Territorial claims often involve disputes over land or maritime boundaries between nations, driven by historical evidence, strategic importance, or natural resource access. Understanding the legal frameworks and international laws that govern these claims is crucial for resolving conflicts peacefully. Explore the rest of the article to learn how your awareness of territorial claims can foster informed discussions and solutions.
Table of Comparison
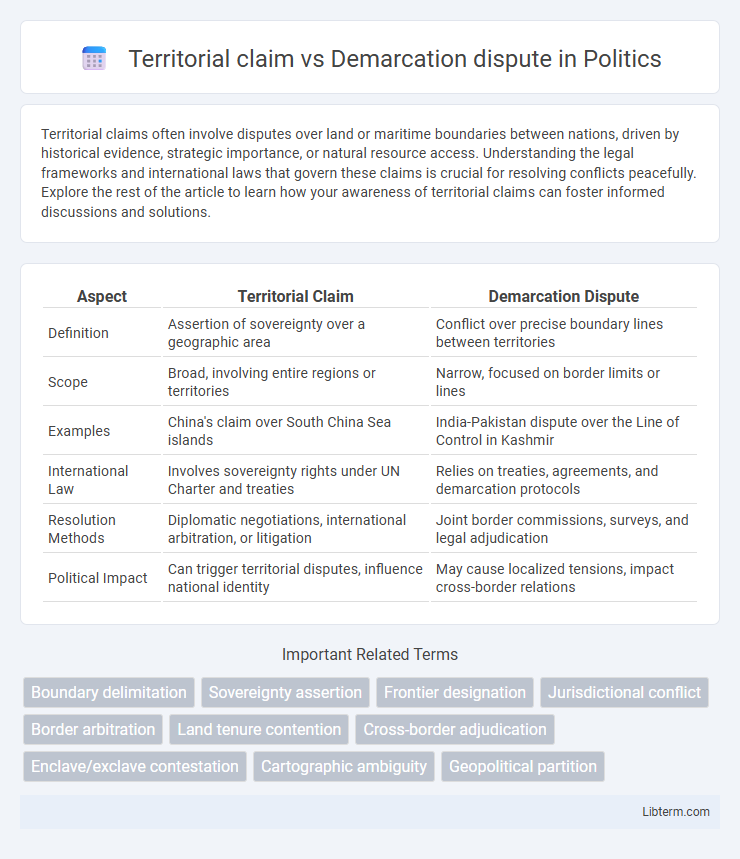
| Aspect | Territorial Claim | Demarcation Dispute |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assertion of sovereignty over a geographic area | Conflict over precise boundary lines between territories |
| Scope | Broad, involving entire regions or territories | Narrow, focused on border limits or lines |
| Examples | China's claim over South China Sea islands | India-Pakistan dispute over the Line of Control in Kashmir |
| International Law | Involves sovereignty rights under UN Charter and treaties | Relies on treaties, agreements, and demarcation protocols |
| Resolution Methods | Diplomatic negotiations, international arbitration, or litigation | Joint border commissions, surveys, and legal adjudication |
| Political Impact | Can trigger territorial disputes, influence national identity | May cause localized tensions, impact cross-border relations |
Understanding Territorial Claims: Definition and Context
Territorial claims refer to assertions by a state or entity over a specific geographic area based on historical ownership, cultural ties, or legal grounds, often rooted in extensive documentation and international law. These claims establish the legal basis for sovereignty but do not always lead to conflict without clear borders. Understanding the context of territorial claims is crucial, as ambiguous or overlapping claims frequently evolve into demarcation disputes where precise boundary lines are contested and negotiated.
What Constitutes a Demarcation Dispute?
A demarcation dispute arises when neighboring states or entities contest the precise positioning of an agreed-upon boundary line on the ground, often due to ambiguous treaties or inadequate mapping. Unlike territorial claims, which involve sovereignty over a land area, demarcation disputes center on the physical manifestation and technical placement of borders established by legal documents. Clarifying demarcation issues typically requires joint surveys, historical records, and diplomatic negotiations to resolve conflicting interpretations without challenging sovereignty.
Key Differences Between Territorial Claims and Demarcation Disputes
Territorial claims involve assertions of sovereignty over a geographic area by a state or entity, often based on historical, cultural, or legal grounds. Demarcation disputes arise when neighbors with established territorial claims disagree on the precise boundary lines, leading to conflicts over where borders are physically delineated. The key difference lies in territorial claims focusing on ownership rights, while demarcation disputes center on exact border placement despite recognized sovereignty.
Legal Frameworks Governing Territorial Claims
Territorial claims are governed primarily by international law, including treaties such as the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and principles outlined in the Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties. Demarcation disputes arise when the precise boundary lines established by these legal frameworks are contested or unclear, often requiring bilateral negotiations or third-party arbitration. International courts and tribunals, like the International Court of Justice (ICJ), play a critical role in interpreting legal documents to resolve disputes and affirm state sovereignty over territories.
International Standards in Demarcation Processes
Territorial claims involve assertions of sovereignty over a specific geographic area, while demarcation disputes arise from the physical marking or delimitation of agreed boundaries between states. International standards in demarcation processes emphasize the use of precise geodetic measurements, adherence to prior treaties, and collaboration between boundary commissions to ensure clarity and prevent conflicts. The United Nations provides guidelines through the International Court of Justice and the UN Cartographic Section to facilitate equitable and transparent boundary demarcation.
Historical Examples of Territorial Claims
Historical examples of territorial claims include the British claim over the Falkland Islands, which is rooted in 19th-century sovereignty assertions, and the Chinese claim over Taiwan based on inherited mandate from the Qing Dynasty. These claims often stem from historical treaties, colonization, or conquest. In contrast, demarcation disputes arise when the precise boundary lines between territories, such as the India-China border disagreements along the Line of Actual Control, remain undefined despite mutual recognition of territorial claims.
Notable Demarcation Disputes in Recent History
Notable demarcation disputes in recent history include the India-China border conflict along the Line of Actual Control, where unclear territorial boundaries have led to multiple standoffs. The South China Sea dispute involves overlapping demarcation claims between China, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Vietnam, centered around strategic islands and maritime rights. Another example is the Ethiopia-Eritrea border conflict, which escalated due to contested demarcation lines established post-independence, resulting in prolonged military confrontations.
The Role of Treaties and Agreements in Resolving Disputes
Treaties and agreements play a crucial role in resolving territorial claims and demarcation disputes by establishing legally binding boundaries between states or parties. These instruments often incorporate principles of international law, such as uti possidetis juris and equitable delimitation, to clarify and formalize territorial limits. Effective treaties reduce the risk of conflict by providing clear guidelines for border management, dispute resolution mechanisms, and cooperative frameworks for joint resource utilization.
Impact of Territorial and Demarcation Disputes on International Relations
Territorial claims often involve sovereignty over large, undefined areas, leading to prolonged diplomatic tensions and instability between states, whereas demarcation disputes focus on precisely defined boundary lines, causing localized conflicts that hinder cross-border cooperation. Both types of disputes disrupt international relations by fostering mistrust, escalating military postures, and complicating negotiations for peace treaties or trade agreements. The resolution processes require multilateral diplomacy, legal arbitration under international law, and confidence-building measures to restore stability and facilitate regional integration.
Pathways to Peaceful Resolution and Conflict Prevention
Territorial claim disputes involve competing national sovereignty assertions over a defined geographic area, while demarcation disputes focus on disagreements concerning the precise boundaries within agreed territories. Pathways to peaceful resolution include diplomatic negotiations, third-party mediation, and adjudication by international courts such as the International Court of Justice (ICJ). Conflict prevention relies on confidence-building measures, joint boundary commissions, and adherence to international legal frameworks like the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and the Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties.
Territorial claim Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com