Opinion polls provide valuable insights into public sentiment by collecting and analyzing responses from a diverse group of individuals. They help predict election outcomes, gauge consumer preferences, and inform policy decisions based on statistically significant data. Discover how opinion polls can influence your understanding of societal trends by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
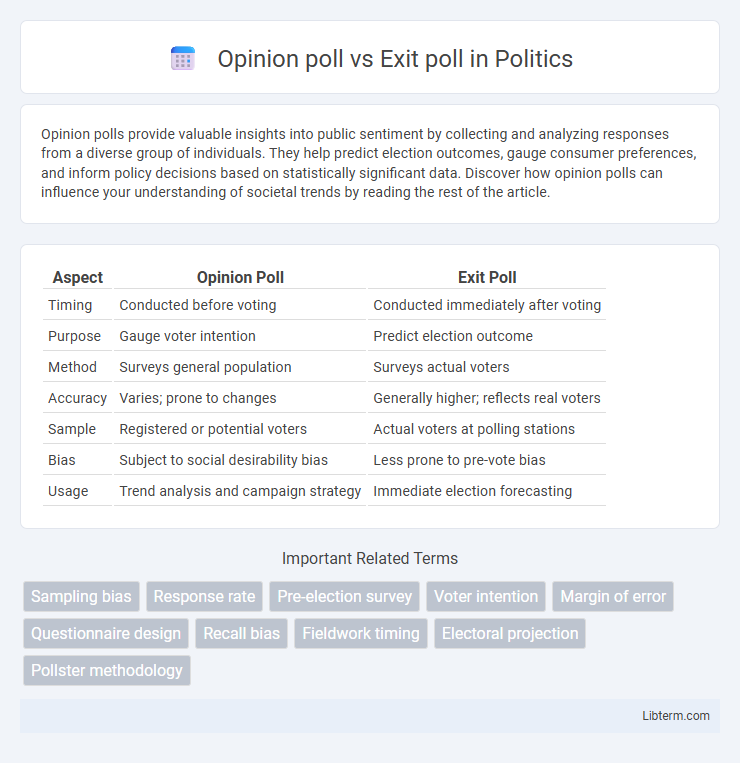
| Aspect | Opinion Poll | Exit Poll |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Conducted before voting | Conducted immediately after voting |
| Purpose | Gauge voter intention | Predict election outcome |
| Method | Surveys general population | Surveys actual voters |
| Accuracy | Varies; prone to changes | Generally higher; reflects real voters |
| Sample | Registered or potential voters | Actual voters at polling stations |
| Bias | Subject to social desirability bias | Less prone to pre-vote bias |
| Usage | Trend analysis and campaign strategy | Immediate election forecasting |
Introduction to Opinion Polls and Exit Polls
Opinion polls collect data on voters' intentions before an election by surveying a sample of the population, aiming to predict overall election outcomes and understand public sentiment. Exit polls gather information immediately after voters leave polling stations, providing real-time insights into actual voting behavior and preliminary election results. Both methods use statistical sampling but differ in timing and purpose, with opinion polls focusing on anticipated choices and exit polls capturing completed votes.
Defining Opinion Polls
Opinion polls are surveys conducted before an election to gauge voter intentions, preferences, and opinions on candidates or issues. They use randomized sampling techniques to represent a broader population and predict possible election outcomes. Opinion polls provide insights into trends and public sentiment but may vary in accuracy due to timing and respondent honesty.
Defining Exit Polls
Exit polls collect voters' choices immediately after they leave polling stations, providing real-time data on election outcomes before official results are announced. These polls rely on direct interviews with a representative sample of voters, aiming to predict the winner and voter demographics with high accuracy. Unlike opinion polls conducted before voting, exit polls capture actual voter behavior, making them a critical tool for media and analysts during elections.
Key Differences Between Opinion Polls and Exit Polls
Opinion polls measure public preferences and opinions before an election, sampling a broad demographic to predict voting trends, while exit polls survey voters immediately after they leave polling stations to capture actual voting behavior. Opinion polls rely on hypothetical intentions, often influenced by current events or opinions, whereas exit polls provide real-time data on voter choices, offering more precise election outcome projections. The accuracy of opinion polls can vary due to sample bias and response errors, while exit polls face challenges such as non-response bias and the timing of data collection.
Methodologies: How Opinion Polls and Exit Polls Are Conducted
Opinion polls gather data by surveying a representative sample of the population before an election, using structured questionnaires to capture voter intentions and demographic information through phone, online, or face-to-face interviews. Exit polls are conducted immediately after voters leave polling stations, interviewing a randomly selected subset of actual voters to record who they voted for, ensuring real-time data on voting behavior. Both methodologies require rigorous sampling techniques and weighting adjustments to minimize biases and accurately reflect the electorate's preferences.
Timing: When Are Opinion and Exit Polls Used?
Opinion polls are conducted during the election campaign to gauge voter intentions and predict possible outcomes before Election Day. Exit polls take place immediately after voters cast their ballots, providing near-instant insights into election results based on actual voter behavior. The distinct timing of these polls influences their accuracy, with exit polls offering more precise data due to being collected post-voting.
Accuracy and Reliability in Polling
Opinion polls gather data before an event by surveying a representative sample, which may be influenced by respondents' changing opinions or social desirability bias, affecting accuracy. Exit polls collect information immediately after voting, providing more reliable and precise predictions by capturing actual voter behavior at polling stations. Despite their strengths, both polls can face errors from sampling methods or nonresponse, but exit polls generally exhibit higher reliability in forecasting election outcomes.
Impact on Election Outcomes and Public Perception
Opinion polls influence election outcomes by shaping voter expectations and campaign strategies through pre-election data on candidate popularity and issue importance. Exit polls offer immediate insights into voter behavior after leaving polling stations, impacting media narratives and public perception before official results are announced. Both types affect democratic processes by informing or potentially swaying voter decisions and trust in electoral integrity.
Common Challenges and Controversies
Opinion polls and exit polls frequently face challenges such as sampling bias, where unrepresentative demographics skew results, and response bias, affecting the authenticity of participant answers. Both methodologies often encounter controversies surrounding accuracy, with exit polls sometimes criticized for influencing voter behavior and opinion polls for failing to predict actual election outcomes due to timing or question phrasing. The reliability of data interpretation remains a persistent issue, as misreporting or misanalysis can lead to public misinformation and erode trust in polling institutions.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Opinion Polls and Exit Polls
Choosing between opinion polls and exit polls depends on the timing and purpose of data collection; opinion polls gather voter intentions before the election, offering predictive insights, while exit polls collect data immediately after voting, providing more accurate estimations of actual outcomes. Exit polls tend to be more reliable for final results but require complex logistics and access at polling stations. Opinion polls are useful for tracking voter trends and shifts over a campaign period but carry risks of bias and inaccuracies due to sampling and changing voter preferences.
Opinion poll Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com