Constitutional law defines the fundamental principles and structures that govern a nation, ensuring the protection of individual rights and the distribution of governmental powers. It serves as the supreme legal framework that guides the functioning of legislative, executive, and judicial branches. Explore the rest of this article to understand how constitutional law impacts your everyday legal rights and responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
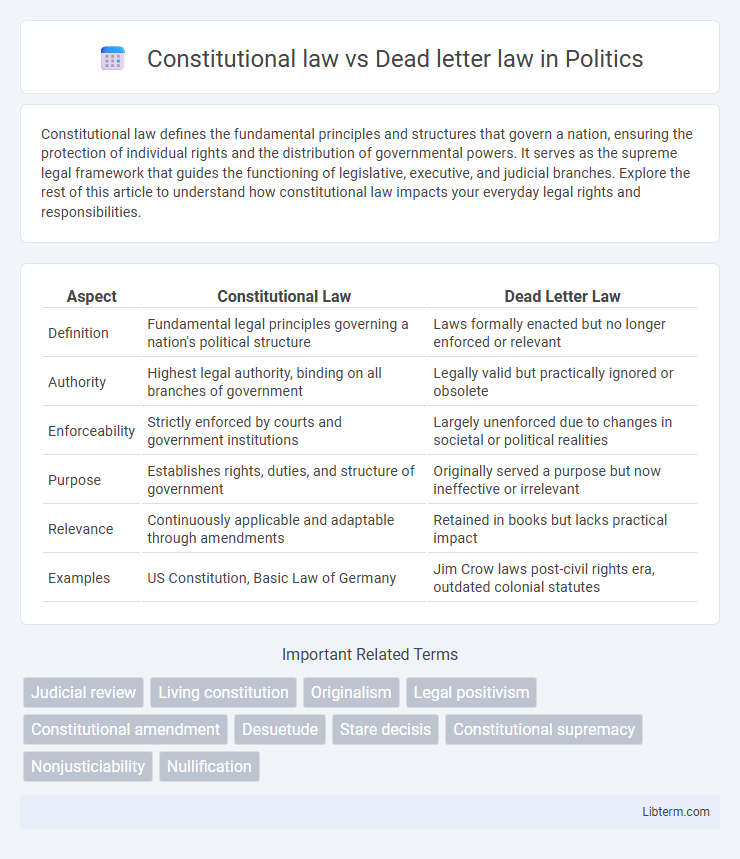
| Aspect | Constitutional Law | Dead Letter Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fundamental legal principles governing a nation's political structure | Laws formally enacted but no longer enforced or relevant |
| Authority | Highest legal authority, binding on all branches of government | Legally valid but practically ignored or obsolete |
| Enforceability | Strictly enforced by courts and government institutions | Largely unenforced due to changes in societal or political realities |
| Purpose | Establishes rights, duties, and structure of government | Originally served a purpose but now ineffective or irrelevant |
| Relevance | Continuously applicable and adaptable through amendments | Retained in books but lacks practical impact |
| Examples | US Constitution, Basic Law of Germany | Jim Crow laws post-civil rights era, outdated colonial statutes |
Defining Constitutional Law: Core Principles
Constitutional law establishes the foundational framework of government authority, individual rights, and the separation of powers as enshrined in a nation's constitution. It governs the interpretation and application of constitutional provisions, ensuring laws and government actions comply with constitutional mandates. Unlike dead letter law, which refers to statutes no longer enforced or relevant, constitutional law remains actively binding and shapes legal and political structures.
Understanding Dead Letter Law: Meaning and Implications
Dead letter law refers to statutes or regulations that remain officially valid but are no longer enforced or applied in practice, often due to changes in societal values or judicial interpretation. Understanding dead letter law highlights the gap between written constitutional provisions and their real-world implementation, revealing potential obsolescence within a country's legal framework. This phenomenon underscores the dynamic nature of constitutional law, where formal legal texts may lose practical relevance despite remaining part of the legal code.
Historical Origins of Constitutional Law
Constitutional law originates from the foundational principles and historical documents that establish the structure, functions, and limits of government authority, such as the Magna Carta (1215) and the U.S. Constitution (1787). Dead letter law refers to statutes or provisions that remain in legal texts but have become obsolete or unenforced over time. The historical evolution of constitutional law reflects the dynamic adaptation of legal frameworks to societal changes, contrasting with dead letter laws which signify stagnation within legal codes.
How Laws Become Dead Letters
Laws become dead letters when they are no longer enforced, respected, or relevant within society, often due to changes in social values, judicial interpretation, or political will. Constitutional law maintains its authority because it provides a framework for governance and fundamental rights, while dead letter laws lack practical application or enforcement mechanisms. The shift from active constitutional provisions to dead letter statutes commonly occurs through legislative neglect, judicial limitation, or societal disregard.
Constitutional Law in Practice: Modern Applications
Constitutional law governs the interpretation and implementation of a nation's constitution, directly influencing modern legal frameworks, civil rights, and government powers. Unlike dead letter law, which refers to statutes no longer enforced or relevant, constitutional law remains a living framework actively shaping judicial decisions and public policy. Modern applications of constitutional law include safeguarding individual liberties, regulating governmental authority, and resolving conflicts between federal and state powers.
Factors Leading to Dead Letter Laws
Factors leading to dead letter laws include shifting social norms, judicial interpretation, and legislative changes that render constitutional provisions ineffective or obsolete. Constitutional law may remain formally valid but fail in practice due to lack of enforcement, political resistance, or evolving public attitudes. Such dynamics cause once-critical legal mandates to lose practical significance, becoming symbolic rather than actionable.
Constitutional Law vs Dead Letter Law: Key Differences
Constitutional law establishes the fundamental principles and framework governing a nation's legal system, reflecting contemporary values and ensuring enforceability through judicial review. Dead letter law refers to statutes or constitutional provisions that remain formally in force but are obsolete, unenforced, or ignored in practice, lacking practical impact on legal outcomes. Key differences lie in constitutional law's active role in shaping governance and protecting rights, whereas dead letter law symbolizes legal provisions rendered ineffective due to shifts in societal norms or judicial interpretation.
The Role of Judiciary in Addressing Dead Letter Laws
The judiciary plays a critical role in addressing dead letter laws by interpreting and applying constitutional principles to revive or invalidate obsolete statutes that no longer serve contemporary legal purposes. Courts utilize judicial review to ensure that these dated laws conform with current constitutional mandates, effectively preventing injustices arising from irrelevant or unenforced provisions. Through active adjudication, judges bridge gaps between archaic legislation and modern constitutional requirements, reinforcing the dynamic nature of constitutional law.
Impact of Dead Letter Laws on Legal Systems
Dead letter laws, despite their apparent obsolescence, can create inconsistencies within constitutional legal frameworks by remaining codified but unenforced, leading to legal ambiguity and undermining the rule of law. These dormant statutes may complicate judicial interpretation and enforcement, resulting in inefficiencies and challenges in upholding constitutional principles. Understanding the influence of dead letter laws is essential for modernizing legal systems and ensuring coherent application of constitutional law.
Revitalizing or Repealing Dead Letter Laws: Reform Strategies
Revitalizing dead letter laws requires strategic legislative reforms that clarify ambiguous provisions and align outdated statutes with contemporary constitutional principles, ensuring enforceability and relevance. Repealing obsolete or conflicting dead letter laws prevents legal redundancies and promotes a coherent legal framework based on prevailing constitutional mandates. Effective reform strategies involve comprehensive legal reviews, stakeholder consultations, and the integration of judicial interpretations to bridge gaps between constitutional law and defunct statutory provisions.
Constitutional law Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com