A liberal state prioritizes individual freedoms, equality, and the protection of civil rights within its governance structure. It upholds democratic principles and ensures that laws reflect the values of justice and personal liberty. Explore the article further to understand how a liberal state impacts your rights and society as a whole.
Table of Comparison
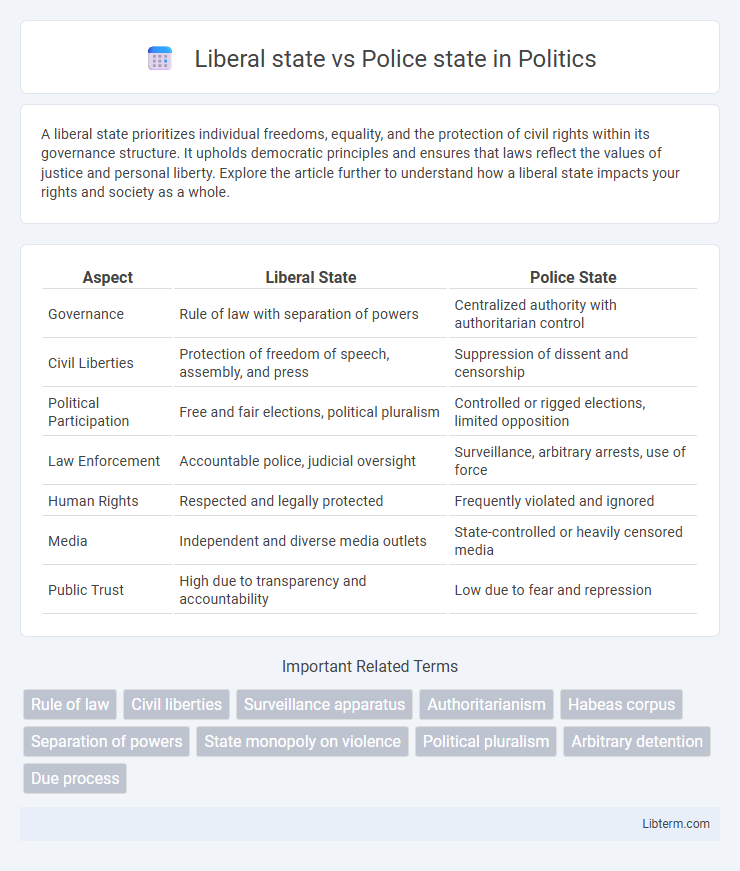
| Aspect | Liberal State | Police State |
|---|---|---|
| Governance | Rule of law with separation of powers | Centralized authority with authoritarian control |
| Civil Liberties | Protection of freedom of speech, assembly, and press | Suppression of dissent and censorship |
| Political Participation | Free and fair elections, political pluralism | Controlled or rigged elections, limited opposition |
| Law Enforcement | Accountable police, judicial oversight | Surveillance, arbitrary arrests, use of force |
| Human Rights | Respected and legally protected | Frequently violated and ignored |
| Media | Independent and diverse media outlets | State-controlled or heavily censored media |
| Public Trust | High due to transparency and accountability | Low due to fear and repression |
Defining Liberal State and Police State
A Liberal State is defined by the protection of individual rights, rule of law, and democratic governance, ensuring citizens' freedoms and equality before the law. In contrast, a Police State is characterized by centralized authoritarian control, extensive surveillance, and limited civil liberties, where law enforcement agencies exercise power with minimal legal constraints. The core distinction lies in the balance of power, with the Liberal State promoting accountability and transparency, while the Police State prioritizes security and control over personal freedoms.
Historical Evolution of Liberal and Police States
Liberal states evolved from Enlightenment principles advocating individual freedoms, rule of law, and democratic governance, emphasizing limited government intervention and protection of civil rights. Police states historically emerged during periods of political instability or authoritarian regimes, characterized by centralized control, extensive surveillance, and suppression of dissent to maintain order. The transition from liberal to police states often involves erosion of civil liberties and the rise of security apparatuses that prioritize state control over personal freedoms.
Core Principles: Freedom vs. Control
A liberal state prioritizes individual freedoms, civil liberties, and limited government intervention to ensure personal autonomy and democratic governance. In contrast, a police state emphasizes strict control, centralized authority, and extensive surveillance to maintain order and suppress dissent. The core conflict lies in balancing personal freedom against state control, shaping the political and social dynamics within each system.
Civil Liberties in Liberal and Police States
Liberal states prioritize the protection of civil liberties such as freedom of speech, privacy, and due process, ensuring government powers are limited by law and accountable to citizens. Police states, however, restrict these freedoms through extensive surveillance, arbitrary arrests, and suppression of dissent to maintain strict control and order. The contrast lies in the degree of individual rights upheld, with liberal states fostering an environment of personal autonomy and police states emphasizing authoritative governance.
Government Power and Citizen Oversight
A liberal state maintains limited government power through constitutional checks and balances, allowing citizens to exercise oversight via free elections, independent judiciary, and transparent institutions. In contrast, a police state centralizes authority, often employing security forces to monitor, control, and suppress civilian activities, drastically curtailing public accountability. Effective citizen oversight in liberal states ensures protection of civil liberties, while police states prioritize state security over individual freedoms.
Rule of Law: Judicial Independence and Accountability
In a liberal state, the rule of law is upheld through judicial independence, ensuring courts operate free from political influence and deliver fair, impartial justice. Judges in such systems are held accountable through transparent legal frameworks and oversight bodies that protect rights while preventing abuses of power. Conversely, a police state often undermines judicial independence by subjugating courts to executive control, leading to arbitrary rulings that prioritize state security over individual freedoms and weaken accountability mechanisms.
Surveillance, Policing, and Privacy Concerns
Liberal states typically implement surveillance and policing within frameworks that prioritize individual privacy rights and legal oversight, ensuring transparency and accountability to prevent abuse of power. Police states often employ pervasive surveillance systems and aggressive policing tactics with minimal regard for privacy, using these tools to maintain strict control over citizens and suppress dissent. The tension between security measures and personal freedoms in liberal states contrasts sharply with the authoritarian control mechanisms characteristic of police states, where privacy concerns are frequently overridden by state interests.
Political Participation and Dissent
Liberal states protect political participation through free elections, guaranteeing individuals the right to vote, form political parties, and engage in public discourse without fear of reprisal. In contrast, police states restrict dissent by employing surveillance, censorship, and intimidation to suppress opposition and maintain governmental control. The fundamental difference lies in the state's approach to civil liberties: liberal states promote open political engagement, whereas police states enforce conformity and limit freedoms to silence dissent.
Social and Economic Impacts
Liberal states promote individual freedoms and market economies, fostering innovation, social mobility, and diverse economic opportunities while ensuring legal protections and democratic governance. Police states prioritize control and surveillance, often suppressing dissent and limiting economic freedom, which can stifle entrepreneurship and exacerbate social inequality. The contrasting governance models directly influence social cohesion, economic growth, and citizens' quality of life.
Contemporary Examples and Global Trends
Liberal states such as Canada and Germany emphasize individual freedoms, rule of law, and democratic governance, fostering open societies with transparent legal systems and protection of civil rights. Police states like China and Russia exhibit centralized control, extensive surveillance, and limited political pluralism, prioritizing state security over personal liberties. Global trends reveal a rise in authoritarian practices amid ongoing debates on balancing security and freedom in the digital age, highlighting challenges to liberal democratic norms worldwide.
Liberal state Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com