Conservatism emphasizes the preservation of traditional institutions, values, and practices to maintain social stability and continuity. It advocates for gradual change rather than radical reform, valuing the wisdom embedded in cultural heritage and established norms. Explore this article to understand how conservatism shapes political thought and impacts modern society.
Table of Comparison
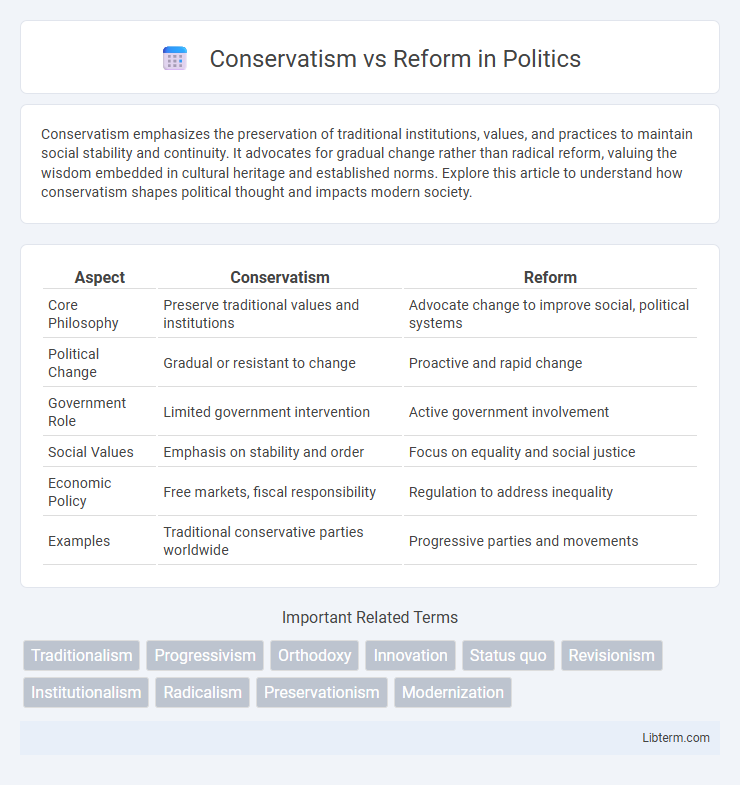
| Aspect | Conservatism | Reform |
|---|---|---|
| Core Philosophy | Preserve traditional values and institutions | Advocate change to improve social, political systems |
| Political Change | Gradual or resistant to change | Proactive and rapid change |
| Government Role | Limited government intervention | Active government involvement |
| Social Values | Emphasis on stability and order | Focus on equality and social justice |
| Economic Policy | Free markets, fiscal responsibility | Regulation to address inequality |
| Examples | Traditional conservative parties worldwide | Progressive parties and movements |
Understanding Conservatism and Reform
Conservatism emphasizes preserving established traditions, institutions, and social orders to maintain stability and continuity within society. Reform advocates seek to modify or replace existing systems to address social injustices, promote progress, and adapt to changing circumstances. Understanding conservatism involves recognizing its preference for cautious change, while reform prioritizes proactive transformation and innovation.
Historical Roots of Conservatism
Conservatism traces its historical roots to the reaction against the radical changes unleashed by the French Revolution, emphasizing the preservation of established institutions, social hierarchy, and tradition. Thinkers like Edmund Burke argued for gradual evolution rather than abrupt reform, advocating stability and continuity within society. This ideological foundation underscores the emphasis on order, authority, and cautious adaptation in conservative thought.
The Emergence of Reform Movements
The emergence of reform movements in the 19th and early 20th centuries was driven by widespread social, economic, and political changes that challenged traditional conservative values and institutions. Reformers sought to address issues such as labor rights, women's suffrage, educational improvements, and government corruption, advocating for policies that promoted social justice and expanded democratic participation. These movements often sparked intense debates between conservatives, who aimed to preserve established order, and reformers pushing for progressive change.
Core Principles of Conservative Thought
Conservative thought emphasizes preserving traditional institutions, valuing social stability, and maintaining established customs to ensure a cohesive society. It prioritizes gradual change over radical reform, stressing the importance of continuity and respect for inherited wisdom. Core principles include a belief in limited government intervention, individual responsibility, and the protection of property rights.
Key Drivers Behind Calls for Reform
Key drivers behind calls for reform include economic inequality, social injustice, and demands for greater political representation and transparency. Rising awareness of systemic flaws and the pressure from progressive movements highlight the urgency for change. Conservatism emphasizes stability and tradition, often resisting rapid reforms due to concerns over societal disruption and loss of established values.
Conservatism in Modern Society
Conservatism in modern society emphasizes preserving traditional values, institutions, and cultural heritage while resisting rapid social change. It advocates for stability, continuity, and respect for established norms in political, economic, and social systems. This ideology often prioritizes family structures, religious principles, and national identity as foundations for societal order and cohesion.
Reform Strategies: Approaches and Tactics
Reform strategies primarily emphasize gradual change through institutional adjustments, policy revisions, and participatory governance to address social inequities and improve public welfare. Key tactics include advocacy for legislative amendments, coalition-building among interest groups, and leveraging public opinion to influence decision-makers. These approaches prioritize sustainable progress while maintaining societal stability by balancing innovation with respect for existing frameworks.
Case Studies: Conservatism vs Reform in Practice
Case studies of conservatism versus reform reveal distinct approaches in governance and societal change, such as the British Industrial Revolution, where conservative policies initially preserved traditional industries before gradual reforms spurred economic modernization. In contrast, China's post-1978 economic reforms under Deng Xiaoping illustrate reformist strategies prioritizing market liberalization and state control adjustments to stimulate growth. Examining these cases highlights how conservative restraint often aims to maintain stability, while reform seeks dynamic transformation through policy innovation.
Societal Impact: Stability versus Progress
Conservatism prioritizes societal stability by preserving established traditions, norms, and institutions, which fosters a sense of order and continuity within communities. Reform drives societal progress by challenging the status quo and advocating for changes that address social inequalities, promote innovation, and adapt to evolving cultural and economic conditions. The tension between stability and progress reflects the ongoing debate over maintaining social cohesion versus embracing transformative change to improve collective well-being.
Navigating the Balance: Finding Common Ground
Conservatism emphasizes preserving established traditions and institutions, while reform advocates for progressive change to address social and political challenges. Navigating the balance requires identifying shared values and goals that allow incremental adjustments without compromising core principles. Effective dialogue and compromise enable societies to evolve thoughtfully, blending stability with necessary innovation.
Conservatism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com