Midterm elections play a crucial role in shaping the balance of power within the United States Congress, affecting policies that impact your daily life. These elections determine control of the House of Representatives and one-third of the Senate, influencing legislative priorities and national direction. Discover how midterm outcomes could reshape the political landscape in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
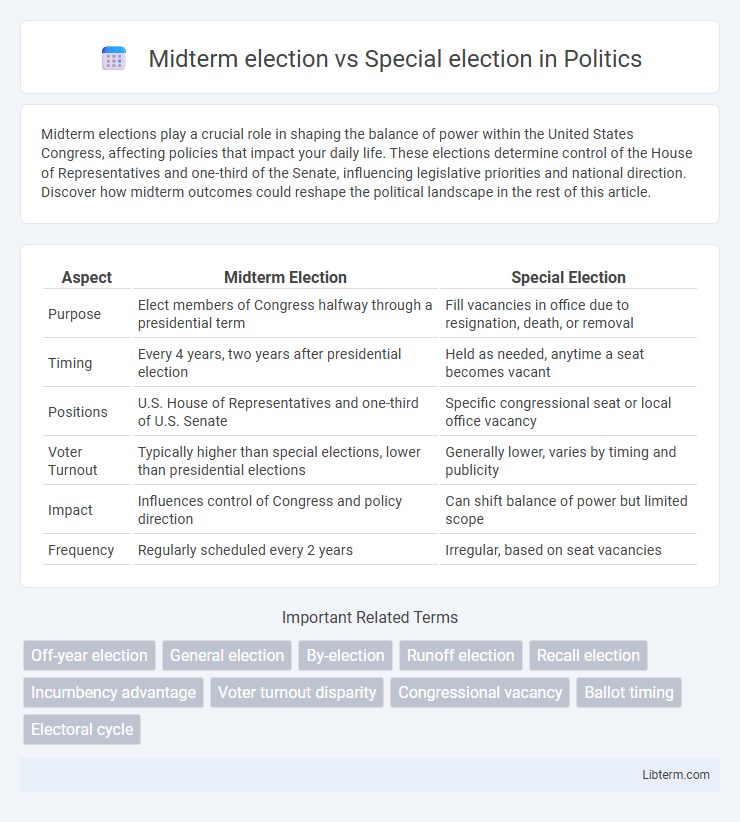
| Aspect | Midterm Election | Special Election |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Elect members of Congress halfway through a presidential term | Fill vacancies in office due to resignation, death, or removal |
| Timing | Every 4 years, two years after presidential election | Held as needed, anytime a seat becomes vacant |
| Positions | U.S. House of Representatives and one-third of U.S. Senate | Specific congressional seat or local office vacancy |
| Voter Turnout | Typically higher than special elections, lower than presidential elections | Generally lower, varies by timing and publicity |
| Impact | Influences control of Congress and policy direction | Can shift balance of power but limited scope |
| Frequency | Regularly scheduled every 2 years | Irregular, based on seat vacancies |
Understanding Midterm Elections
Midterm elections occur every four years, midway through a president's term, allowing voters to elect members of Congress, governors, and local officials, significantly impacting legislative priorities and party control. These elections typically experience lower voter turnout compared to presidential elections but serve as a critical measure of public opinion on the sitting administration. Understanding midterm elections is essential for grasping shifts in political power, legislative agendas, and the broader democratic process.
Defining Special Elections
Special elections are held to fill political offices that become vacant before the term ends, often due to resignation, death, or removal of an officeholder, distinguishing them from regularly scheduled midterm elections. Unlike midterm elections, which occur every four years to elect congressional representatives and senators halfway through a president's term, special elections address unexpected vacancies and can happen at any time. These elections typically focus on single races, providing a quicker resolution to maintain legislative continuity and representation.
Key Differences Between Midterm and Special Elections
Midterm elections occur every four years halfway through a president's term, focusing on all 435 House seats and approximately one-third of the Senate seats, significantly influencing congressional control. Special elections fill unexpected vacancies in federal, state, or local offices and often depend on unique local circumstances and timing rather than a regular election cycle. Voter turnout is typically higher in midterm elections due to national attention, while special elections generally experience lower participation and limited media coverage.
Timing and Frequency of Each Election Type
Midterm elections occur every four years, midway through a presidential term, and determine congressional representation across the entire country. Special elections are held as needed to fill unexpected vacancies in government positions, varying widely in timing based on individual circumstances. The consistent schedule of midterms contrasts with the irregular, case-specific timing of special elections.
Offices and Positions Contested
Midterm elections primarily focus on electing members of the U.S. Congress, including all 435 House of Representatives seats and approximately one-third of the Senate seats, along with various state and local offices. Special elections are held to fill vacancies in these offices that occur between regular election cycles, often targeting specific seats like a single congressional district or state legislative position. While midterm elections encompass a broad array of positions, special elections are isolated events designed to address urgent representation gaps.
Voter Turnout Trends
Midterm elections historically experience higher voter turnout compared to special elections, as they coincide with congressional and state-level races that attract broader public interest. Special elections, often held to fill unexpected vacancies, typically see lower voter participation due to limited campaign visibility and off-cycle scheduling. Data from the United States Election Project shows midterm turnout averages around 40% to 50%, while special election turnout can drop below 20%, reflecting divergent voter engagement patterns.
Impact on Political Balance
Midterm elections significantly influence the political balance by reshaping congressional seats, often serving as a referendum on the sitting president's party and potentially shifting legislative control. Special elections, held to fill unexpected vacancies, can alter the balance in closely divided legislatures, sometimes tipping power in favor of one party between regular election cycles. Both elections affect party dynamics but differ in timing and scope, with midterms having broader implications and special elections providing critical opportunities for localized shifts.
Role in Shaping Government Policies
Midterm elections, occurring every two years, significantly influence government policies by determining the composition of Congress, which controls the legislative agenda and budget priorities. Special elections fill unexpected vacancies in government offices and can shift the balance of power temporarily, impacting urgent policy decisions and local governance. Both elections serve as critical mechanisms for voter influence on legislative direction and policy outcomes.
Recent Examples of Special and Midterm Elections
Recent special elections, such as the 2023 California Gubernatorial Special Election, filled unexpected vacancies and often featured accelerated campaign timelines. In contrast, the 2022 U.S. Midterm Elections involved all 435 House seats and 34 Senate seats, reflecting a comprehensive national political shift. These elections highlight distinct electoral processes, with special elections addressing immediate representation needs and midterms influencing broader congressional control.
Importance for Voters and Civic Engagement
Midterm elections hold significant importance for voters as they determine congressional representation and influence national policy directions during a president's term. Special elections, often focused on filling unexpected vacancies, provide critical opportunities for civic engagement by addressing immediate community needs and ensuring continued local representation. Both election types are essential in sustaining democratic participation and empowering citizens to impact governance at different levels.
Midterm election Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com