Open markets foster competitive pricing and innovation by allowing multiple buyers and sellers to freely exchange goods and services. This environment encourages transparency, efficiency, and economic growth while reducing barriers to entry and monopolistic control. Discover how open markets can shape your economic opportunities and influence global trade by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
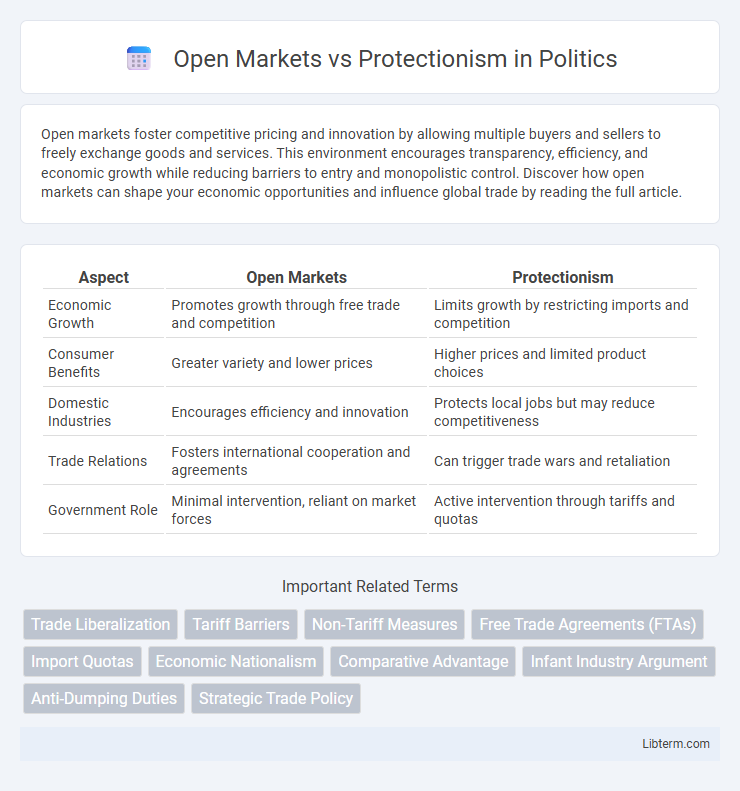
| Aspect | Open Markets | Protectionism |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Growth | Promotes growth through free trade and competition | Limits growth by restricting imports and competition |
| Consumer Benefits | Greater variety and lower prices | Higher prices and limited product choices |
| Domestic Industries | Encourages efficiency and innovation | Protects local jobs but may reduce competitiveness |
| Trade Relations | Fosters international cooperation and agreements | Can trigger trade wars and retaliation |
| Government Role | Minimal intervention, reliant on market forces | Active intervention through tariffs and quotas |
Understanding Open Markets: Key Principles
Open markets emphasize free trade, minimal tariffs, and reduced regulatory barriers to encourage global competition and innovation. Key principles include transparency, nondiscrimination, and market accessibility, allowing businesses to operate efficiently across borders. These elements foster economic growth, consumer choice, and resource allocation based on comparative advantage.
Protectionism Explained: Core Concepts
Protectionism refers to economic policies aimed at shielding domestic industries from foreign competition through tariffs, quotas, and import restrictions. These measures intend to preserve local jobs, protect emerging sectors, and reduce dependency on international markets. Critics argue that protectionism can lead to higher consumer prices, inefficiencies, and retaliatory trade barriers.
Historical Context: Trade Policies Through the Ages
Historical trade policies have oscillated between open markets and protectionism, reflecting economic and political priorities of different eras. The mercantilist period (16th-18th centuries) favored protectionism through tariffs and monopolies to accumulate national wealth, while the 19th century saw a shift toward free trade principles exemplified by Britain's repeal of the Corn Laws in 1846. Post-World War II institutions like GATT and the WTO have since promoted open markets, encouraging multilateral trade liberalization to foster global economic growth.
Economic Impacts: Growth and Efficiency
Open markets promote economic growth by enabling resource allocation based on comparative advantage, leading to increased productivity and innovation. Protectionism often creates inefficiencies by distorting trade flows, raising costs for consumers, and limiting competition, which can hinder long-term economic growth. Empirical studies show countries engaged in open trade policies tend to achieve higher GDP growth rates and improved overall economic efficiency compared to those implementing restrictive trade barriers.
Effects on Domestic Industries: Winners and Losers
Open markets expose domestic industries to international competition, fostering innovation and efficiency among winners who adapt and thrive in global markets, while less competitive firms often face decline or closure. Protectionism shields certain industries through tariffs or quotas, temporarily preserving jobs and market share but risking stagnation and higher costs for consumers. The long-term impact includes potential industry complacency under protectionism versus dynamic growth and restructuring in open economies.
Consumer Benefits and Drawbacks
Open markets increase consumer choices by allowing access to a wide range of foreign goods, often at lower prices due to competitive global supply chains. Protectionism can limit these choices and typically raises prices by imposing tariffs or quotas on imported products, which may protect domestic jobs but reduce consumer purchasing power. However, protectionism can also safeguard local industries and maintain product quality standards, potentially benefiting consumers seeking domestic goods.
Employment and Labor Market Consequences
Open markets typically promote job creation by enabling firms to expand through access to global demand, fostering competitive labor markets and higher wage growth. Protectionism can lead to short-term employment gains in protected industries but often results in inefficiencies, reduced innovation, and job losses in sectors reliant on exports or imported inputs. Empirical studies show that sustained open trade policies correlate with lower unemployment rates and improved labor productivity across diverse economies.
Globalization and International Relations
Open markets drive globalization by enabling free flow of goods, services, and capital, fostering economic interdependence among nations and stimulating innovation through competitive international trade. Protectionism, through tariffs and quotas, restricts global exchange, often leading to trade wars and strained international relations that can impede diplomatic cooperation. The balance between open markets and protectionism significantly impacts global economic stability, influencing alliances and geopolitical strategies within international organizations like the WTO and G20.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures
Open markets have fueled rapid economic growth in countries like South Korea and Singapore by fostering innovation, foreign investment, and export diversification, showcasing the benefits of trade liberalization. In contrast, protectionism in Venezuela led to economic decline due to inefficient industries and poor resource allocation, highlighting the risks of isolationist policies. Brazil's mixed approach demonstrates that moderate protectionist measures can shield nascent industries while open markets drive competitiveness, but imbalance often results in stagnation or inflation.
The Future of Trade: Finding a Balanced Approach
The future of trade demands a balanced approach that leverages the benefits of open markets while addressing the concerns raised by protectionism through strategic regulations. Emphasizing transparent trade policies and fair competition enhances global economic growth and innovation without compromising domestic industries. Integrating sustainable practices and technology-driven solutions ensures resilient supply chains and equitable opportunities for all stakeholders.
Open Markets Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com