Continuance in legal terms refers to the postponement or extension of a court proceeding to a later date, often requested to ensure fairness or adequate preparation time. Understanding when and how to request a continuance can significantly impact the outcome of your case by providing necessary time to gather evidence or consult with legal counsel. Explore the rest of this article to learn more about the types, reasons, and procedures involved in securing a continuance.
Table of Comparison
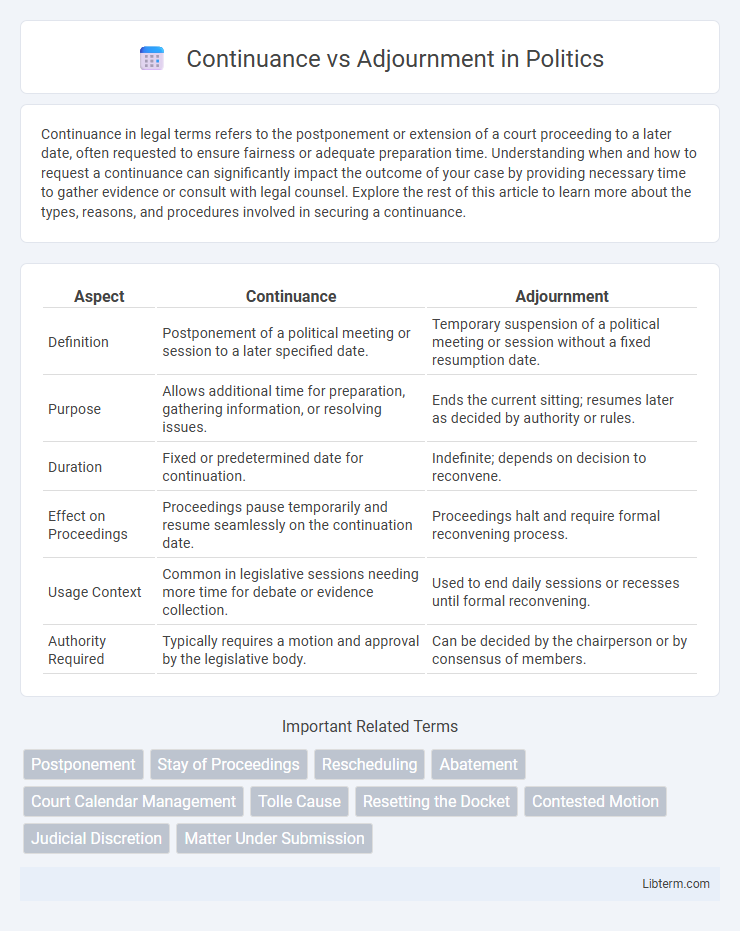
| Aspect | Continuance | Adjournment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Postponement of a political meeting or session to a later specified date. | Temporary suspension of a political meeting or session without a fixed resumption date. |
| Purpose | Allows additional time for preparation, gathering information, or resolving issues. | Ends the current sitting; resumes later as decided by authority or rules. |
| Duration | Fixed or predetermined date for continuation. | Indefinite; depends on decision to reconvene. |
| Effect on Proceedings | Proceedings pause temporarily and resume seamlessly on the continuation date. | Proceedings halt and require formal reconvening process. |
| Usage Context | Common in legislative sessions needing more time for debate or evidence collection. | Used to end daily sessions or recesses until formal reconvening. |
| Authority Required | Typically requires a motion and approval by the legislative body. | Can be decided by the chairperson or by consensus of members. |
Defining Continuance and Adjournment
Continuance refers to the postponement of a court proceeding to a later date, often requested to allow more time for case preparation or to accommodate scheduling conflicts. Adjournment involves temporarily suspending a court session or meeting without setting a specific future date for resumption, usually for short breaks or procedural reasons. Both actions impact the timeline of legal processes but differ in their intent and duration.
Key Differences Between Continuance and Adjournment
Continuance refers to the postponement of a court hearing or trial to a later date, primarily requested to allow more time for preparation or the gathering of evidence, while adjournment denotes the temporary suspension or halt of proceedings during a session, often resuming on a specific subsequent date. Continuance usually involves rescheduling an entire case or hearing, whereas adjournment may apply to daily sessions or individual court appearances. Key differences include the purpose, scope, and timing: continuance extends deadlines and hearing dates, adjournment pauses ongoing proceedings without changing the overall schedule immediately.
Legal Grounds for Continuance
Legal grounds for continuance include the unavailability of a key witness or new evidence that requires additional investigation, ensuring the defendant's right to a fair trial. Continuance may also be granted if counsel needs more time to prepare due to unforeseen circumstances such as illness or scheduling conflicts. Courts evaluate these grounds carefully to balance judicial efficiency with the protection of parties' legal rights.
Legal Grounds for Adjournment
Legal grounds for adjournment typically include the unavailability of a key witness, the absence of crucial evidence, or the need for additional time to prepare a case. Courts may also grant adjournments due to procedural errors, illness of a party involved, or when new information emerges that affects the trial's fairness. Adjournments differ from continuances in that they are often specific to temporary postponements within the same proceeding, while continuances may involve a more extended delay or rescheduling of hearing dates.
Procedural Process for Requesting Each
A continuance is requested by filing a formal motion with the court, specifying reasons such as the need for additional preparation time or unavailability of key witnesses, and must often be submitted well before the trial date. An adjournment involves the postponement of a court session and can be requested informally or formally, typically requiring a demonstration of good cause to the judge on the day of the hearing. Courts evaluate both requests based on factors like prejudice to parties, case progress, and judicial efficiency before granting either a continuance or an adjournment.
Impact on Court Schedules
Continuance often leads to rescheduling that can congest court dockets, increasing delays and impacting overall judicial efficiency. Adjournment typically pauses proceedings temporarily without resetting the trial timeline, minimizing long-term schedule disruptions. Both affect court calendars, but continuance generally causes more significant delays due to resetting deadlines and notifications.
Common Scenarios for Granting Continuance vs Adjournment
Continuance is commonly granted when new evidence emerges, a key witness is unavailable, or the defense needs additional time for case preparation, ensuring a fair trial process. Adjournment typically occurs due to procedural delays, unforeseen court scheduling conflicts, or administrative reasons that temporarily halt proceedings without affecting substantive case rights. Courts assess the specific circumstances, such as the impact on justice and potential prejudice, before deciding whether a continuance or adjournment is appropriate.
Judicial Discretion in Granting Delays
Judicial discretion plays a critical role in granting continuances or adjournments, balancing the need for timely justice against fairness to parties. Courts consider factors such as reasons for the delay, potential prejudice, and case complexity before deciding whether to extend deadlines or postpone hearings. This discretionary power ensures flexibility in managing court schedules while protecting litigants' rights to a fair trial.
Consequences of Continuance and Adjournment for Parties
Continuance often results in delayed resolution, increased legal costs, and prolonged emotional stress for parties, potentially affecting their ability to gather evidence or maintain witness availability. Adjournment typically provides a temporary pause without altering the trial schedule, which may benefit parties needing short-term relief but can disrupt momentum and court resource planning. Both continuance and adjournment impact case timelines and party preparedness, influencing overall litigation strategy and outcomes.
Tips for Successfully Requesting Court Delays
When requesting continuance or adjournment in court, clearly articulate valid reasons such as needing more time for evidence gathering or witness availability, supported by documented proof. Submit the request well in advance of the scheduled hearing date to demonstrate good faith and avoid last-minute denials. Ensure compliance with local court rules and procedures, including proper filing formats and timely notifications to opposing parties.
Continuance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com