Authoritarian persistence describes the ability of authoritarian regimes to maintain control and resist democratic transitions despite internal and external pressures. These regimes often employ strategies such as repression, propaganda, and institutional manipulation to sustain their power. Explore the article to understand how authoritarian persistence shapes political landscapes worldwide.
Table of Comparison
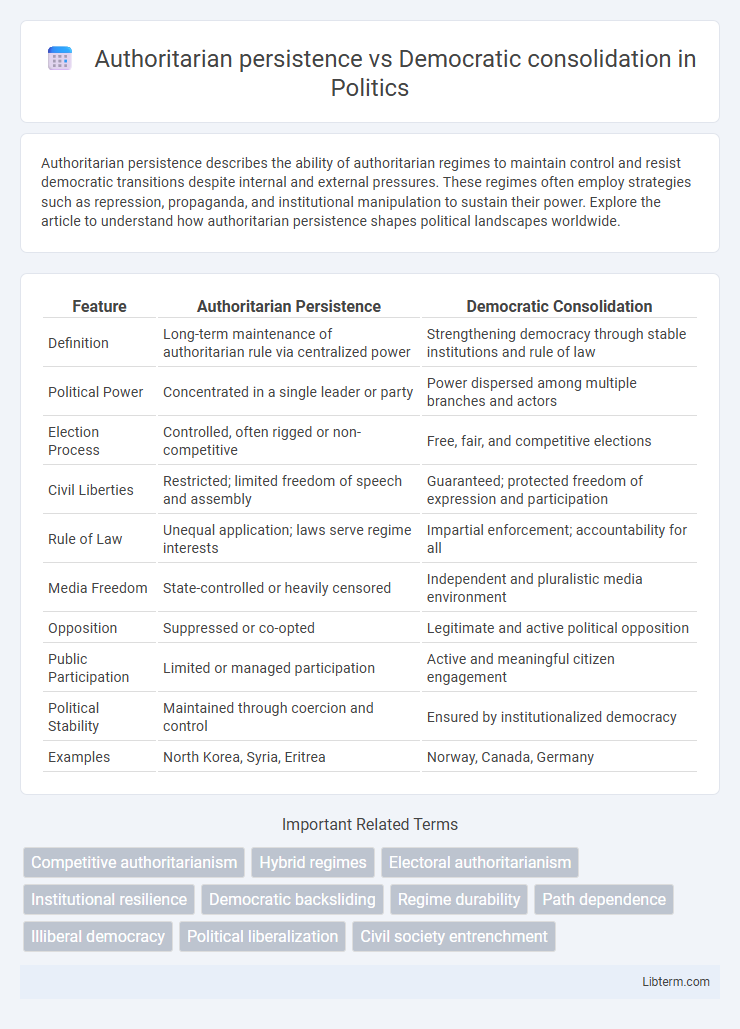
| Feature | Authoritarian Persistence | Democratic Consolidation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Long-term maintenance of authoritarian rule via centralized power | Strengthening democracy through stable institutions and rule of law |
| Political Power | Concentrated in a single leader or party | Power dispersed among multiple branches and actors |
| Election Process | Controlled, often rigged or non-competitive | Free, fair, and competitive elections |
| Civil Liberties | Restricted; limited freedom of speech and assembly | Guaranteed; protected freedom of expression and participation |
| Rule of Law | Unequal application; laws serve regime interests | Impartial enforcement; accountability for all |
| Media Freedom | State-controlled or heavily censored | Independent and pluralistic media environment |
| Opposition | Suppressed or co-opted | Legitimate and active political opposition |
| Public Participation | Limited or managed participation | Active and meaningful citizen engagement |
| Political Stability | Maintained through coercion and control | Ensured by institutionalized democracy |
| Examples | North Korea, Syria, Eritrea | Norway, Canada, Germany |
Defining Authoritarian Persistence and Democratic Consolidation
Authoritarian persistence refers to the sustained survival and stability of non-democratic regimes characterized by limited political pluralism, restricted civil liberties, and centralized power often maintained through coercion and controlled elections. Democratic consolidation is the process by which a democracy matures, ensuring that democratic institutions, norms, and practices become deeply rooted and resistant to authoritarian reversals or democratic breakdowns. Understanding these concepts involves analyzing regime durability, political culture, institutional strength, and the balance between state control and citizen participation.
Historical Contexts: Origins of Political Systems
Authoritarian persistence often emerges from colonial legacies, weak institutional foundations, and concentrated power structures that hinder democratic development. Democratically consolidated states usually have historical trajectories marked by inclusive political reforms, rule of law, and the establishment of accountable governance systems. Key factors influencing these origins include economic conditions, social cleavages, and the interplay between local elites and external influences during critical junctures.
Key Characteristics of Authoritarian Regimes
Authoritarian regimes are characterized by centralized power, limited political pluralism, and restricted civil liberties, often maintained through coercive institutions like security forces and controlled media. They rely on elite cohesion and patronage networks to sustain authority while suppressing opposition and dissent. The persistence of authoritarianism contrasts with democratic consolidation, which requires institutionalized rule of law, competitive elections, and active civil society participation.
Indicators and Stages of Democratic Consolidation
Indicators of democratic consolidation include the stability of democratic institutions, widespread public support for democracy, and the rule of law consistently applied. Key stages involve the transition from authoritarian rule, the establishment of competitive elections, and the institutionalization of checks and balances. Authoritarian persistence is often characterized by weak political pluralism, restricted civil liberties, and the manipulation of electoral processes that hinder democratic consolidation.
Socioeconomic Factors Influencing Regime Stability
Socioeconomic factors such as income inequality, education levels, and economic development critically influence regime stability by shaping public support and political participation patterns. In authoritarian regimes, persistent poverty and limited social mobility often reinforce elite control and suppress democratic demands, while democratic consolidation benefits from a growing middle class and expanded access to education that foster civic engagement and accountability. Economic crises or stark disparities can destabilize both regimes, but democracies typically have stronger institutional mechanisms to manage tensions and implement reforms, enhancing their long-term resilience.
The Role of Political Institutions in Regime Durability
Political institutions critically shape regime durability by structuring power distribution, enabling authoritarian persistence through centralized control, or fostering democratic consolidation via checks and balances. Authoritarian regimes often rely on strong security apparatuses and controlled electoral systems to suppress opposition and maintain stability. In contrast, democratic consolidation depends on inclusive institutions that promote political competition, rule of law, and citizen participation, reinforcing regime legitimacy and resilience.
Civil Society’s Impact on Political Evolution
Civil society plays a crucial role in shaping political evolution by either sustaining authoritarian persistence or promoting democratic consolidation. Strong, autonomous civil society organizations enhance political participation, accountability, and government transparency, which are essential for democratic consolidation. In contrast, restricted or state-controlled civil societies often reinforce authoritarian regimes by limiting dissent and suppressing opposition voices, thereby sustaining authoritarian persistence.
External Influences: International Actors and Foreign Policy
External influences shape authoritarian persistence and democratic consolidation through strategic international actors and targeted foreign policy interventions. Authoritarian regimes often benefit from support by powerful states through military aid, economic investments, and diplomatic backing, reinforcing regime stability and limiting democratic reforms. Conversely, democratic consolidation is frequently propelled by multilateral organizations, conditional foreign aid, and international norms promoting transparency, human rights, and institutional reforms that pressure regimes toward democratization.
Case Studies: Successful Consolidation vs Persistent Authoritarianism
Case studies of successful democratic consolidation often highlight processes such as inclusive political institutions, strong rule of law, and active civil society engagement, as seen in post-apartheid South Africa and post-dictatorship Chile. In contrast, persistent authoritarianism cases like Belarus and Venezuela demonstrate entrenched political elites, restricted media freedom, and manipulated electoral systems that hinder democratic reforms. Comparative analysis of these cases underscores the critical role of institutional reforms and international support in shifting regimes towards sustainable democracy or maintaining authoritarian resilience.
Prospects and Challenges for Future Political Transformation
Authoritarian persistence often undermines democratic consolidation by restricting political freedoms, manipulating electoral processes, and suppressing civil society, which challenges the establishment of accountable governance. Prospects for future political transformation hinge on factors like increased civic engagement, international pressures for democratic reforms, and the resilience of opposition movements. However, persistent economic inequalities, institutional weaknesses, and external authoritarian support pose significant obstacles to sustainable democratic development.
Authoritarian persistence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com