Proactive policy involves anticipating challenges and implementing measures before problems arise, ensuring smoother governance and better outcomes. This approach helps organizations and governments adapt quickly to changing environments and minimize risks. Discover how proactive policy can transform your decision-making by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
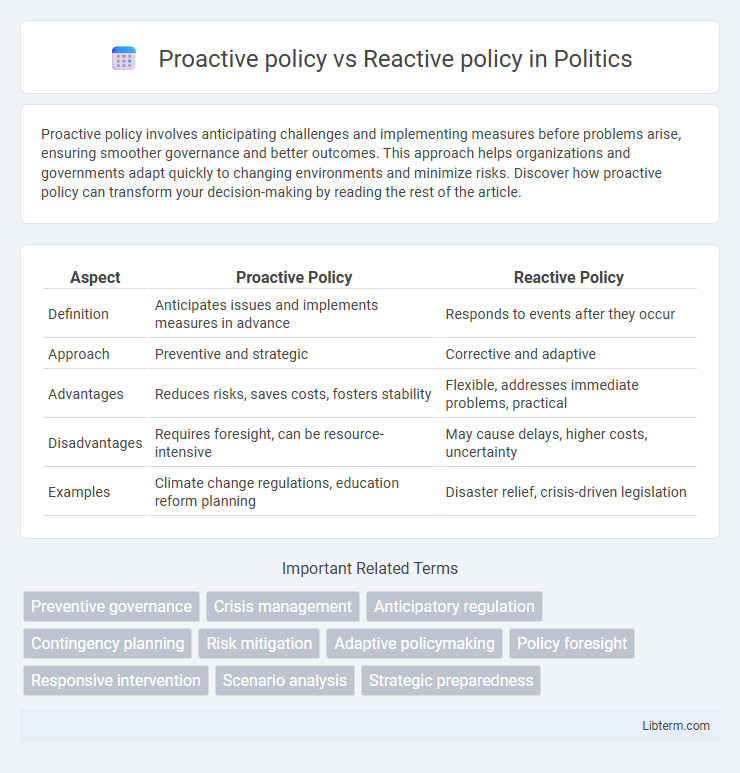
| Aspect | Proactive Policy | Reactive Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Anticipates issues and implements measures in advance | Responds to events after they occur |
| Approach | Preventive and strategic | Corrective and adaptive |
| Advantages | Reduces risks, saves costs, fosters stability | Flexible, addresses immediate problems, practical |
| Disadvantages | Requires foresight, can be resource-intensive | May cause delays, higher costs, uncertainty |
| Examples | Climate change regulations, education reform planning | Disaster relief, crisis-driven legislation |
Understanding Proactive and Reactive Policies
Proactive policies anticipate potential challenges and implement preventive measures to mitigate risks before issues arise, ensuring long-term benefits and stability. Reactive policies respond to problems after they occur, focusing on immediate resolution rather than prevention, which may lead to recurring challenges and higher costs. Understanding the differences between these approaches highlights the strategic advantage of proactively addressing policy concerns to enhance organizational resilience and efficiency.
Key Differences Between Proactive and Reactive Approaches
Proactive policy involves anticipating potential issues and implementing measures to prevent problems before they arise, emphasizing foresight and strategic planning. Reactive policy, on the other hand, responds to events after they occur, focusing on immediate solutions and damage control. Key differences include timing of response, with proactive policies being preemptive and reactive policies being responsive, and the overall impact on risk management, where proactive approaches reduce risks while reactive methods manage consequences.
Advantages of Proactive Policy Formulation
Proactive policy formulation enables governments to anticipate economic challenges and implement strategic measures that mitigate risks before they escalate, ensuring greater stability and sustainable growth. By leveraging data analytics and forecasting models, proactive policies facilitate timely interventions that promote innovation, resource optimization, and long-term social welfare improvements. This approach enhances resilience against market volatility and fosters a competitive advantage by adapting swiftly to changing global trends.
Drawbacks of Relying on Reactive Policies
Relying on reactive policies often leads to delayed responses that can exacerbate crises and increase recovery costs, as they address issues only after they arise rather than preventing them. This approach can strain resources, create inefficiencies, and undermine long-term strategic goals by prioritizing short-term fixes over sustainable solutions. Organizations depending on reactive policies risk reputational damage and diminished stakeholder confidence due to inconsistent and unpredictable handling of challenges.
Case Studies: Successes with Proactive Governance
Proactive policies in urban development have led to significant improvements in air quality and public health as demonstrated by Singapore's Early Green Urban Planning initiative, which incorporated extensive green spaces to reduce pollution. In contrast, reactive policies often resulted in costly emergency responses and infrastructure overhauls, such as New Orleans' response to Hurricane Katrina. The success of Portland's proactive land-use regulations further underscores the economic and environmental benefits of anticipating urban growth rather than responding to its consequences.
Common Pitfalls of Reactive Policymaking
Reactive policymaking often suffers from delayed responses that fail to address root causes, leading to repeated crises and escalating social costs. Common pitfalls include short-term fixes that overlook long-term implications, insufficient stakeholder engagement, and a lack of comprehensive data analysis, which collectively undermine effective governance. These issues exacerbate policy inefficiencies, increase public dissatisfaction, and strain governmental resources.
Stakeholder Engagement in Policy Development
Proactive policy development emphasizes early and continuous stakeholder engagement, allowing for diverse input and collaborative problem-solving before issues escalate. This approach fosters transparency and trust, enabling policymakers to anticipate challenges and tailor solutions to stakeholder needs effectively. In contrast, reactive policy often involves stakeholders later in the process, limiting feedback opportunities and potentially resulting in resistance or inadequate responses.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Policy Approaches
Measuring the effectiveness of proactive policies involves tracking long-term indicators such as risk reduction, resource allocation efficiency, and prevention outcomes before issues escalate. Reactive policy effectiveness is evaluated by response time, resolution rates, and the ability to minimize damage after a problem occurs. Comparative analysis often uses cost-benefit metrics and impact assessments to determine which approach yields better social, economic, and environmental results.
Strategies for Transitioning to Proactive Policies
Transitioning to proactive policies requires implementing predictive analytics and real-time data monitoring to identify potential risks before they escalate. Incorporating cross-departmental collaboration enhances strategic foresight, enabling rapid response frameworks that anticipate policy challenges. Organizations must also invest in continuous training and adaptive governance structures to sustain long-term proactive policy management.
Future Trends in Policy Planning and Implementation
Proactive policy planning leverages advanced data analytics, AI, and scenario modeling to anticipate future challenges and opportunities, enabling more adaptive and resilient governance frameworks. Reactive policy, while essential in crisis management, often struggles to keep pace with rapid technological, environmental, and social changes, highlighting the importance of integrating real-time data monitoring and predictive tools into policy processes. Future trends emphasize hybrid models that combine proactive foresight with agile response mechanisms, ensuring both preparedness and flexibility in dynamic policy environments.
Proactive policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com