Political apathy leads to low voter turnout and weak civic engagement, undermining democratic processes and community representation. Understanding the causes and consequences of political disengagement is crucial for fostering informed and active citizenship. Discover how political apathy affects your society and what steps can be taken to overcome it in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
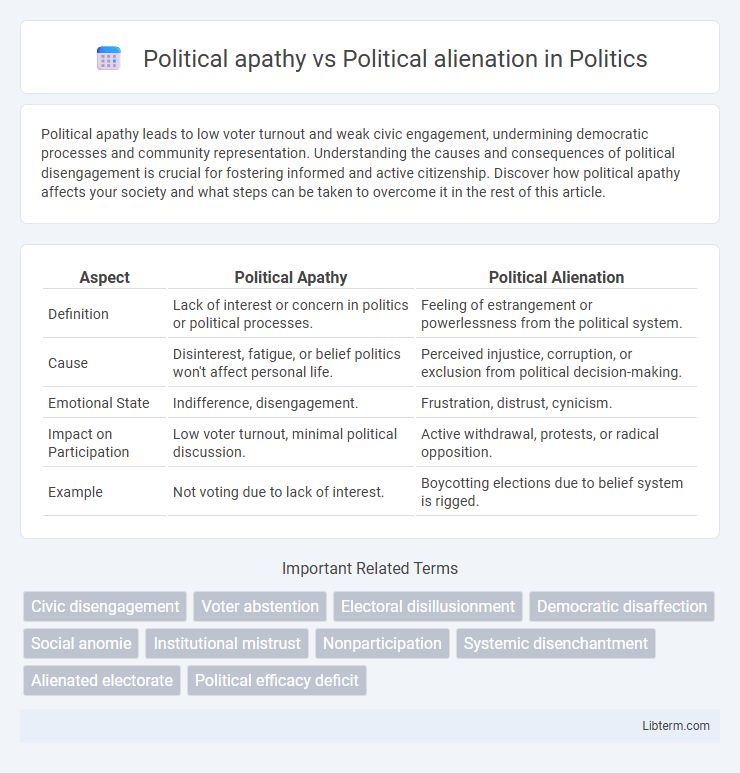
| Aspect | Political Apathy | Political Alienation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lack of interest or concern in politics or political processes. | Feeling of estrangement or powerlessness from the political system. |
| Cause | Disinterest, fatigue, or belief politics won't affect personal life. | Perceived injustice, corruption, or exclusion from political decision-making. |
| Emotional State | Indifference, disengagement. | Frustration, distrust, cynicism. |
| Impact on Participation | Low voter turnout, minimal political discussion. | Active withdrawal, protests, or radical opposition. |
| Example | Not voting due to lack of interest. | Boycotting elections due to belief system is rigged. |
Understanding Political Apathy and Political Alienation
Political apathy refers to a lack of interest or concern in participating in political processes, often caused by feelings of indifference or perceived irrelevance of politics to one's life. Political alienation, on the other hand, involves a deeper sense of estrangement and disenchantment with the political system, characterized by distrust, powerlessness, and belief that the political system is unresponsive or corrupt. Understanding the psychological and sociological roots of both conditions is crucial for addressing voter disengagement and promoting democratic participation.
Defining the Core Differences
Political apathy refers to a lack of interest or motivation to participate in political processes, often caused by indifference or skepticism about politics. Political alienation involves a deeper estrangement from the political system, characterized by feelings of powerlessness, disenfranchisement, and distrust toward political institutions. While apathy centers on passive disengagement, alienation reflects an active emotional disconnection and hostility toward political structures.
Historical Roots of Political Disengagement
Political apathy and political alienation both stem from distinct historical roots of political disengagement, shaping citizen behavior and attitudes toward governance. Political apathy often arises from prolonged periods of political stability or oppression, leading to voter indifference and passive citizenship, while political alienation originates from systemic exclusion, corruption, and perceived injustices that create distrust and emotional estrangement from political institutions. Key historical events such as disenfranchisement during Reconstruction in the United States or disenchantment following authoritarian regimes exemplify these divergent pathways to disengagement.
Causes Behind Political Apathy
Political apathy stems primarily from a lack of interest or perceived irrelevance of political processes to individuals' daily lives, often caused by insufficient political knowledge and feelings of inefficacy. Economic instability, social disenfranchisement, and distrust in political institutions further exacerbate this disengagement by reinforcing the belief that participation will not lead to meaningful change. Unlike political alienation, which involves active feelings of estrangement and opposition toward politics, apathy is characterized by indifference and passive withdrawal from political activities.
Triggers of Political Alienation
Political alienation is primarily triggered by perceived systemic corruption, lack of political efficacy, and unresponsiveness of government institutions, leading individuals to feel powerless and disconnected from the political process. Unlike political apathy, which involves indifference or lack of interest, alienation stems from active dissatisfaction and mistrust toward political actors and policies. Factors such as economic inequality, media bias, and exclusion from decision-making intensify the sense of alienation, fostering a critical stance against mainstream politics.
Societal Impact of Apathy vs Alienation
Political apathy, characterized by lack of interest or indifference toward political participation, often leads to lower voter turnout and weakened democratic engagement, thereby undermining effective governance and public accountability. Political alienation, marked by feelings of powerlessness and distrust toward political institutions, fosters social fragmentation and can escalate political instability or radicalization. Both phenomena impede societal cohesion but while apathy diminishes collective action through disengagement, alienation breeds active opposition and erosion of institutional legitimacy.
Psychological Factors Influencing Each Phenomenon
Political apathy stems from a lack of interest or motivation to engage in political processes, often influenced by feelings of helplessness, low political efficacy, and cognitive overload. Political alienation involves a deeper psychological estrangement characterized by distrust, powerlessness, and disillusionment with political institutions, contributing to emotional withdrawal. Both phenomena are shaped by individual psychological factors such as perceived self-efficacy, emotional response to political events, and social identity, impacting citizen participation and democratic engagement.
Youth Perspectives: Apathy or Alienation?
Youth political apathy reflects a lack of interest or motivation to engage in political processes, often due to feelings of insignificance or fatigue with complex issues. Political alienation among young people involves a deeper disconnection, where they perceive the political system as unresponsive or unjust, leading to distrust and disengagement. Understanding whether youth exhibit apathy or alienation is crucial for designing targeted interventions that foster meaningful political participation.
Addressing Disengagement: Solutions and Interventions
Political apathy involves a lack of interest or motivation to participate in political processes, while political alienation encompasses feelings of powerlessness and estrangement from the political system. Addressing disengagement requires targeted interventions such as civic education programs that increase political literacy, community engagement initiatives that foster a sense of belonging, and inclusive policymaking that ensures marginalized voices are heard. Empowering citizens through transparent communication and accessible political platforms can mitigate both apathy and alienation, enhancing overall democratic participation.
Future Implications for Democracy
Political apathy, characterized by voter disengagement and indifference, can weaken democratic participation by reducing electoral turnout and citizen involvement in governance processes. Political alienation, marked by distrust and feelings of powerlessness toward political institutions, risks deepening societal divisions and fostering extremism or withdrawal from civic duties. Both phenomena threaten the resilience of democracy by undermining accountability, representation, and the legitimacy of democratic systems in the future.
Political apathy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com