Factional disputes often arise from conflicting interests within a group, leading to tension and division. These internal conflicts can undermine cohesion and productivity, making resolution strategies essential for maintaining harmony. Discover effective approaches to managing and resolving factional disputes in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
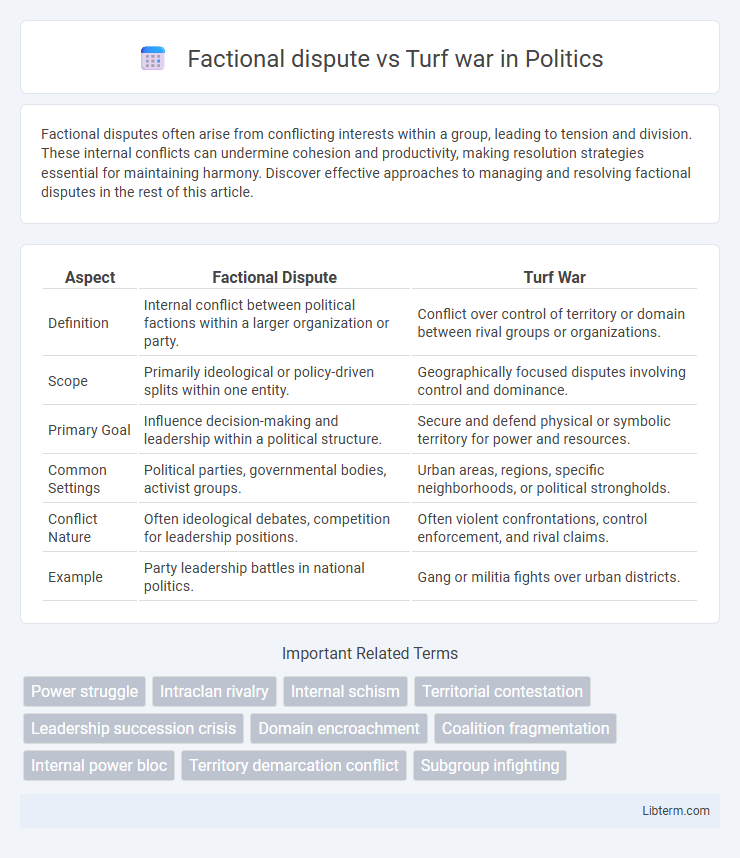
| Aspect | Factional Dispute | Turf War |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Internal conflict between political factions within a larger organization or party. | Conflict over control of territory or domain between rival groups or organizations. |
| Scope | Primarily ideological or policy-driven splits within one entity. | Geographically focused disputes involving control and dominance. |
| Primary Goal | Influence decision-making and leadership within a political structure. | Secure and defend physical or symbolic territory for power and resources. |
| Common Settings | Political parties, governmental bodies, activist groups. | Urban areas, regions, specific neighborhoods, or political strongholds. |
| Conflict Nature | Often ideological debates, competition for leadership positions. | Often violent confrontations, control enforcement, and rival claims. |
| Example | Party leadership battles in national politics. | Gang or militia fights over urban districts. |
Understanding Factional Disputes
Factional disputes occur within a larger group when subgroups compete for power, influence, or control, often driven by ideological differences or leadership struggles. Understanding factional disputes involves analyzing underlying causes such as resource allocation, political ambitions, or cultural tensions that fuel internal divisions. These conflicts differ from turf wars, which primarily revolve around control of physical territories or economic resources between distinct groups.
Defining Turf Wars
Turf wars are conflicts between groups or organizations competing for control over a specific geographic area or market. These disputes often involve aggressive tactics to establish dominance and secure resources within a defined territory. Unlike factional disputes, which arise from internal divisions within a larger group, turf wars center on external competition for spatial or economic influence.
Key Differences Between Factional Disputes and Turf Wars
Factional disputes primarily arise from internal conflicts within a group or organization, driven by power struggles or ideological differences, whereas turf wars involve competition between distinct groups or gangs over control of geographic areas or resources. Key differences include the scope and participants: factional disputes occur among members of the same faction, while turf wars are inter-factional conflicts. The objectives also vary, with factional disputes aiming at dominance or policy control internally, and turf wars seeking territorial control and economic advantage externally.
Historical Examples of Factional Disputes
Factional disputes often emerge within political parties or social movements, as seen in the Roman Republic's conflict between the Optimates and Populares, which shaped the late Republic's power struggles. The intense factional rivalry during the Wars of the Roses in 15th century England exemplifies how internal aristocratic disputes can escalate into prolonged civil conflicts. These historical factional disputes illustrate internal divisions driven by competing ideologies or power bases, distinct from turf wars that primarily involve territorial control between rival groups.
Notable Turf Wars in History
Notable turf wars in history often center around control of valuable resources, territories, or influence, such as the Mafia turf wars in 20th-century America or the drug cartel conflicts in Latin America. These turf wars typically involve violent clashes between rival gangs or organizations seeking dominance over specific geographic areas. Unlike factional disputes, turf wars primarily emphasize physical control and direct competition for real estate or criminal enterprises.
Causes Behind Factional Disputes
Factional disputes commonly arise from internal power struggles, ideological differences, and competition for leadership within a group, driving members to vie for authority or control. Divergent goals, resource allocation disagreements, and personal rivalries further intensify factional tensions, creating fractures that destabilize organizational unity. These disputes are often fueled by lack of clear communication and unequal distribution of influence, distinguishing them from turf wars that primarily revolve around territorial dominance.
Motivations for Turf Wars
Turf wars are primarily motivated by the desire to control valuable resources, territory, or influence within a specific area, often driven by economic gain or strategic advantage. Unlike factional disputes, which arise from ideological differences or internal power struggles within a group, turf wars focus on external competition between rival groups seeking dominance over shared geographic or market spaces. These motivations lead to intense conflicts as groups attempt to assert control and protect their interests against encroachment.
Impacts on Organizations and Communities
Factional disputes generate internal divisions within organizations, leading to decreased productivity, eroded trust, and impaired decision-making processes. Turf wars often escalate beyond internal conflicts, causing resource wastage, increased hostility, and fragmentation within communities or organizational units. Both phenomena disrupt collaboration, but turf wars typically result in more pronounced external tensions and long-term destabilization of social or corporate structures.
Strategies for Resolving Factional Disputes and Turf Wars
Resolving factional disputes requires strategies centered on open communication channels, impartial mediation, and establishing shared goals to rebuild trust among competing groups. Turf wars often benefit from clearly defined boundaries, conflict de-escalation techniques, and negotiated agreements that respect the interests of all involved parties. Implementing ongoing dialogue frameworks and regular conflict resolution training supports sustainable peace and cooperation.
Lessons Learned and Prevention Tactics
Factional disputes often arise from internal power struggles within groups, while turf wars involve competition over territorial control between distinct entities. Effective prevention tactics include establishing clear communication channels, defined boundaries, and conflict resolution protocols to address grievances early and reduce misunderstandings. Lessons learned emphasize the importance of proactive leadership, transparency, and fostering collaboration to mitigate escalation in both scenarios.
Factional dispute Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com