Neoliberalism emphasizes free-market policies, deregulation, and reduced government intervention to promote economic growth and individual responsibility. This ideology shapes global economic practices and impacts social welfare systems worldwide. Explore the rest of the article to understand how neoliberalism influences your daily life and future.
Table of Comparison
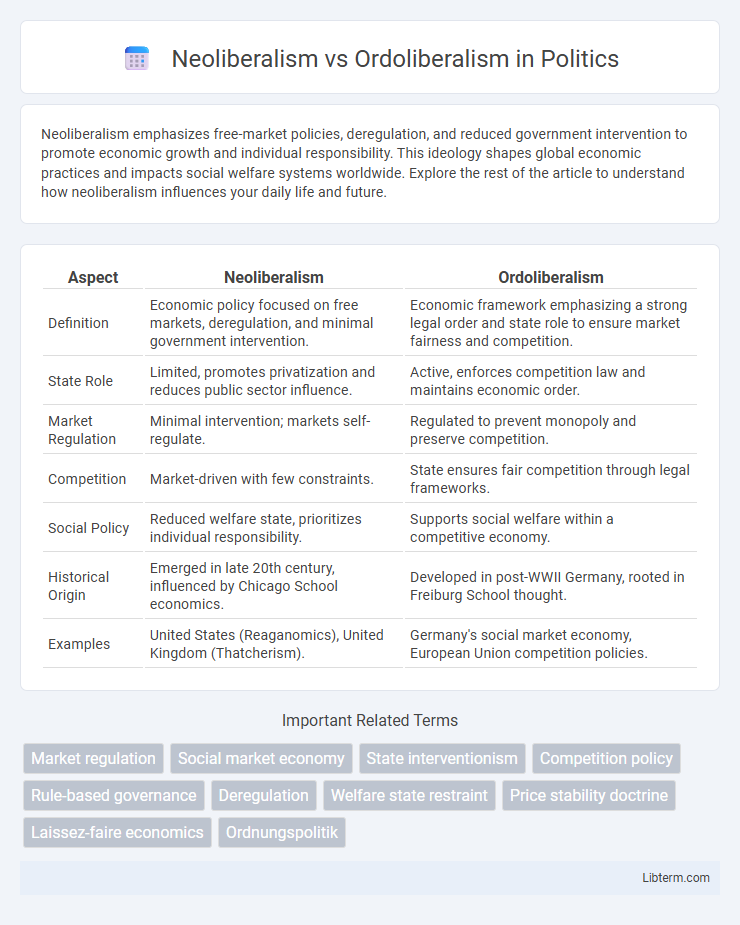
| Aspect | Neoliberalism | Ordoliberalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic policy focused on free markets, deregulation, and minimal government intervention. | Economic framework emphasizing a strong legal order and state role to ensure market fairness and competition. |
| State Role | Limited, promotes privatization and reduces public sector influence. | Active, enforces competition law and maintains economic order. |
| Market Regulation | Minimal intervention; markets self-regulate. | Regulated to prevent monopoly and preserve competition. |
| Competition | Market-driven with few constraints. | State ensures fair competition through legal frameworks. |
| Social Policy | Reduced welfare state, prioritizes individual responsibility. | Supports social welfare within a competitive economy. |
| Historical Origin | Emerged in late 20th century, influenced by Chicago School economics. | Developed in post-WWII Germany, rooted in Freiburg School thought. |
| Examples | United States (Reaganomics), United Kingdom (Thatcherism). | Germany's social market economy, European Union competition policies. |
Defining Neoliberalism: Core Principles and Origins
Neoliberalism emerged in the mid-20th century as an economic philosophy advocating for free-market capitalism, deregulation, and reduced state intervention to foster competition and innovation. Rooted in Classical liberal ideas, its core principles emphasize privatization, fiscal austerity, and open global markets to stimulate economic growth and individual entrepreneurship. Influential figures such as Friedrich Hayek and Milton Friedman shaped neoliberalism's ideological foundation, promoting policies that contrast with the more state-oriented Ordoliberalism approach.
Understanding Ordoliberalism: Historical Context and Main Ideas
Ordoliberalism emerged in post-World War II Germany as a response to the failures of both laissez-faire capitalism and central planning, emphasizing the need for a strong legal framework to ensure competitive markets and prevent monopolies. Key figures like Walter Eucken advocated for the state to create and maintain the economic order through regulation that supports free enterprise while safeguarding social stability. This approach contrasts with neoliberalism by insisting on a rules-based economy where state intervention is necessary to maintain market fairness and prevent economic concentration.
The Role of the State: Neoliberalism vs. Ordoliberalism
Neoliberalism advocates for a minimal state role, emphasizing market freedom, deregulation, and limited government intervention to promote individual entrepreneurship and economic efficiency. Ordoliberalism supports a strong regulatory state that ensures market competition and prevents monopolies, emphasizing legal frameworks and institutional structures to maintain economic order. While neoliberalism prioritizes market self-regulation, ordoliberalism views active state involvement as essential to preserve fair competition and social stability.
Market Regulation: Contrasting Approaches
Neoliberalism advocates minimal government intervention in markets, emphasizing deregulation and free-market competition as drivers of economic efficiency and growth. Ordoliberalism supports a strong regulatory framework to ensure market order, prevent monopolies, and protect social welfare by balancing economic freedom with state oversight. This fundamental difference shapes policies where neoliberalism prioritizes market self-regulation while ordoliberalism enforces rules to maintain fair competition and social stability.
Social Policy and Welfare Systems
Neoliberalism promotes minimal government intervention in social policy, emphasizing individual responsibility and market-driven welfare systems to enhance efficiency and reduce state dependency. Ordoliberalism advocates for a strong regulatory framework ensuring social equity, supporting welfare systems that balance free-market competition with social protection and public goods provision. The two approaches differ fundamentally in their view of the state's role, with neoliberalism favoring deregulation and ordoliberalism endorsing regulatory oversight to safeguard social stability.
Competition Policy in Both Frameworks
Neoliberalism emphasizes minimal state intervention, advocating for free markets where competition is driven by supply and demand forces, with competition policy primarily ensuring the prevention of monopolies and promoting consumer choice. Ordoliberalism, rooted in the German Freiburg School, stresses the state's role in creating a strong legal framework to maintain market order and ensure fair competition, emphasizing rules that prevent abuse of market power and promote social welfare. While neoliberalism favors deregulation to foster innovation, ordoliberalism supports regulatory measures to uphold competitive structures and prevent market failures.
Globalization and Economic Policy
Neoliberalism emphasizes deregulation, free markets, and minimal state intervention to promote globalization and economic growth, favoring open competition and international trade liberalization. Ordoliberalism advocates for a strong regulatory framework ensuring fair competition and social stability within globalization, insisting state intervention is necessary to prevent market failures and monopolies. Economic policies under neoliberalism prioritize privatization and fiscal austerity, while ordoliberalism focuses on maintaining legal order and balancing market efficiency with social welfare in a globalized economy.
Financial Stability and Crisis Response
Neoliberalism emphasizes minimal state intervention, advocating for free markets to drive financial stability through competitive forces and self-regulation, often favoring market-based crisis responses such as bailouts and monetary policy adjustments. Ordoliberalism stresses the necessity of a strong regulatory framework to ensure market order, promoting proactive state involvement to prevent financial imbalances and maintain stability through rules-based crisis management and robust oversight institutions. The contrasting approaches affect how financial crises are anticipated, managed, and mitigated, with ordoliberalism prioritizing systemic safeguards and neoliberalism relying on market-driven corrections.
Influence on Modern Economic Systems
Neoliberalism promotes deregulation, free-market capitalism, and reduced government intervention, emphasizing individual entrepreneurship and global trade to drive economic growth. Ordoliberalism advocates for a strong regulatory framework ensuring competition and social welfare, influencing the design of the social market economy in countries like Germany. Modern economic systems blend these approaches by balancing market freedom with state oversight to maintain stability, innovation, and equitable wealth distribution.
Contemporary Relevance: Debates and Future Directions
Neoliberalism emphasizes market deregulation and privatization to drive economic growth, whereas Ordoliberalism advocates for strong regulatory frameworks to ensure market competition and prevent monopolies. Contemporary debates revolve around balancing economic efficiency with social equity, especially as rising inequality and financial crises challenge purely market-driven approaches. Future directions suggest integrating Ordoliberal principles of rule-based governance with selective Neoliberal market freedoms to create resilient and inclusive economic policies.
Neoliberalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com