Hybrid regimes combine elements of democracy and authoritarianism, often maintaining elections while limiting political freedoms and media independence. These systems create a complex political landscape where government control coexists with nominal democratic institutions. Explore the rest of this article to understand how hybrid regimes affect governance and citizen participation.
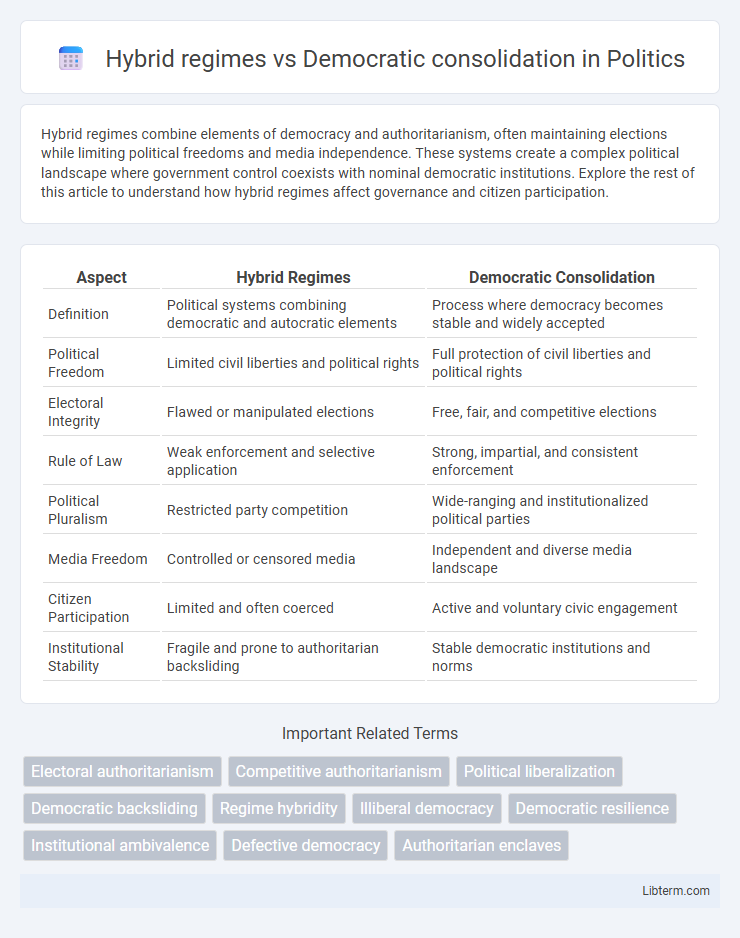
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hybrid Regimes | Democratic Consolidation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political systems combining democratic and autocratic elements | Process where democracy becomes stable and widely accepted |
| Political Freedom | Limited civil liberties and political rights | Full protection of civil liberties and political rights |
| Electoral Integrity | Flawed or manipulated elections | Free, fair, and competitive elections |
| Rule of Law | Weak enforcement and selective application | Strong, impartial, and consistent enforcement |
| Political Pluralism | Restricted party competition | Wide-ranging and institutionalized political parties |
| Media Freedom | Controlled or censored media | Independent and diverse media landscape |
| Citizen Participation | Limited and often coerced | Active and voluntary civic engagement |
| Institutional Stability | Fragile and prone to authoritarian backsliding | Stable democratic institutions and norms |
Understanding Hybrid Regimes: Definition and Features
Hybrid regimes exhibit a blend of democratic and autocratic elements where competitive elections occur alongside significant restrictions on political freedoms and civil liberties. These systems maintain formal democratic institutions but manipulate them through media control, judicial interference, and limitations on opposition parties, hindering true democratic consolidation. Understanding the characteristics of hybrid regimes is crucial for analyzing the obstacles that prevent a stable, fully functioning democracy from emerging.
Key Characteristics of Democratic Consolidation
Democratic consolidation is marked by the stable institutionalization of democratic norms, widespread legitimacy of democratic processes, and effective checks and balances within government structures. It features the protection of civil liberties, regular and competitive elections, and the presence of a politically engaged and informed citizenry. Unlike hybrid regimes, democratic consolidation ensures the rule of law prevails over authoritarian tendencies, securing long-term political stability and accountability.
Historical Evolution of Hybrid Regimes
Hybrid regimes have emerged historically as political systems blending democratic and authoritarian features, often arising from incomplete transitions or backsliding of democratic institutions. These regimes typically exhibit multiparty elections alongside persistent constraints on civil liberties, media freedom, and judicial independence, creating challenges for democratic consolidation. Understanding their evolution reveals patterns of elite manipulation and institutional weaknesses that hinder the full establishment of liberal democracy.
Factors Driving Democratic Consolidation
Hybrid regimes often exhibit a blend of democratic and autocratic features, which can hinder democratic consolidation by fostering political instability and undermining institutional trust. Key factors driving democratic consolidation include the establishment of strong, independent institutions, sustained political participation, and the protection of civil liberties and rule of law. Economic development and effective governance also play crucial roles in reinforcing democratic norms and encouraging citizen engagement in hybrid political systems.
Comparisons: Hybrid Regimes vs Democratic Systems
Hybrid regimes combine authoritarian and democratic features, often exhibiting electoral manipulation, restricted civil liberties, and limited political competition, unlike fully consolidated democracies characterized by free, fair elections, rule of law, and protection of individual rights. Democratic consolidation involves stable institutions, widespread political legitimacy, and active citizen participation, which hybrid regimes lack due to their ambiguous governance structures and weakened checks and balances. Comparatively, hybrid regimes show vulnerability to authoritarian backsliding, whereas democratic systems demonstrate resilience through institutionalized democratic norms and accountability mechanisms.
Challenges to Democratic Consolidation
Hybrid regimes blur the line between authoritarianism and democracy, often undermining democratic consolidation by fostering weak institutions and limited political pluralism. Challenges to democratic consolidation include the persistence of electoral fraud, restricted civil liberties, and the co-optation of opposition parties, which weaken trust in democratic processes. Furthermore, socioeconomic inequalities and pervasive corruption hinder the development of accountable governance and robust rule of law essential for sustainable democratic consolidation.
Role of Institutions in Hybrid Regimes
Institutions in hybrid regimes often exhibit limited autonomy and are frequently manipulated by ruling elites to maintain power, undermining democratic consolidation. These institutions, such as electoral commissions, judiciaries, and legislatures, serve as arenas for controlled political competition rather than genuine democratic processes. Weak institutional checks and balances in hybrid regimes hinder transparency and accountability, impeding the transition toward full democratic consolidation.
Electoral Processes: Free, Fair, or Flawed?
Hybrid regimes often manipulate electoral processes, using tactics like voter intimidation, media bias, and incomplete vote counts to maintain power despite nominal elections. Democratic consolidation requires consistently free and fair elections characterized by transparent procedures, equal media access, and credible electoral commissions to ensure genuine competition. Flawed electoral processes in hybrid regimes undermine public trust and hinder the transition to stable democracy.
Media Freedom and Civil Society Influence
Hybrid regimes often restrict media freedom through censorship and state control, limiting independent journalism and hindering civil society's capacity to mobilize. In contrast, democratic consolidation is marked by robust protections for media freedom that enable diverse and free-flowing information, strengthening civil society's influence in political processes. Active civil society organizations in consolidated democracies leverage media independence to advocate transparency, accountability, and citizen participation.
Pathways Toward Democratization in Hybrid Regimes
Hybrid regimes often exhibit a complex interplay between authoritarian practices and democratic institutions, presenting unique pathways toward democratic consolidation. Transitional processes in these regimes typically involve gradual institutional reforms, increased political competition, and improved civil liberties, which collectively enhance the prospects for democratic stability. Key factors influencing successful democratization include robust civil society engagement, independent judiciary systems, and sustained international support promoting accountability and transparent governance.
Hybrid regimes Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com