are clauses within legislation that set an automatic expiration date unless renewed, while sunset laws refer to statutes that require periodic review and legislative approval to remain in effect. Notable cases of sunset laws include the expiration and review processes of the U.S. Intelligence Reform and Terrorism Prevention Act of 2004 and the USA PATRIOT Act, where Congress periodically assessed their necessity and scope. These cases highlight how sunset laws promote government accountability and legislative oversight by enforcing systematic evaluation of policies.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sunset Mechanisms
Sunset provisions, embedded within specific laws, automatically terminate the law or provision after a set period unless renewed, ensuring regular legislative review and preventing outdated policies from lingering. Sunset laws, which are broader statutes mandating reviews of various regulations or programs on a scheduled basis, promote governmental accountability and reduce unnecessary bureaucracy. However, sunset mechanisms can create uncertainty for stakeholders and may result in administrative burdens due to frequent evaluations and the risk of unintended policy gaps if renewals are delayed or overlooked.
Comparing Effectiveness: Sunset Provision vs. Sunset Law
Sunset provisions specify expiration dates within individual laws or regulations, enabling periodic review and renewal to maintain legislative relevance, while sunset laws establish a broader legal framework mandating systematic evaluation of multiple statutes. The effectiveness of sunset provisions lies in their targeted application, allowing lawmakers to address specific policy areas with precision, whereas sunset laws ensure comprehensive oversight and consistency across various legal instruments. Both mechanisms promote accountability and legislative efficiency, but sunset laws often provide a more structured and uniform approach to managing the lifecycle of statutes.
Sunset provision Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com