Conventions serve as essential frameworks that guide social behavior and communication across various contexts, establishing shared expectations and norms. These unwritten rules influence etiquette, cultural practices, and professional interactions, helping maintain order and mutual understanding. Explore the rest of the article to discover how conventions impact your daily life and social dynamics.
Table of Comparison
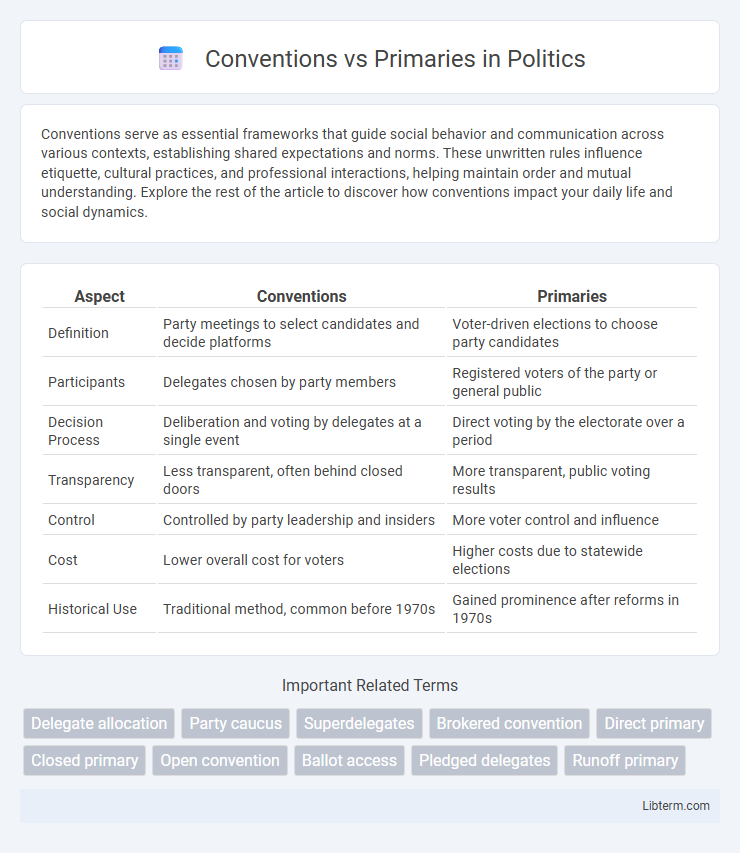
| Aspect | Conventions | Primaries |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Party meetings to select candidates and decide platforms | Voter-driven elections to choose party candidates |
| Participants | Delegates chosen by party members | Registered voters of the party or general public |
| Decision Process | Deliberation and voting by delegates at a single event | Direct voting by the electorate over a period |
| Transparency | Less transparent, often behind closed doors | More transparent, public voting results |
| Control | Controlled by party leadership and insiders | More voter control and influence |
| Cost | Lower overall cost for voters | Higher costs due to statewide elections |
| Historical Use | Traditional method, common before 1970s | Gained prominence after reforms in 1970s |
Understanding Conventions and Primaries
Conventions are gatherings where party delegates formally select a presidential nominee, establish party platforms, and unify members before the general election. Primaries are preliminary elections in which party members vote directly for their preferred candidate to represent the party in the general election. Understanding the distinction between conventions and primaries is crucial for grasping the candidate selection process and party organization in U.S. politics.
Historical Evolution of Party Nominations
The historical evolution of party nominations reveals a shift from conventions, where party leaders and delegates selected candidates, to primaries that empower party members to vote directly for nominees, reflecting broader democratic participation. Conventions dominated the 19th and early 20th centuries, serving as elite-controlled decision-making arenas, while the Progressive Era reforms introduced primaries to reduce corruption and increase transparency. This transformation intensified during the mid-20th century, especially after the 1968 Democratic National Convention, leading to the widespread adoption of primary elections as key mechanisms for candidate selection in U.S. presidential races.
Key Differences Between Conventions and Primaries
Conventions are party meetings where delegates officially select a candidate, finalize platforms, and unify support, whereas primaries are state-level elections where party members vote directly for their preferred candidate. Conventions occur after primaries and caucuses, serving as a formal affirmation of the nominee, while primaries function as preliminary contests that determine delegate allocation. Primaries tend to be more participatory and democratic, whereas conventions emphasize party organization and consensus-building.
Advantages of the Convention System
The convention system centralizes candidate selection, enabling party leaders and delegates to build consensus and unify diverse voter blocs under a single platform, which strengthens overall party cohesion. It facilitates extensive media coverage and public engagement, boosting voter awareness and enthusiasm ahead of the general election. The structured format of conventions also allows for the clear presentation of policy agendas, helping candidates differentiate themselves and articulate their vision on a national stage.
Strengths of the Primary Election Process
The primary election process empowers voters by enabling direct participation in selecting party candidates, enhancing democratic representation and accountability. It encourages transparency and increases candidate competition, which often leads to stronger, more viable nominees for the general election. Primaries also help parties gauge public support and refine campaign strategies based on voter feedback, ultimately strengthening the electoral process.
Impact on Voter Participation and Engagement
Conventions often result in lower voter participation due to limited accessibility and timing constraints, whereas primaries typically encourage higher engagement by allowing broader voter involvement throughout the nomination process. Primaries enable constituents to influence candidate selection directly, fostering a greater sense of political efficacy and enthusiasm. This increased accessibility in primaries correlates with higher turnout rates compared to party-specific convention events that restrict participation to delegates.
Transparency and Accountability Concerns
Conventions often lack the transparency seen in primaries, as they involve selected delegates rather than direct voter participation, raising accountability concerns. Primaries provide a more open and democratic process by allowing registered voters to choose candidates, enhancing transparency in candidate selection. The direct involvement in primaries helps hold candidates and party officials accountable to the electorate, whereas conventions may obscure this responsibility behind party elites.
Influence of Party Elites vs Voter Voice
Conventions historically concentrated party elites' influence, enabling leaders to shape candidate selection through delegate control and strategic negotiations. Primaries shifted power toward voter voice, allowing the electorate to directly participate in choosing nominees, thus diluting party insiders' gatekeeping abilities. This transition highlights the evolving dynamic where grassroots voter preferences increasingly determine party candidates, reducing exclusive elite dominance.
Case Studies: Successes and Controversies
Case studies comparing conventions and primaries reveal varied successes, with conventions often praised for fostering party unity and offering a controlled platform for consensus-building. Primaries allow broader voter participation, increasing democratic legitimacy but sometimes causing intra-party divisions and prolonged conflicts, as seen in the 2016 U.S. presidential race. Controversies frequently arise around delegate allocation and voter suppression in primaries, while conventions face criticism over perceived lack of transparency and the influence of party elites.
Future Trends in Political Candidate Selection
Future trends in political candidate selection indicate a shift from traditional party conventions to increased reliance on primary elections, reflecting a demand for greater voter participation and transparency. The rise of digital platforms enables broader grassroots engagement, allowing candidates to harness online tools for campaigning and fundraising more effectively. Data analytics and AI-driven voter targeting are becoming essential in primaries, reshaping candidate outreach and influencing nomination outcomes.
Conventions Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com