Party identification shapes voter behavior and influences political attitudes by aligning individuals with specific parties based on shared values and beliefs. This psychological attachment often guides voting decisions and engagement in political processes. Discover how your party identification impacts your political perspective by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
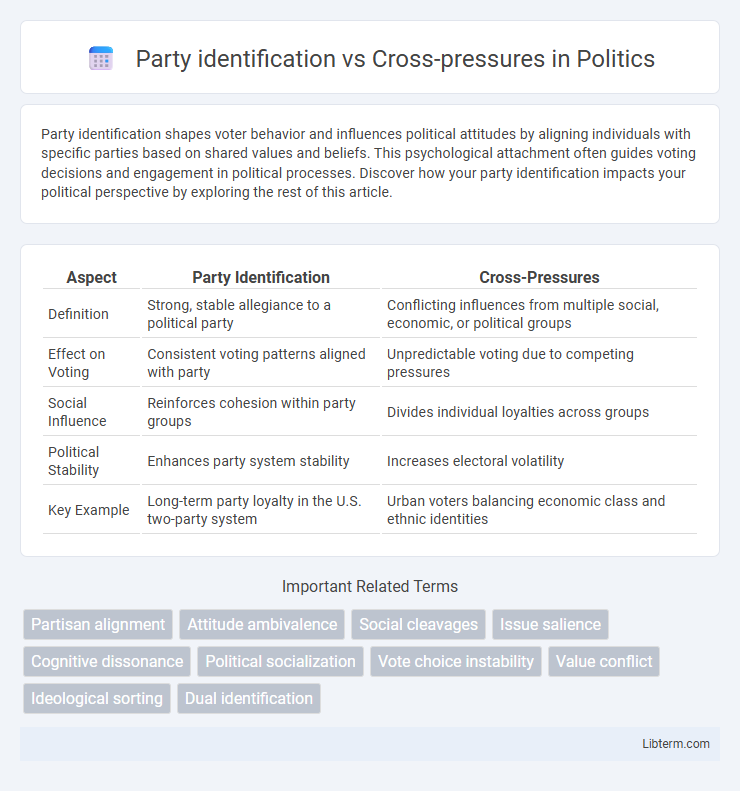
| Aspect | Party Identification | Cross-Pressures |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strong, stable allegiance to a political party | Conflicting influences from multiple social, economic, or political groups |
| Effect on Voting | Consistent voting patterns aligned with party | Unpredictable voting due to competing pressures |
| Social Influence | Reinforces cohesion within party groups | Divides individual loyalties across groups |
| Political Stability | Enhances party system stability | Increases electoral volatility |
| Key Example | Long-term party loyalty in the U.S. two-party system | Urban voters balancing economic class and ethnic identities |
Understanding Party Identification
Party identification reflects a long-term psychological attachment to a specific political party, serving as a key predictor of voting behavior and political attitudes. Cross-pressures occur when individuals face conflicting influences, such as social, economic, or ideological factors, which challenge their party loyalty and create internal conflict. Understanding party identification requires analyzing how these cross-pressures impact voter consistency and political decision-making patterns.
Defining Cross-Pressures
Cross-pressures occur when individuals experience conflicting influences from social groups or personal beliefs that pull their political loyalties in different directions, challenging strong party identification. These conflicting pressures often arise from diverging factors such as religion, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status, creating ambivalence in voting behavior. Voters under cross-pressure may resist aligning strictly with a single party, leading to fluctuating or split-ticket voting patterns during elections.
Historical Overview of Party Loyalty
Party identification has historically served as a stable psychological attachment to a political party, significantly influencing voter behavior and electoral outcomes since the early 20th century. Cross-pressures, arising from conflicting social identities such as religion, ethnicity, or economic status, have increasingly challenged this loyalty by introducing complexity into voters' decision-making processes. Studies of political realignments, particularly during the 1960s and 1980s in the United States, reveal shifts where cross-pressures weakened traditional party bonds, leading to more volatile and issue-driven voting patterns.
Factors Influencing Party Identification
Party identification is primarily shaped by long-term socialization factors such as family influence, socioeconomic status, and regional culture. Cross-pressures arise when individuals face conflicting influences from different social groups or issues, weakening their allegiance to a single party. Demographic variables like education level and income also significantly impact the stability and intensity of party identification.
Sources of Cross-Pressures in Voters
Cross-pressures in voters arise when multiple social groups or issue positions pull individuals in conflicting political directions, weakening traditional party identification. Key sources include demographic factors such as religion, socioeconomic status, ethnicity, and geographic region, which may align voters with different parties on various issues. Exposure to diverse media and social networks further intensifies these cross-pressures by presenting competing political messages and values.
Impact on Voting Behavior
Party identification serves as a stable predictor of voting behavior, anchoring voter preferences and simplifying decision-making processes during elections. Cross-pressures, arising from conflicting social identities or issue positions, create internal conflicts that can weaken party loyalty and lead to ticket splitting or abstention. The interplay between strong party identification and cross-pressures significantly influences electoral volatility, with voters facing cross-pressures exhibiting less predictable voting patterns and greater susceptibility to campaign influence.
Psychological Aspects of Political Alignment
Party identification often serves as a psychological anchor, providing individuals with a sense of belonging and a framework to interpret political information. Cross-pressures arise when conflicting influences from social groups, values, or personal experiences challenge this alignment, leading to internal conflict and cognitive dissonance. The psychological tension between party loyalty and cross-pressures shapes political behavior by influencing voting decisions, issue preferences, and susceptibility to persuasion.
Social and Demographic Influences
Party identification is significantly shaped by social and demographic factors such as age, race, gender, and socioeconomic status, which create stable political alignments over time. Cross-pressures arise when individuals experience conflicting social influences, like belonging to multiple groups with opposing political preferences, leading to ambivalence or split-ticket voting behaviors. These social and demographic cross-pressures can weaken party loyalty and increase electoral volatility by prompting voters to diverge from their traditional party identification.
Cross-Pressures and Electoral Volatility
Cross-pressures arise when voters experience conflicting influences from social groups, such as religion, ethnicity, and income, leading to weakened party identification and increased electoral volatility. This fragmentation reduces loyalty to traditional parties and prompts fluctuations in voting behavior across elections. As a result, cross-pressures contribute significantly to the unpredictability and shifting dynamics observed in contemporary electoral landscapes.
Implications for Political Campaigns
Party identification provides a stable base of voter loyalty that political campaigns target through tailored messaging and mobilization strategies. Cross-pressures, arising from conflicting social identities or issue stances, create unpredictable voter behavior, compelling campaigns to adopt more nuanced and issue-specific outreach tactics. Understanding the interplay between party identification and cross-pressures is crucial for maximizing voter turnout and persuasion effectiveness in contemporary elections.
Party identification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com