Populist politics focus on representing the interests of ordinary people against a perceived elite or establishment, often emphasizing national sovereignty and direct democracy. This approach can reshape policy debates and influence elections by appealing to widespread frustration and demands for change. Discover how populist movements impact governance and society in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
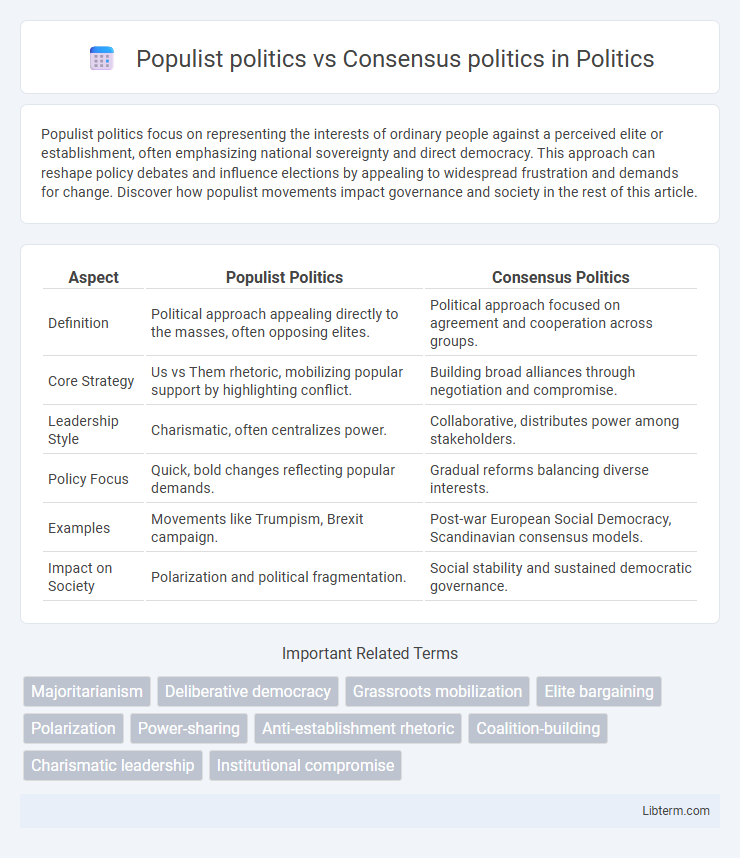
| Aspect | Populist Politics | Consensus Politics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political approach appealing directly to the masses, often opposing elites. | Political approach focused on agreement and cooperation across groups. |
| Core Strategy | Us vs Them rhetoric, mobilizing popular support by highlighting conflict. | Building broad alliances through negotiation and compromise. |
| Leadership Style | Charismatic, often centralizes power. | Collaborative, distributes power among stakeholders. |
| Policy Focus | Quick, bold changes reflecting popular demands. | Gradual reforms balancing diverse interests. |
| Examples | Movements like Trumpism, Brexit campaign. | Post-war European Social Democracy, Scandinavian consensus models. |
| Impact on Society | Polarization and political fragmentation. | Social stability and sustained democratic governance. |
Understanding Populist Politics
Populist politics centers on appealing directly to the interests and emotions of the general populace, often portraying elites as corrupt and disconnected from ordinary citizens. This approach leverages simplified narratives and charismatic leadership to mobilize support, emphasizing majoritarian rule and direct political engagement. Understanding populist politics involves analyzing how it challenges established consensus politics by prioritizing popular will over negotiated agreements among diverse political actors.
Defining Consensus Politics
Consensus politics emphasizes broad agreement among diverse political groups, prioritizing compromise and cooperation to achieve stable governance and inclusive policy outcomes. This approach often involves negotiation to accommodate varying interests, ensuring decisions reflect collective support rather than majoritarian dominance. By fostering unity and reducing polarization, consensus politics aims to create durable solutions in democratic systems.
Historical Roots of Populism
Populist politics trace their historical roots to late 19th-century agrarian movements in the United States, such as the People's Party, which mobilized disenfranchised farmers against economic elites and political establishments. The emphasis on a charismatic leader representing "the people" against "the elite" diverges sharply from consensus politics, which prioritize compromise, institutional stability, and incremental policy-making. Populism's historical emergence often correlates with periods of economic distress and social inequality, fueling anti-establishment rhetoric and mass mobilization that challenge the cooperative, centrist approach of consensus politics.
Evolution of Consensus Politics
Consensus politics evolved through post-World War II efforts to stabilize democracies by promoting inclusive dialogue, institutional cooperation, and broad-based policy agreements among diverse political actors. This approach emphasizes gradual reform, compromise, and maintaining social harmony, contrasting with populist politics that often prioritize direct appeals to popular sentiment and challenge established elites. Over time, consensus politics has adapted to increasing political polarization by fostering mechanisms for negotiation and power-sharing to prevent governance deadlock.
Key Characteristics of Populist Movements
Populist movements emphasize a direct appeal to "the people," often contrasting them against a perceived corrupt elite, and employ simplified, emotive rhetoric to mobilize mass support. They typically advocate for majoritarian rule, reject institutional consensus and pluralism, and promote nationalist or anti-establishment themes. Populist politics prioritize charismatic leadership, politicization of identity, and often challenge traditional democratic norms to achieve swift policy changes.
Mechanisms of Building Consensus
Consensus politics relies on mechanisms such as negotiation, compromise, and inclusive dialogue to build agreement among diverse stakeholders, fostering cooperation and long-term stability. Populist politics often bypass these mechanisms by appealing directly to popular sentiments, prioritizing majoritarian rule and charismatic leadership over collaborative decision-making. Effective consensus-building requires institutional frameworks that encourage transparency, trust, and mutual respect among political actors.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Populism
Populist politics energizes disenfranchised voters by addressing grievances related to economic inequality and political corruption, often leading to increased political engagement and rapid policy changes. However, its emphasis on simplistic solutions and charismatic leadership can undermine democratic institutions, polarize societies, and hinder long-term policy stability. Populism's benefits include mobilizing marginalized groups and challenging elite dominance, while drawbacks involve potential erosion of checks and balances and increased social division.
Advantages and Limitations of Consensus Approach
Consensus politics fosters collaborative decision-making, promoting stability and long-term solutions by incorporating diverse perspectives from multiple stakeholders. This approach enhances policy legitimacy and reduces polarization, ensuring broader acceptance and smoother implementation of laws. However, the consensus model can lead to slow decision processes and may dilute bold reforms due to the need for compromise among conflicting interests.
Populist vs. Consensus Politics: Societal Impact
Populist politics often amplifies societal divisions by promoting an "us versus them" rhetoric that can undermine social cohesion and polarize communities. In contrast, consensus politics seeks to bridge differences through dialogue and compromise, fostering stability and inclusive governance. The societal impact of populist politics tends to challenge democratic norms, whereas consensus politics supports collaborative decision-making and long-term social trust.
Future Trends in Political Governance
Populist politics, characterized by direct appeals to the public and often challenging established institutions, is likely to persist as a force in political governance, driven by societal dissatisfaction and polarization. Consensus politics, emphasizing collaboration and compromise among diverse political actors, may evolve through digital platforms and data-driven decision-making to adapt to complex global challenges. Future governance trends suggest a hybrid approach that leverages populist mobilization with consensus-building mechanisms to address legitimacy and inclusivity in policymaking.
Populist politics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com