A vote of no confidence is a parliamentary mechanism used to express that a governing body or leader no longer has the support of a majority. This vote can lead to the resignation of the leader or the dissolution of the legislative body, prompting new elections or a change in government. Discover how a vote of no confidence may impact Your political landscape by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
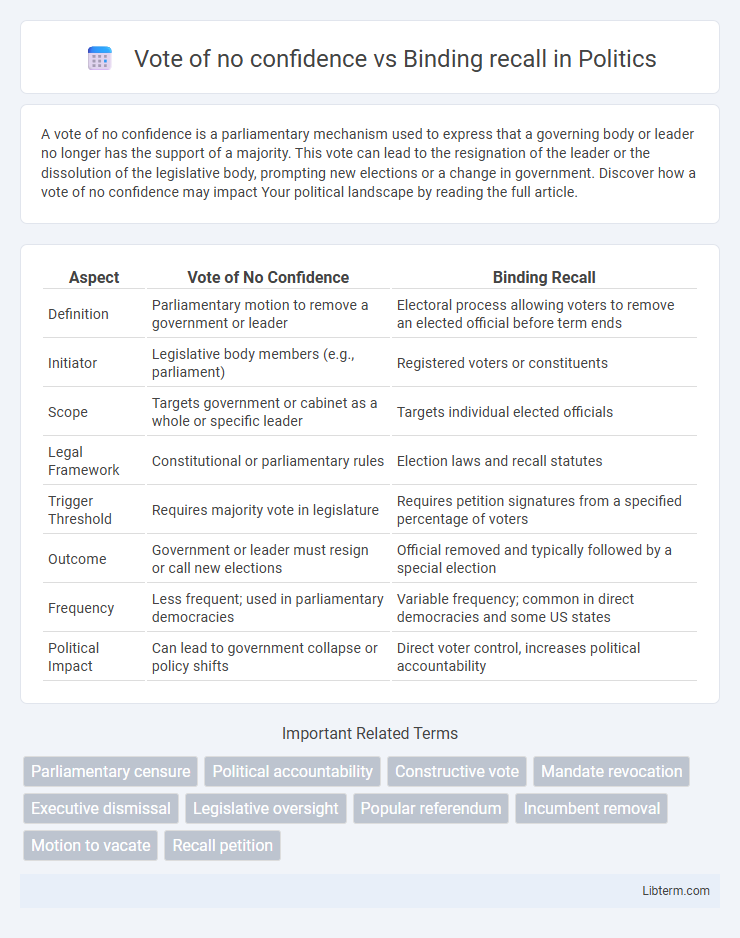
| Aspect | Vote of No Confidence | Binding Recall |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Parliamentary motion to remove a government or leader | Electoral process allowing voters to remove an elected official before term ends |
| Initiator | Legislative body members (e.g., parliament) | Registered voters or constituents |
| Scope | Targets government or cabinet as a whole or specific leader | Targets individual elected officials |
| Legal Framework | Constitutional or parliamentary rules | Election laws and recall statutes |
| Trigger Threshold | Requires majority vote in legislature | Requires petition signatures from a specified percentage of voters |
| Outcome | Government or leader must resign or call new elections | Official removed and typically followed by a special election |
| Frequency | Less frequent; used in parliamentary democracies | Variable frequency; common in direct democracies and some US states |
| Political Impact | Can lead to government collapse or policy shifts | Direct voter control, increases political accountability |
Introduction: Understanding Political Accountability
A Vote of No Confidence is a parliamentary mechanism allowing legislators to remove a sitting government or leader without a general election, emphasizing legislative control and political stability. In contrast, a Binding Recall empowers voters to directly remove elected officials through a popular vote, highlighting grassroots democratic accountability. Both tools serve as critical instruments for ensuring political accountability but operate at different levels of governance and public engagement.
Defining Vote of No Confidence
A Vote of No Confidence is a parliamentary motion that expresses the legislature's lack of support for a government or leader, potentially leading to their removal from office. Unlike a Binding Recall, which is a direct electoral process initiated by voters to remove an elected official before the end of their term, a Vote of No Confidence is typically initiated within the legislative body itself. This mechanism plays a critical role in parliamentary systems to ensure government accountability and stability.
What is a Binding Recall?
A Binding Recall is a political process allowing voters to remove an elected official from office before their term ends through a direct vote, ensuring the outcome is enforceable and final. Unlike a Vote of No Confidence, which is typically initiated by a legislative body and may have political consequences without immediate removal, a Binding Recall empowers the electorate to trigger a new election or replacement. This mechanism increases accountability by giving citizens a direct tool to respond to perceived underperformance or misconduct by officials.
Legal Framework and Mechanisms
The vote of no confidence is a parliamentary tool allowing legislators to remove a government or executive by majority vote, grounded in constitutional or legislative rules that define its initiation, procedure, and consequences. Binding recall is a direct democratic mechanism enabling constituents to remove elected officials before the end of their term via a petition and subsequent vote, governed by specific electoral laws and thresholds to validate the recall process. Legal frameworks for both mechanisms establish procedural safeguards, eligibility criteria, and timelines to balance democratic accountability and political stability.
Historical Context and Origins
The vote of no confidence originated in parliamentary systems during the 19th century, serving as a critical tool for legislatures to remove an executive lacking majority support, primarily in the United Kingdom. Binding recall has its roots in early 20th-century American progressive reforms, designed to empower voters to directly remove elected officials before the end of their term through petition-driven elections. Both mechanisms reflect evolving democratic practices but differ significantly in origin--parliamentary accountability versus direct voter intervention.
Political Implications and Impact
Votes of no confidence primarily influence parliamentary systems by enabling legislatures to remove a sitting government or prime minister, reinforcing legislative oversight and promoting political stability through orderly transitions. Binding recall mechanisms empower voters to directly remove elected officials before their term ends, increasing accountability and responsiveness but potentially leading to greater political volatility and frequent electoral disruptions. The political impact of votes of no confidence centers on institutional checks within representative democracy, whereas binding recalls emphasize direct democratic control, reshaping power dynamics between elected officials and constituents.
Key Differences: Vote of No Confidence vs. Binding Recall
A Vote of No Confidence primarily applies to parliamentary systems as a legislative procedure to remove a sitting government or prime minister without an election, whereas a Binding Recall involves a direct voter-initiated process to remove an elected official from office before their term ends. The Vote of No Confidence is typically initiated by members of the legislature, reflecting a loss of political support within the government, while Binding Recall empowers constituents by allowing them to bypass the legislature and directly demand an official's removal through a referendum. Procedurally, a Vote of No Confidence can lead to the dissolution of the government or new elections, whereas a successful Binding Recall results in a vacancy filled by a special election or appointment.
Case Studies: Global Examples
The Vote of No Confidence serves as a parliamentary tool enabling legislatures to remove elected officials, often prime ministers, without a general election, as demonstrated in the United Kingdom's 1979 removal of James Callaghan's government. Binding recall enables voters to directly remove elected representatives before term completion, illustrated by California's 2003 recall of Governor Gray Davis. These case studies underscore differences in political accountability mechanisms, with parliamentary votes reflecting legislative consensus and recalls emphasizing direct voter intervention.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Mechanism
A vote of no confidence enables legislative bodies to remove executives swiftly, promoting accountability but risking political instability and frequent government changes. Binding recall empowers voters to directly remove elected officials, enhancing democratic control yet possibly leading to costly, frequent elections and potential abuse for political vendettas. Both mechanisms serve as checks on power, but votes of no confidence rely on representative judgment while recalls emphasize direct citizen intervention, each with trade-offs in efficiency and democratic responsiveness.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Tool for Democratic Governance
Vote of no confidence is a parliamentary mechanism allowing legislators to remove executives through formal legislative procedures, ensuring stability and representative accountability. Binding recall empowers citizens directly to remove elected officials before term completion, enhancing direct democracy but potentially risking political volatility. Selecting between these tools depends on the desired balance between legislative oversight and popular sovereignty in democratic governance frameworks.
Vote of no confidence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com