Elections are fundamental to democratic governance, allowing citizens to choose their representatives and influence public policy directly. Understanding the different types, processes, and implications of elections can empower you to make informed decisions at the ballot box. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your knowledge about how elections shape societies and affect your everyday life.
Table of Comparison
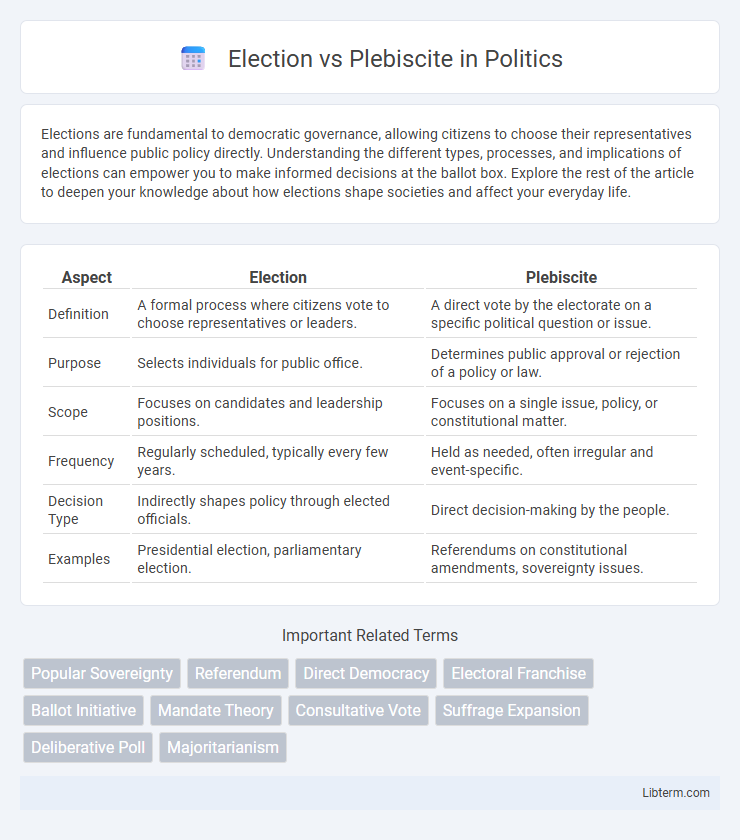
| Aspect | Election | Plebiscite |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A formal process where citizens vote to choose representatives or leaders. | A direct vote by the electorate on a specific political question or issue. |
| Purpose | Selects individuals for public office. | Determines public approval or rejection of a policy or law. |
| Scope | Focuses on candidates and leadership positions. | Focuses on a single issue, policy, or constitutional matter. |
| Frequency | Regularly scheduled, typically every few years. | Held as needed, often irregular and event-specific. |
| Decision Type | Indirectly shapes policy through elected officials. | Direct decision-making by the people. |
| Examples | Presidential election, parliamentary election. | Referendums on constitutional amendments, sovereignty issues. |
Understanding Elections: A Comprehensive Overview
Elections are formal processes where citizens vote to choose representatives or decide on policies, ensuring democratic governance through systematic voting mechanisms. These events involve candidates, political parties, and legal frameworks designed to uphold fairness, transparency, and accountability in selecting public officials or determining legislative measures. Unlike plebiscites, elections focus on selecting individuals for public office rather than directly deciding specific policy questions or constitutional changes.
Defining Plebiscite: Meaning and Purpose
A plebiscite is a direct vote by the electorate to decide on a specific constitutional or political issue, often relating to sovereignty or major policy changes. Unlike elections, which select representatives or officials, plebiscites serve as a tool for gauging public opinion on critical national decisions. This process strengthens democratic participation by enabling citizens to directly influence major government actions or territorial status.
Key Differences Between Elections and Plebiscites
Elections involve choosing representatives or leaders through voting, enabling citizens to influence government formation and policy direction, while plebiscites are direct votes by the electorate on specific issues or policies, serving as a tool for public consultation. Elections typically feature multiple candidates or parties competing for positions, whereas plebiscites present a binary or limited set of options related to a particular question. The key difference lies in the purpose: elections decide officeholders, and plebiscites gauge public opinion on policy matters.
Historical Context: Elections vs Plebiscites Worldwide
Elections and plebiscites have played distinct roles in shaping political histories globally, with elections serving as representative mechanisms in democratic societies to choose leaders and lawmakers, while plebiscites historically resolve specific policy or territorial questions directly from the populace. The 1919 Treaty of Versailles plebiscites, such as in Schleswig and Silesia, exemplify how plebiscites were used for self-determination after World War I, contrasting with regular electoral processes underpinning parliamentary democracies. Electoral systems developed over centuries in countries like the United Kingdom and the United States emphasize representative governance, whereas plebiscites have often been pivotal during periods of constitutional change or sovereignty disputes worldwide.
Legal Framework: Electoral and Plebiscite Processes
Elections are governed by comprehensive legal frameworks that outline voter eligibility, candidate qualifications, campaign regulations, and vote counting procedures, ensuring transparency and fairness in representative governance. Plebiscite processes operate under specific legal statutes that define the scope of issues to be voted on, the conditions for validity, and mechanisms for implementing the outcome, often focusing on direct public consent for constitutional or territorial matters. Both systems require adherence to electoral laws and administrative guidelines tailored to their distinct functions within democratic decision-making.
Roles and Impacts in Democratic Governance
Elections serve as a fundamental mechanism in democratic governance by enabling citizens to choose representatives who legislate and make policy decisions, thus ensuring accountability and political legitimacy. Plebiscites function as direct democratic tools allowing the electorate to decide on specific issues, often shaping constitutional changes or major public policies with immediate societal impact. Both processes enhance civic engagement and can influence government responsiveness, but elections establish long-term leadership while plebiscites address singular, critical questions.
Voter Participation: Elections Compared to Plebiscites
Voter participation in elections typically shows higher engagement due to the broader impact on representation and governance, motivating citizens to vote for candidates or parties. Plebiscites often experience lower turnout as they address specific issues, leading to less widespread interest among the electorate. Differences in legal requirements and perceived significance directly influence participation rates between elections and plebiscites.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each System
Elections offer a structured, representative democratic process that enables citizens to choose candidates or parties, promoting political stability and accountability but can lead to voter apathy and disproportionate representation. Plebiscites provide direct citizen participation on specific issues, ensuring clear public mandates and legitimacy but risk oversimplification of complex policies and susceptibility to populist manipulation. Both systems have distinct advantages: elections foster long-term governance choices, while plebiscites deliver immediate public consent, yet their disadvantages highlight challenges in inclusivity and informed decision-making.
Case Studies: Notable Elections and Plebiscites
The 2016 Brexit referendum in the United Kingdom exemplifies a plebiscite used to determine the public's stance on EU membership, resulting in a 52% vote to leave. In contrast, the 2020 United States presidential election showcased a direct vote where Joe Biden secured 306 electoral votes against Donald Trump's 232, reflecting a representative democratic process. The 1999 Australian republic referendum, a plebiscite, failed to pass with 55% voting no, highlighting the difference in binding authority compared to regular elections like those in India's Lok Sabha, where parliamentary representatives are elected through a multi-phase voting process.
Future Trends: The Evolving Role of Public Consultation
Future trends in public consultation emphasize digital platforms that enhance voter engagement in elections and plebiscites, facilitating real-time feedback and broader participation. Advances in blockchain technology are expected to increase transparency and security in electoral processes, fostering greater public trust. The evolving role of artificial intelligence enables more precise analysis of public opinion, shaping policy decisions and democratic governance.
Election Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com