Acclamation represents widespread approval or enthusiastic praise expressed by a group, often seen in political or public settings as a vocal show of agreement. It signifies strong support without the need for a formal vote, highlighting the collective endorsement of ideas or individuals. Discover more about how acclamation influences decision-making and its impact in various contexts by reading further.
Table of Comparison
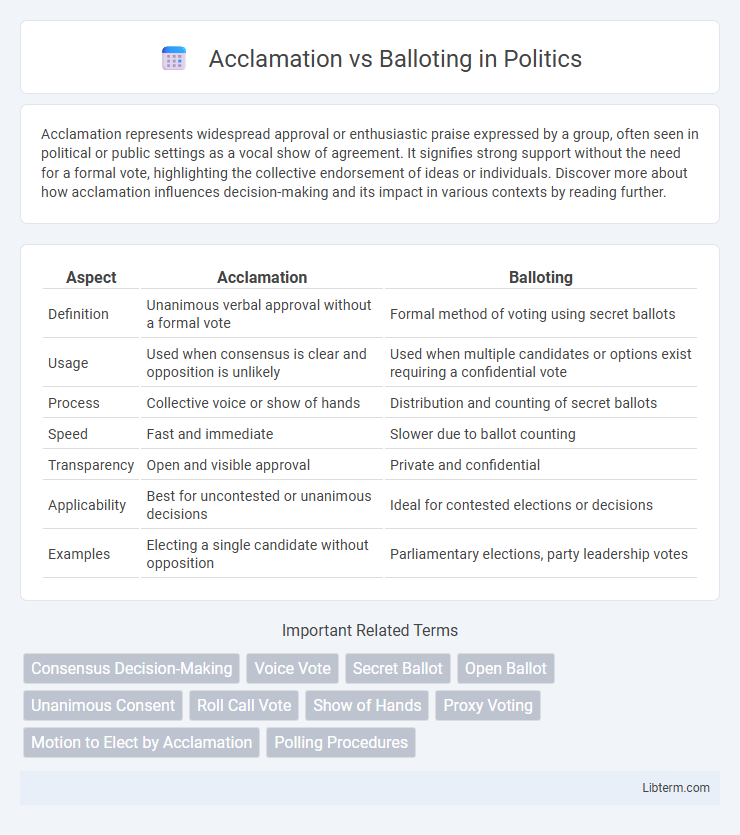
| Aspect | Acclamation | Balloting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unanimous verbal approval without a formal vote | Formal method of voting using secret ballots |
| Usage | Used when consensus is clear and opposition is unlikely | Used when multiple candidates or options exist requiring a confidential vote |
| Process | Collective voice or show of hands | Distribution and counting of secret ballots |
| Speed | Fast and immediate | Slower due to ballot counting |
| Transparency | Open and visible approval | Private and confidential |
| Applicability | Best for uncontested or unanimous decisions | Ideal for contested elections or decisions |
| Examples | Electing a single candidate without opposition | Parliamentary elections, party leadership votes |
Understanding Acclamation and Balloting
Understanding acclamation involves recognizing it as a unanimous verbal or non-verbal expression of approval, typically used in meetings or elections where consensus is clear and swift, eliminating the need for a formal vote. Balloting, in contrast, refers to the structured process of casting and counting votes, often secretive, to determine the outcome objectively when unanimity is not present. Both methods serve to validate decisions, with acclamation emphasizing immediate consensus and balloting ensuring democratic fairness through private voting.
Historical Overview of Voting Methods
Acclamation and balloting represent two foundational voting methods with deep historical roots in democratic processes. Acclamation, often used in ancient assemblies and early civilizations, involved vocal or unanimous approval without formal ballots, reflecting communal consensus in small groups. Balloting emerged later as societies grew complex, introducing secret ballots and structured voting to ensure individual privacy and reduce coercion, marking a significant evolution in electoral transparency and fairness.
Key Differences Between Acclamation and Balloting
Acclamation involves making decisions by voice or show of hands, allowing immediate consensus without a formal vote count, while balloting requires secret voting and tabulation for privacy and accuracy. Acclamation suits unanimous or non-controversial issues, speeding up decision-making, whereas balloting ensures confidentiality and fairness in contested elections or sensitive matters. The key difference lies in transparency and procedure: acclamation is open and informal, balloting is private and structured to prevent influence or bias.
Advantages of Acclamation
Acclamation offers the advantage of swift decision-making by allowing unanimous or near-unanimous agreement without the need for formal voting procedures. This method fosters unity and reflects strong collective support, minimizing conflict and dissent within groups. It also reduces administrative time and costs associated with organizing a ballot, making it efficient for straightforward or non-controversial decisions.
Advantages of Balloting
Balloting ensures confidentiality by allowing voters to cast their votes anonymously, reducing the risk of peer pressure or coercion. The process provides an accurate and verifiable method to gauge genuine preferences, enhancing transparency and legitimacy in decision-making. Balloting facilitates broad participation by enabling remote or absentee voting, improving inclusivity and accessibility.
Situations Suitable for Acclamation
Acclamation is suitable in situations where consensus is clear, such as small meetings, unanimous decisions, or when candidates run unopposed. This method streamlines the voting process, saving time and fostering group cohesion. Balloting is preferred when anonymity or multiple candidate choices require formal vote counting.
Situations Suitable for Balloting
Balloting is suitable in situations where anonymity is crucial to ensure honest voting, such as in union elections or confidential board decisions. It is preferred when multiple candidates or options require clear, unbiased results through individual voting. Complex or contentious issues benefit from balloting to prevent peer pressure and ensure a transparent, verifiable outcome.
Challenges and Limitations of Acclamation
Acclamation often faces challenges such as lack of transparency and potential bias due to the absence of formal voting processes, which can undermine legitimacy in decision-making. It limits participant engagement by not providing an opportunity for dissent or alternative options, potentially sidelining minority opinions. The informal nature of acclamation can lead to disputes and decreased accountability, especially in large or contentious assemblies.
Challenges and Limitations of Balloting
Balloting faces challenges such as susceptibility to voter manipulation and confidentiality breaches, which can compromise election integrity. The process demands rigorous administrative oversight to prevent errors and delays, increasing operational costs and complexity. Limited accessibility for remote or disabled voters can further reduce participation rates, highlighting significant limitations compared to acclamation methods.
Choosing the Right Method: Acclamation or Balloting
Choosing between acclamation and balloting depends on the size and formality of the group as well as the importance of transparency in decision-making. Acclamation is ideal for smaller groups or unanimous decisions where efficiency and consensus are prioritized, while balloting suits larger organizations requiring confidentiality and precise vote counts. Organizations must assess their need for speed versus accuracy and member participation when selecting the appropriate nomination or election method.
Acclamation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com