Confirming your data accuracy ensures smooth transactions and avoids costly errors. Reliable verification processes protect your business integrity and customer trust. Dive into our article to explore effective methods for confirming essential information.
Table of Comparison
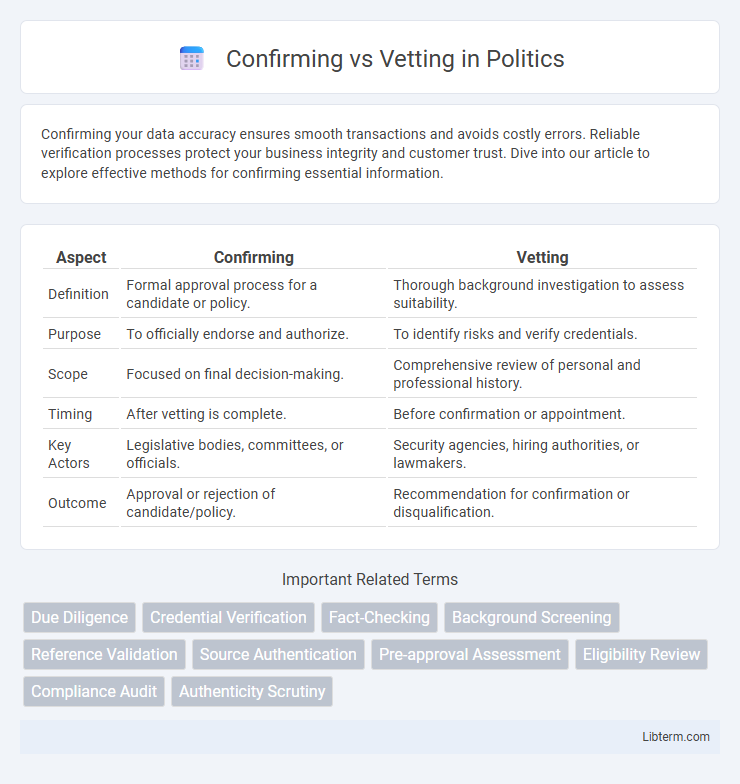
| Aspect | Confirming | Vetting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal approval process for a candidate or policy. | Thorough background investigation to assess suitability. |
| Purpose | To officially endorse and authorize. | To identify risks and verify credentials. |
| Scope | Focused on final decision-making. | Comprehensive review of personal and professional history. |
| Timing | After vetting is complete. | Before confirmation or appointment. |
| Key Actors | Legislative bodies, committees, or officials. | Security agencies, hiring authorities, or lawmakers. |
| Outcome | Approval or rejection of candidate/policy. | Recommendation for confirmation or disqualification. |
Understanding Confirming and Vetting: Definitions
Confirming involves verifying the accuracy of information or the authenticity of documents by cross-checking sources, ensuring data alignment and correctness. Vetting refers to the thorough evaluation or investigation of individuals or materials to assess credibility, suitability, or compliance with standards. Understanding confirming and vetting requires recognizing that confirming primarily validates facts while vetting encompasses a comprehensive assessment for risk and reliability.
Key Differences Between Confirming and Vetting
Confirming involves verifying specific information or facts to ensure accuracy and consistency, often through direct validation or simple checks. Vetting entails a comprehensive evaluation process, assessing credibility, background, and suitability to make informed decisions, especially in recruitment or partnerships. Key differences lie in the depth and scope: confirming is a focused verification, while vetting is an extensive assessment.
The Purpose of Confirming in Business Processes
Confirming in business processes serves to verify the accuracy and authenticity of information or transactions to ensure compliance with established standards and reduce errors. It establishes trust between parties by validating data such as orders, shipments, and payments before finalizing agreements. This step streamlines operations, mitigates risks, and enhances overall efficiency in supply chain and financial workflows.
The Role of Vetting in Risk Management
Vetting plays a crucial role in risk management by thoroughly evaluating potential risks through comprehensive background checks and validation processes. It ensures that individuals, partners, or investments meet predefined standards, significantly reducing the likelihood of fraud, compliance issues, and operational failures. Unlike simple confirmation, vetting involves deeper scrutiny to safeguard organizational integrity and maintain regulatory compliance.
Common Scenarios for Confirming vs Vetting
Confirming typically involves verifying basic facts such as identity, credentials, or information provided in resumes during hiring processes or vendor selections. Vetting goes deeper, encompassing background checks, reference verification, and risk assessments, often used in security clearances, high-level recruitment, or partnership evaluations. Common scenarios for confirming include simple fact-checking, while vetting addresses thorough due diligence to mitigate potential risks.
Advantages and Limitations of Confirming
Confirming offers advantages such as faster verification processes and reduced administrative costs by directly confirming transactions or data with third parties. However, its limitations include potential reliance on the accuracy and honesty of external sources, which may lead to incomplete or misleading information. The approach is less thorough compared to vetting, which involves comprehensive background checks and detailed validation of credentials.
Benefits and Challenges of Vetting
Vetting offers the benefit of thorough evaluation and risk mitigation by systematically verifying credentials, background, and qualifications, ensuring trustworthiness and compliance. Challenges of vetting include time-consuming processes, potential privacy concerns, and the need for specialized expertise to interpret complex information accurately. Effective vetting enhances decision-making quality but requires balancing thoroughness with efficiency to avoid delays and maintain candidate engagement.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Confirm Information
Confirming information involves systematically verifying facts through reputable sources such as official documents, expert testimony, or validated databases to ensure accuracy and reliability. The process typically starts by identifying the key data points, cross-referencing these with multiple independent sources, and documenting the findings to create a clear audit trail. Utilizing technology tools like fact-checking software or verification platforms enhances efficiency and reduces the risk of misinformation during confirmation.
Vetting Procedures: Best Practices and Tools
Vetting procedures involve a thorough evaluation process to assess the credibility, qualifications, and background of individuals or entities, ensuring compliance with organizational standards and legal requirements. Best practices include comprehensive background checks, reference verification, and leveraging advanced digital tools such as AI-driven screening platforms and blockchain for transparent record-keeping. Implementing multi-layered vetting protocols enhances risk management and strengthens the integrity of hiring or partnership decisions.
Choosing the Right Approach: When to Confirm vs When to Vet
Choosing the right approach between confirming and vetting depends on the context and the depth of verification required. Confirming is ideal for quick validation of facts, such as verifying appointment details or simple qualifications. Vetting involves a comprehensive evaluation, including background checks and credibility assessments, and is necessary when making critical decisions like hiring or partnerships.
Confirming Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com