Authoritarianism concentrates power in the hands of a single leader or elite group, suppressing political opposition and limiting individual freedoms. This governance style often employs censorship, propaganda, and state control to maintain authority and restrict civil liberties. Explore the rest of the article to understand how authoritarianism impacts societies and what signs to watch for in your own country.
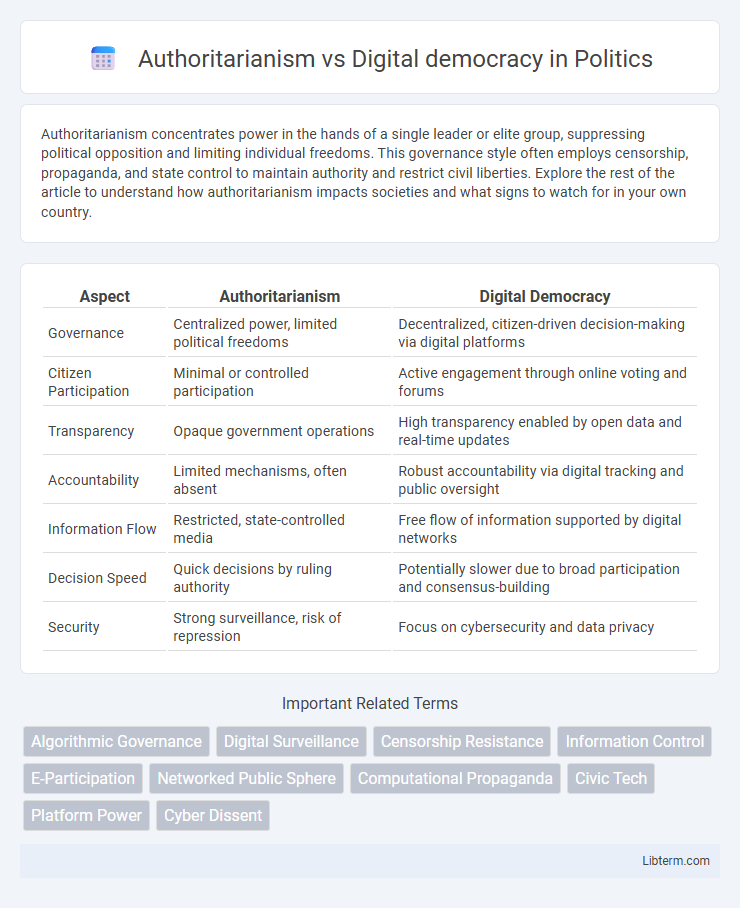
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Authoritarianism | Digital Democracy |
|---|---|---|
| Governance | Centralized power, limited political freedoms | Decentralized, citizen-driven decision-making via digital platforms |
| Citizen Participation | Minimal or controlled participation | Active engagement through online voting and forums |
| Transparency | Opaque government operations | High transparency enabled by open data and real-time updates |
| Accountability | Limited mechanisms, often absent | Robust accountability via digital tracking and public oversight |
| Information Flow | Restricted, state-controlled media | Free flow of information supported by digital networks |
| Decision Speed | Quick decisions by ruling authority | Potentially slower due to broad participation and consensus-building |
| Security | Strong surveillance, risk of repression | Focus on cybersecurity and data privacy |
Understanding Authoritarianism in the Digital Age
Authoritarianism in the digital age leverages advanced surveillance technologies, data analytics, and censorship tools to consolidate power and suppress dissent more efficiently. Governments use digital platforms to monitor citizens' online activities, manipulate information flow, and restrict access to opposing viewpoints, creating controlled digital environments. This fusion of authoritarian control with digital infrastructure challenges traditional democratic principles by undermining transparency, privacy, and free expression.
Defining Digital Democracy: Principles and Practices
Digital democracy embodies the use of digital technologies to enhance citizen participation, transparency, and accountability in governance. Core principles include inclusivity, open access, and real-time engagement through platforms like e-voting, online consultations, and social media forums. These practices aim to empower individuals by decentralizing decision-making and fostering direct interaction between governments and constituents.
Historical Context: From Traditional to Digital Governance
Authoritarianism traditionally relies on centralized control, limiting public participation and suppressing dissent to maintain power. Digital democracy leverages internet technologies and social media platforms to enhance transparency, citizen engagement, and participatory decision-making processes. The historical transition from traditional governance to digital governance reflects a shift from hierarchical authority structures to more decentralized and interactive political models.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Political Systems
Technology significantly influences political systems by enabling surveillance and control in authoritarian regimes, restricting citizens' access to information and suppressing dissent through advanced digital tools. In contrast, digital democracy leverages technology to enhance transparency, facilitate citizen participation, and promote decentralized decision-making via online platforms, social media, and e-governance initiatives. The deployment of artificial intelligence, blockchain, and big data analytics further transforms political engagement, with authoritarian governments exploiting these tools for control, while democratic systems utilize them to strengthen accountability and inclusivity.
Censorship and Surveillance: Tools of Authoritarian Regimes
Authoritarian regimes deploy extensive censorship and surveillance to control information flow and suppress dissent, using advanced technologies such as AI-driven content filtering and mass data collection systems. These tools enable real-time monitoring of citizens' communications and online activities, effectively stifling free expression and political opposition. In contrast, digital democracy leverages open internet platforms and encryption to promote transparency, protect privacy, and empower citizen participation in governance.
Digital Platforms as Arenas for Democratic Engagement
Digital platforms serve as pivotal arenas for democratic engagement by facilitating direct interaction between citizens and policymakers, enhancing transparency, and promoting civic participation. These platforms enable real-time public discourse, access to diverse perspectives, and mobilization around social issues, counterbalancing authoritarian control over information. The decentralized nature of digital networks supports greater accountability and peer-to-peer collaboration, fostering a more inclusive and responsive democratic process.
Propaganda, Misinformation, and Digital Manipulation
Authoritarian regimes leverage propaganda, misinformation, and digital manipulation to control public opinion, suppress dissent, and maintain power through state-controlled media and sophisticated cyber tactics. Digital democracy faces challenges from these tactics, which undermine transparent information flow and distort online discourse, making it difficult for citizens to discern factual content from falsehoods. Effective countermeasures such as digital literacy, fact-checking initiatives, and algorithmic transparency are critical to mitigating the impact of propaganda and preserving democratic participation.
Case Studies: Authoritarianism and Digital Democracy in Action
China's social credit system exemplifies authoritarianism through extensive surveillance and data control, restricting individual freedoms while promoting state loyalty. In contrast, Estonia demonstrates digital democracy by leveraging e-governance platforms like e-Residency and online voting, enhancing transparency, citizen participation, and policymaking efficiency. These case studies highlight how technology can either reinforce state control or empower democratic engagement depending on governance frameworks.
The Challenges of Safeguarding Rights in the Digital Era
Authoritarianism in the digital era leverages advanced surveillance technologies and censorship algorithms to suppress dissent and control information flow, posing significant challenges to safeguarding human rights online. Digital democracy advocates face obstacles such as data privacy breaches, misinformation campaigns, and state-sponsored cyberattacks that undermine transparent governance and citizen empowerment. Protecting digital rights requires robust cybersecurity frameworks, legal protections for free expression, and international cooperation to counteract authoritarian digital repression.
Future Prospects: Bridging Authoritarian Control and Democratic Innovation
Future prospects for governance involve integrating authoritarian control mechanisms with digital democracy innovations, leveraging advanced data analytics and AI-driven platforms to enhance citizen engagement while maintaining centralized oversight. Hybrid models may emerge, where governments employ blockchain technology and secure digital identities to enable transparent voting and participation, yet retain strategic control over information flow and public discourse. This convergence could redefine political power structures, balancing efficient decision-making with inclusive digital participation to address complex societal challenges.
Authoritarianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com