An ad hoc committee is a temporary group formed to address a specific issue or complete a particular task within an organization. Its members have specialized skills relevant to the matter at hand, enabling focused decision-making and problem-solving. Explore the article to learn how creating an effective ad hoc committee can benefit Your projects.
Table of Comparison
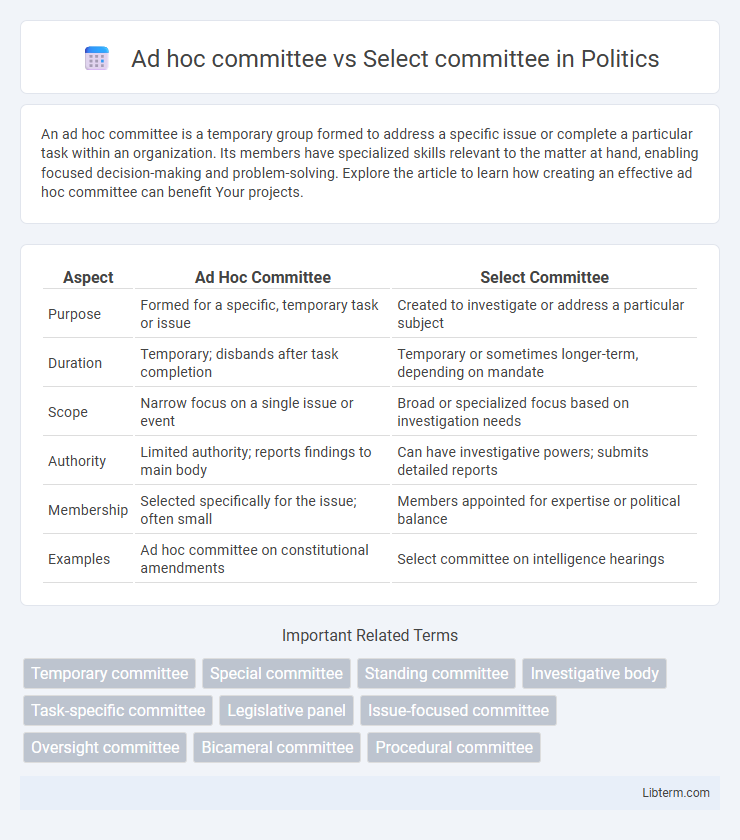
| Aspect | Ad Hoc Committee | Select Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Formed for a specific, temporary task or issue | Created to investigate or address a particular subject |
| Duration | Temporary; disbands after task completion | Temporary or sometimes longer-term, depending on mandate |
| Scope | Narrow focus on a single issue or event | Broad or specialized focus based on investigation needs |
| Authority | Limited authority; reports findings to main body | Can have investigative powers; submits detailed reports |
| Membership | Selected specifically for the issue; often small | Members appointed for expertise or political balance |
| Examples | Ad hoc committee on constitutional amendments | Select committee on intelligence hearings |
Introduction to Committee Types
Ad hoc committees are temporary groups formed to address specific issues or tasks, dissolving after completing their objectives. Select committees also focus on particular areas or problems but may continue over multiple sessions for ongoing oversight and investigation. Both types play crucial roles in legislative processes by enabling detailed examination and specialized expertise outside the scope of standing committees.
Definition of Ad Hoc Committee
An ad hoc committee is a temporary panel formed to address a specific issue or task, dissolving once its objective is achieved. Unlike a select committee, which may have ongoing responsibilities and broader jurisdiction, an ad hoc committee operates with a narrowly defined purpose and limited lifespan. This committee type is commonly established in legislative bodies, corporations, and organizations to swiftly handle urgent or specialized matters.
Definition of Select Committee
A Select Committee is a temporary legislative body established to investigate or consider specific issues outside the jurisdiction of standing committees, targeting detailed examination and reporting. Unlike Ad Hoc Committees, which are often formed for emergency or special assignments with limited scopes, Select Committees may have broader or ongoing mandates until their objectives are fulfilled. They play a crucial role in legislative oversight, fact-finding, and policy recommendations, often influencing significant legislative decisions.
Key Differences Between Ad Hoc and Select Committees
Ad hoc committees are temporary groups established for a specific task or issue, dissolving after their objective is achieved, whereas select committees are usually permanent or semi-permanent bodies tasked with ongoing oversight or investigation. Ad hoc committees have a narrowly defined scope and limited duration, focusing on immediate, specific problems, while select committees often have broader mandates covering continuous policy areas or government functions. The distinction lies primarily in duration, scope, and purpose: ad hoc committees address transient, specialized issues, and select committees maintain long-term scrutiny and legislative recommendations.
Purpose and Functions of Ad Hoc Committees
Ad hoc committees are temporary groups formed to address specific issues or tasks outside the scope of standing committees, designed for focused investigation or problem-solving. Their primary functions include conducting detailed studies, reviewing specialized subjects, and providing recommendations to the larger legislative body. Unlike select committees, which may have more permanent roles, ad hoc committees dissolve after fulfilling their assigned purpose.
Purpose and Functions of Select Committees
Select committees are established to investigate specific issues or areas of policy, providing detailed scrutiny and oversight of government actions or legislation within their specialized domain. Their functions include gathering evidence, holding hearings, and producing reports that influence policy decisions and legislative amendments. Unlike ad hoc committees, which are temporary and dissolve after fulfilling a particular task, select committees often have ongoing responsibilities in monitoring government departments and ensuring accountability.
Formation and Appointment Process
Ad hoc committees are formed for a specific, temporary purpose and are appointed by legislative bodies to address particular issues or tasks. Select committees are also established to investigate or consider specific matters but may have a more formalized structure and longer duration than ad hoc committees. The appointment process for ad hoc committees is typically more flexible and issue-driven, while select committees often involve a more standardized selection of members based on expertise or party representation.
Duration and Dissolution
An ad hoc committee is established for a specific purpose and exists only until its designated task is completed, after which it is automatically dissolved. In contrast, a select committee is usually formed to investigate or consider ongoing issues and may continue its work over a longer duration, sometimes renewing its mandate periodically. The dissolution of select committees depends on the completion of their purpose or decisions by the legislative body, making their lifespan potentially more flexible than ad hoc committees.
Examples in Legislative Context
An ad hoc committee in a legislative context is formed for a specific, temporary purpose, such as the U.S. House Select Committee on the Events Surrounding the 2012 Benghazi Attack, which investigated a singular event. Select committees, like the Senate Select Committee on Intelligence, often have a broader mandate and can be permanent or semi-permanent, addressing ongoing issues such as national security or intelligence matters. Both types differ from standing committees, which handle routine legislation and oversight within defined policy areas.
Summary: Choosing the Right Committee Type
Ad hoc committees are temporary groups formed to address specific issues, dissolving after task completion, while select committees are established for ongoing oversight and detailed investigation within a legislative body. Selecting the right committee depends on the scope and duration of the issue, with ad hoc committees suited for short-term, focused tasks and select committees better for sustained, specialized review. Understanding this distinction optimizes legislative efficiency and ensures appropriate resource allocation.
Ad hoc committee Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com