Bill management plays a crucial role in organizing your finances and avoiding late payments that can harm your credit score. Understanding different types of bills, such as utilities, subscriptions, and loans, ensures you allocate your budget effectively. Explore this article to learn practical tips for mastering bill payments and achieving financial stability.
Table of Comparison
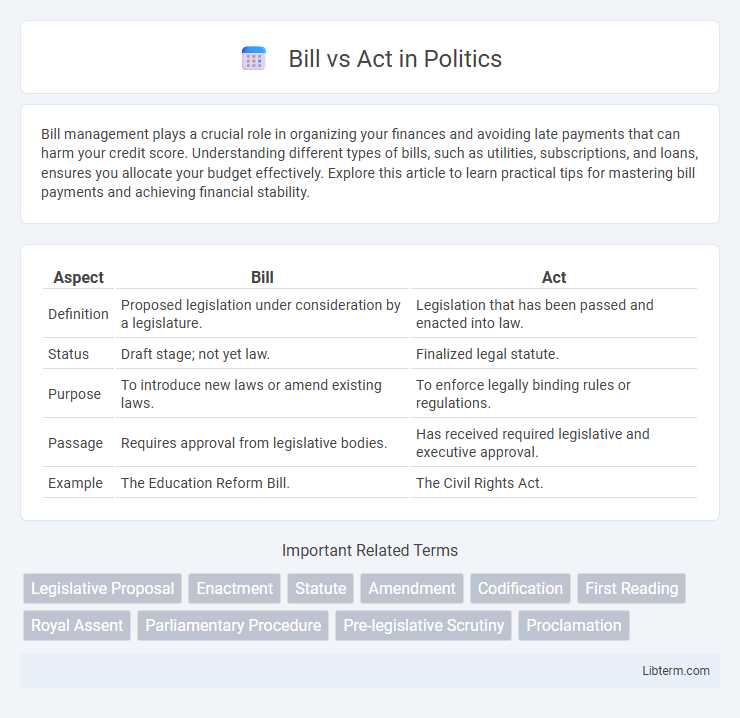
| Aspect | Bill | Act |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proposed legislation under consideration by a legislature. | Legislation that has been passed and enacted into law. |
| Status | Draft stage; not yet law. | Finalized legal statute. |
| Purpose | To introduce new laws or amend existing laws. | To enforce legally binding rules or regulations. |
| Passage | Requires approval from legislative bodies. | Has received required legislative and executive approval. |
| Example | The Education Reform Bill. | The Civil Rights Act. |
Introduction: Understanding Bills and Acts
A bill is a proposed piece of legislation introduced in a legislative body for debate and approval, while an act is a bill that has successfully passed all legislative stages and received formal assent, becoming law. Bills undergo rigorous examination, amendments, and votes before becoming acts, which serve as enforceable statutes within the legal system. Understanding the distinction between bills and acts is crucial for grasping the legislative process and how laws are formally enacted.
Definition of a Bill
A bill is a formal proposal presented for legislative consideration, aiming to introduce, amend, or repeal laws. It undergoes multiple readings and debates within a legislative body before approval. Once passed and formally enacted, it becomes an act, legally binding and enforceable.
Definition of an Act
An Act is a law formally enacted by a legislative body, having passed all required stages including approval by the executive authority. It represents the final, legally binding statute that governs specific areas such as criminal law, commerce, or education. Unlike a bill, which is a proposal under consideration, an Act has full legal force and effect within its jurisdiction.
Key Differences Between a Bill and an Act
A bill is a proposal introduced in a legislative body for discussion and approval, while an act is a bill that has passed all necessary stages and received formal enactment, becoming law. Bills undergo multiple readings, debates, and amendments before becoming acts, which carry legal authority and enforceability. The key difference lies in the legislative status: a bill is a draft law in progress, whereas an act is the finalized statute.
The Process of Passing a Bill
The process of passing a bill involves multiple legislative stages, including introduction, committee review, debates, and voting in both chambers of the legislature. After approval by both the House of Representatives and the Senate, the bill is sent to the executive branch for signature into law, officially becoming an act. Key steps include committee hearings, floor debates, amendments, and the final presidential or gubernatorial approval.
How a Bill Becomes an Act
A bill becomes an act by first being introduced and thoroughly debated in both houses of Parliament or Congress, where it undergoes examination in committees and possible amendments. After passing votes in both chambers, the bill proceeds to the executive branch, where the president or monarch can sign it into law or veto it. If signed, the bill officially becomes an act, enforceable as part of the legal framework.
Types of Bills in Legislation
Bills in legislation are categorized primarily into several types based on their purpose and scope. Public bills address general matters affecting the entire population, while private bills focus on specific individuals, organizations, or localities. Hybrid bills combine elements of both public and private bills, affecting the public broadly but also impacting particular groups or interests.
Importance of Acts in Legal Framework
Acts represent laws formally enacted by a legislative body, solidifying legal authority and ensuring enforceability within the judicial system. Unlike bills, which are proposals subject to debate and modification, Acts provide definitive rules that govern societal conduct and protect rights. Their importance lies in establishing clear, binding regulations essential for maintaining order and promoting justice.
Challenges in Transforming a Bill into an Act
Transforming a bill into an act involves navigating complex challenges such as negotiating amendments, securing majority support, and addressing conflicting stakeholder interests. Legislative procedures often require rigorous committee reviews, detailed debates, and multiple readings, which can delay or derail progress. Political dynamics, public opinion, and lobbying efforts further complicate the process, making the passage of a bill into law a demanding endeavor.
Conclusion: Bill vs Act in Legislative Procedures
A bill is a proposed law submitted for debate and approval, while an act is a bill that has successfully passed through all legislative stages and received formal enactment. The transition from bill to act signifies the completion of the legislative process, granting the legal authority needed for enforcement and implementation. Understanding this distinction is crucial for comprehending how laws are created and institutionalized within governmental frameworks.
Bill Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com