Elections serve as the cornerstone of democratic societies, empowering citizens to choose their leaders and influence government policies. Voter turnout and electoral integrity play critical roles in shaping the legitimacy and effectiveness of any electoral process. Explore the full article to understand how elections impact your voice and the future of governance.
Table of Comparison
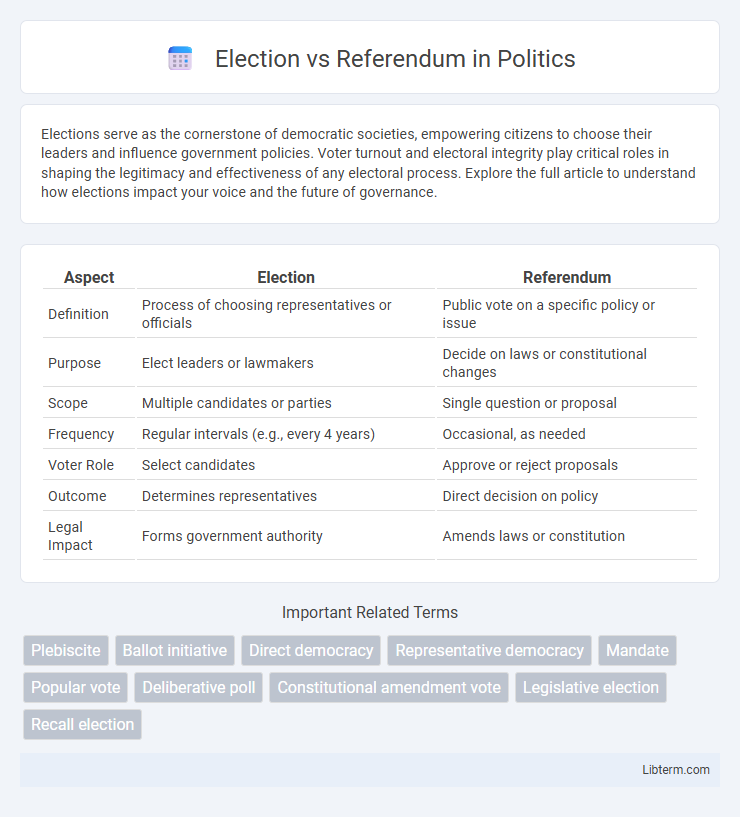
| Aspect | Election | Referendum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of choosing representatives or officials | Public vote on a specific policy or issue |
| Purpose | Elect leaders or lawmakers | Decide on laws or constitutional changes |
| Scope | Multiple candidates or parties | Single question or proposal |
| Frequency | Regular intervals (e.g., every 4 years) | Occasional, as needed |
| Voter Role | Select candidates | Approve or reject proposals |
| Outcome | Determines representatives | Direct decision on policy |
| Legal Impact | Forms government authority | Amends laws or constitution |
Understanding Elections and Referendums
Elections are formal processes where citizens vote to choose representatives or decide leadership positions, playing a crucial role in democratic governance. Referendums, on the other hand, are direct votes by the electorate on specific policy issues or legislative proposals, allowing public participation in decision-making. Understanding elections involves recognizing their role in representative democracy, while referendums highlight direct democracy mechanisms for policy approval or rejection.
Key Differences Between Elections and Referendums
Elections involve selecting individuals for public office through voting, while referendums are direct votes on specific policy issues or laws. Elections typically feature multiple candidates or parties competing for positions, whereas referendums present a binary choice, such as yes or no, on a particular proposal. Voters in elections influence government leadership, but in referendums, they directly shape legislation or constitutional changes.
The Purpose of Elections
Elections serve as a fundamental mechanism for selecting representatives and leaders who make decisions on behalf of the electorate, ensuring effective governance and political accountability. They enable citizens to influence public policy through their vote, reflecting diverse interests and democratic participation. The purpose of elections is to confer legitimacy on government officials and establish a structured system for political succession and power distribution.
The Purpose of Referendums
Referendums serve as a direct democratic tool allowing voters to decide on specific policy issues or constitutional amendments, bypassing legislative bodies. Unlike elections, which select representatives, referendums focus on gauging public opinion on particular questions or proposals, ensuring citizens have a direct voice in decision-making. This mechanism promotes increased political participation and legitimacy by reflecting the electorate's stance on critical national or local matters.
Types of Elections and Referendums
Elections include various types such as general, local, primary, and by-elections, each designed to select representatives or decide leadership within different levels of government. Referendums, classified by binding or advisory nature, allow voters to directly approve or reject specific legislative measures or constitutional amendments. Both mechanisms serve democratic processes but differ fundamentally in voter participation and decision-making roles.
Voting Processes in Elections vs Referendums
Voting processes in elections typically involve selecting candidates or parties to represent the electorate in various government positions through ballots cast in designated polling stations or via absentee methods. Referendums require voters to decide on specific policy questions or constitutional changes, often limited to a straightforward yes/no choice, with similar logistical voting arrangements as elections. Both processes emphasize transparency, voter identification, and secure ballot handling to ensure legitimacy and accurate representation of public will.
Advantages of Elections
Elections offer a structured and representative decision-making process by allowing citizens to choose leaders who can address diverse societal interests and implement comprehensive policies. They facilitate accountability through periodic voting, enabling voters to remove ineffective officials and support those who align with their values. The competitive nature of elections fosters political engagement and public debate, strengthening democratic institutions and promoting transparency.
Advantages of Referendums
Referendums offer a direct form of democracy, allowing citizens to vote on specific issues rather than relying solely on elected representatives. This process increases political participation and ensures that government decisions more accurately reflect the public's will. Furthermore, referendums can promote transparency and accountability by clearly presenting important policy choices to the electorate.
Challenges and Criticisms
Elections face challenges such as voter suppression, misinformation campaigns, and concerns over electoral fraud, which can undermine democratic legitimacy and public trust. Referendums often encounter criticisms related to oversimplification of complex issues, potential manipulation by interest groups, and low voter turnout that questions the representativeness of outcomes. Both processes struggle with ensuring informed participation and preventing undue influence from polarized media or political actors.
Impact on Democratic Governance
Elections empower citizens to select representatives, ensuring accountability and fostering political pluralism, which strengthens democratic governance. Referendums enable direct voter participation on specific policy issues, enhancing political legitimacy and promoting public engagement. Both mechanisms complement each other by balancing representative decision-making with direct democracy, thereby deepening democratic responsiveness and inclusivity.
Election Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com