Regulatory reform reshapes the legal framework to enhance efficiency, transparency, and fairness within industries. By streamlining compliance processes and eliminating outdated rules, these reforms foster innovation and economic growth. Explore the rest of the article to understand how regulatory reform impacts your business and the broader market.
Table of Comparison
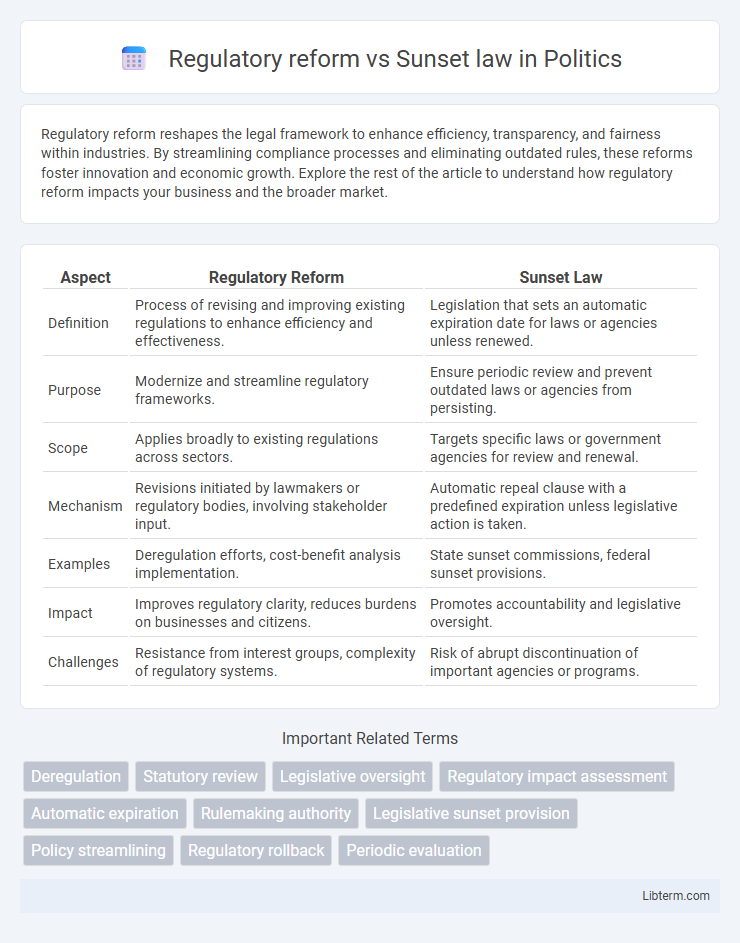
| Aspect | Regulatory Reform | Sunset Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of revising and improving existing regulations to enhance efficiency and effectiveness. | Legislation that sets an automatic expiration date for laws or agencies unless renewed. |
| Purpose | Modernize and streamline regulatory frameworks. | Ensure periodic review and prevent outdated laws or agencies from persisting. |
| Scope | Applies broadly to existing regulations across sectors. | Targets specific laws or government agencies for review and renewal. |
| Mechanism | Revisions initiated by lawmakers or regulatory bodies, involving stakeholder input. | Automatic repeal clause with a predefined expiration unless legislative action is taken. |
| Examples | Deregulation efforts, cost-benefit analysis implementation. | State sunset commissions, federal sunset provisions. |
| Impact | Improves regulatory clarity, reduces burdens on businesses and citizens. | Promotes accountability and legislative oversight. |
| Challenges | Resistance from interest groups, complexity of regulatory systems. | Risk of abrupt discontinuation of important agencies or programs. |
Introduction to Regulatory Reform and Sunset Laws
Regulatory reform involves overhauling existing regulations to enhance efficiency, reduce redundancy, and promote innovation within regulatory frameworks. Sunset laws mandate automatic expiration of specific regulations or agencies after a set period unless explicitly renewed by legislative action, ensuring periodic review and accountability. Both mechanisms aim to improve regulatory effectiveness but apply different principles: reform focuses on improving or replacing rules, while sunset laws enforce regular reassessment and elimination of outdated regulations.
Historical Background of Regulatory Policies
Regulatory reform emerged during the mid-20th century as governments sought to reduce excessive bureaucratic control and increase market efficiency, particularly in industries like telecommunications and airlines. Sunset laws, first implemented in the 1970s starting with Oklahoma, established automatic expiration dates for regulations to ensure periodic review and prevent outdated rules from persisting. Both approaches reflect evolving regulatory policies aimed at balancing effective oversight with economic flexibility and accountability.
Defining Regulatory Reform
Regulatory reform involves the systematic review and modification of existing regulations to improve efficiency, reduce burdens, and enhance compliance while supporting economic growth. It targets outdated, redundant, or excessive rules, aiming to streamline governmental oversight and promote innovation. Defining regulatory reform requires understanding its role in balancing public interest with regulatory flexibility to adapt to changing market and social conditions.
Understanding Sunset Laws
Sunset laws mandate the automatic expiration of government agencies, programs, or regulations after a specified period unless they are reviewed and explicitly renewed by the legislature. These laws aim to increase accountability and prevent outdated or ineffective regulations from remaining in effect indefinitely. Understanding sunset laws is essential for grasping how regulatory reform seeks to streamline government functions and promote transparency in the policymaking process.
Key Differences Between Regulatory Reform and Sunset Laws
Regulatory reform involves updating or modifying existing regulations to improve efficiency, eliminate redundancies, or respond to new developments, whereas sunset laws establish predetermined expiration dates for specific laws or regulations unless actively renewed. Key differences include that regulatory reform is a continuous process focused on adjustment and enhancement, while sunset laws impose automatic termination requiring legislative action for continuation. Regulatory reform targets the content and framework of regulations, whereas sunset laws emphasize regulatory accountability and periodic review through enforced time limits.
Benefits of Regulatory Reform
Regulatory reform streamlines government rules to enhance efficiency, reduce compliance costs, and promote innovation by eliminating outdated or redundant regulations. It creates a more transparent and predictable business environment, attracting investment and fostering economic growth. Unlike sunset laws that automatically terminate regulations after a set period, regulatory reform involves thorough evaluation and modernization to ensure policies remain relevant and effective.
Advantages of Implementing Sunset Laws
Implementing sunset laws enhances regulatory efficiency by mandating regular review and expiration dates for existing statutes, preventing obsolete or redundant regulations from persisting. These laws promote government accountability and transparency by requiring legislative bodies to reassess the effectiveness and relevance of policies periodically. As a result, sunset laws streamline regulatory frameworks, reduce bureaucratic complexity, and encourage adaptive policymaking based on current socio-economic conditions.
Challenges and Criticisms of Both Approaches
Regulatory reform faces challenges such as resistance from entrenched interests, complexity in balancing innovation with oversight, and the risk of regulatory uncertainty impacting businesses. Sunset laws encounter criticisms including potential disruptions to essential services due to automatic expiration clauses, administrative burdens from continuous reviews, and political influences affecting the objective assessment of regulations. Both approaches struggle with maintaining regulatory effectiveness while ensuring accountability and adaptability in rapidly changing environments.
Impact on Governance and Public Policy
Regulatory reform streamlines existing rules to enhance efficiency, reduce bureaucracy, and improve compliance, directly influencing governance by promoting transparency and accountability. Sunset laws mandate periodic review and expiration of regulations, fostering dynamic policy adjustments and preventing outdated or redundant rules from persisting. Together, these mechanisms ensure adaptive public policy frameworks that respond effectively to changing societal and economic conditions.
Future Trends in Regulation and Legislative Oversight
Future trends in regulation emphasize dynamic regulatory reform to enhance adaptability and responsiveness in legislative oversight frameworks. Sunset laws increasingly integrate automated review mechanisms, ensuring that obsolete regulations are systematically identified and repealed to maintain regulatory efficiency. Data-driven policy evaluation tools are projected to revolutionize how lawmakers assess the impact and necessity of regulations in evolving economic and technological landscapes.
Regulatory reform Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com