A special envoy is a diplomat appointed to represent a government in specific negotiations or missions, often dealing with complex international issues or conflicts. Their role is critical in facilitating dialogue, fostering diplomatic relations, and achieving targeted political or humanitarian goals. Discover how special envoys shape global diplomacy and why their work matters to your understanding of international affairs in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
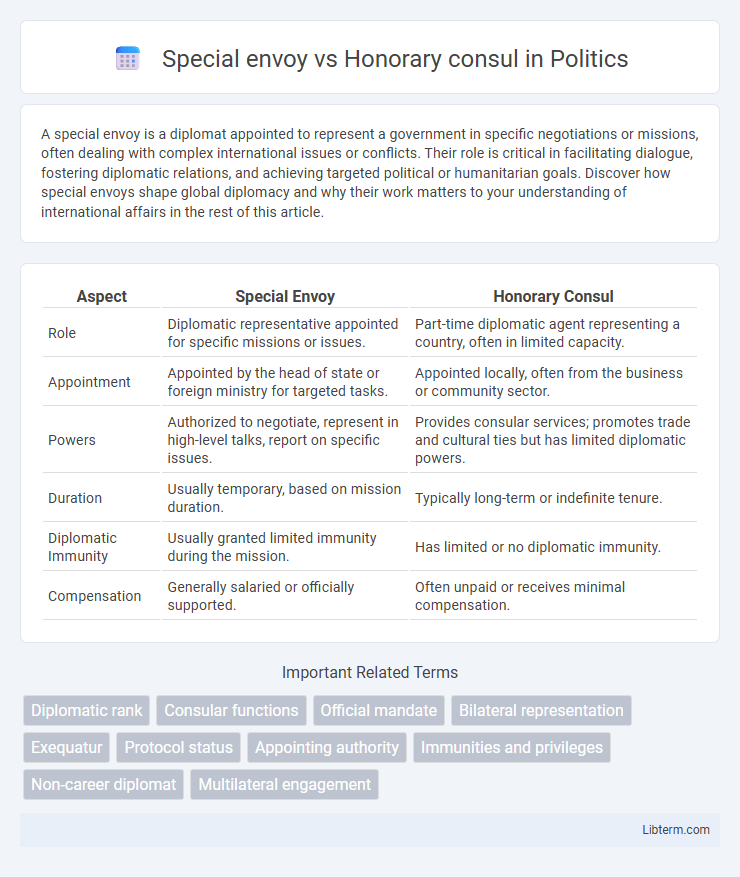
| Aspect | Special Envoy | Honorary Consul |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Diplomatic representative appointed for specific missions or issues. | Part-time diplomatic agent representing a country, often in limited capacity. |
| Appointment | Appointed by the head of state or foreign ministry for targeted tasks. | Appointed locally, often from the business or community sector. |
| Powers | Authorized to negotiate, represent in high-level talks, report on specific issues. | Provides consular services; promotes trade and cultural ties but has limited diplomatic powers. |
| Duration | Usually temporary, based on mission duration. | Typically long-term or indefinite tenure. |
| Diplomatic Immunity | Usually granted limited immunity during the mission. | Has limited or no diplomatic immunity. |
| Compensation | Generally salaried or officially supported. | Often unpaid or receives minimal compensation. |
Introduction: Understanding Diplomatic Titles
Special envoys serve as high-level diplomats appointed to address specific international issues or missions, often representing their country in sensitive negotiations or crisis situations. Honorary consuls, typically local citizens or residents, represent a foreign government's interests on a part-time basis, facilitating trade, cultural exchanges, and providing consular services without diplomatic immunity. Both roles enhance diplomatic presence but differ in scope, authority, and official status within international relations.
Special Envoy: Definition and Core Functions
A Special Envoy is a diplomatic agent appointed by a government or international organization to address specific issues or represent interests in high-stakes negotiations, often involving conflict resolution, peace talks, or targeted diplomacy. Unlike permanent diplomats, Special Envoys have a focused mandate with specialized expertise and operate with flexible authority to respond rapidly to complex situations. Their core functions include facilitating dialogue, coordinating international efforts, and advancing diplomatic solutions in areas such as security, humanitarian crises, or strategic partnerships.
Honorary Consul: Role and Responsibilities
Honorary consuls act as official representatives of a foreign government, primarily focusing on promoting trade, cultural exchanges, and assisting citizens abroad within a limited jurisdiction. Their responsibilities include facilitating business contacts, providing consular services such as passport and visa assistance, and supporting diplomatic missions without the full diplomatic immunity or salary of career diplomats. Special envoys, by contrast, are appointed for specific diplomatic tasks or negotiations and operate under a different mandate with broader political or strategic roles.
Appointment Process: Special Envoy vs Honorary Consul
The appointment process for a Special Envoy involves a formal designation by a head of state or government, often requiring approval from higher diplomatic authorities and clear mandate definitions. Conversely, an Honorary Consul is typically appointed by a foreign government but must receive consent from the host country's authorities, with a process focused on local legal compliance and community ties. The Special Envoy's appointment is more politically driven and mission-specific, whereas the Honorary Consul's selection emphasizes diplomatic protocol and functional consular responsibilities.
Diplomatic Rank and Authority Comparison
A Special Envoy is typically appointed by the head of state or government to handle specific diplomatic missions with high-ranking authority and direct representation powers, often possessing diplomatic rank equivalent to or above ministerial level. In contrast, an Honorary Consul holds a part-time, often local position without full diplomatic status, mainly focusing on promoting trade and assisting citizens, with limited diplomatic immunity and lower rank. Therefore, Special Envoys wield greater diplomatic credentials and operational authority compared to Honorary Consuls, who act in a supplementary and localized capacity.
Duration of Service: Temporary vs Long-Term Roles
Special envoys typically serve on a temporary basis, assigned to specific missions or diplomatic tasks with a defined timeframe, reflecting their targeted and short-term roles. Honorary consuls often hold long-term, sometimes indefinite positions, representing their nation's interests in regions without a full consulate, and their tenure is usually sustained by ongoing local engagement. The temporary nature of special envoy service contrasts sharply with the enduring, community-based responsibilities of honorary consuls.
Legal Status and Immunities
A Special Envoy typically holds a diplomatic role appointed by a government to undertake specific missions and enjoys diplomatic immunities under international law, including protection from arrest and legal process during official duties. An Honorary Consul, often a local citizen appointed to represent the interests of a foreign state, has limited immunities restricted primarily to official acts within their consular functions and lacks full diplomatic immunity. The legal status of a Special Envoy is generally governed by the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations, while that of an Honorary Consul is outlined in the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, reflecting differing scopes of privileges and immunities.
Key Duties and Areas of Focus
A Special Envoy primarily focuses on high-level diplomatic missions, negotiation, and representing a government in specific political or humanitarian issues often requiring specialized expertise or urgent attention. An Honorary Consul handles consular services such as assisting nationals abroad, promoting trade, and cultural exchanges within a defined geographical area, often on a part-time or voluntary basis. Key duties of a Special Envoy involve strategic diplomacy and international relations, while Honorary Consuls emphasize community support and consular protection.
Impact on International Relations
A special envoy serves as a high-level diplomatic agent appointed to address specific international issues or crises, often facilitating direct communication between governments and influencing policy decisions at the executive level. An honorary consul, usually a local individual appointed to represent the interests of a foreign country on a part-time basis, primarily supports trade, cultural exchanges, and assists nationals abroad without possessing formal diplomatic immunity or extensive negotiation powers. The impact on international relations of a special envoy is typically more significant and strategic, as they directly shape bilateral dialogues and conflict resolution, whereas honorary consuls contribute to grassroots diplomatic presence and economic ties without altering high-level diplomatic agendas.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Diplomatic Representative
Special envoys typically handle high-level, sensitive negotiations with specific mandates, while honorary consuls provide localized support and promote bilateral relations without full diplomatic status. Selecting the right representative depends on the mission's scope, required authority, and duration, with special envoys suited for strategic tasks and honorary consuls ideal for ongoing community engagement and facilitation. Understanding the distinct roles ensures effective diplomatic representation aligned with political objectives and resource allocation.
Special envoy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com