Term-limited policies restrict the duration an individual can hold certain public offices, promoting political diversity and preventing power consolidation. These limits encourage fresh ideas while potentially hindering experienced leadership continuity. Discover how term limits impact governance and what they mean for your community in the following article.
Table of Comparison
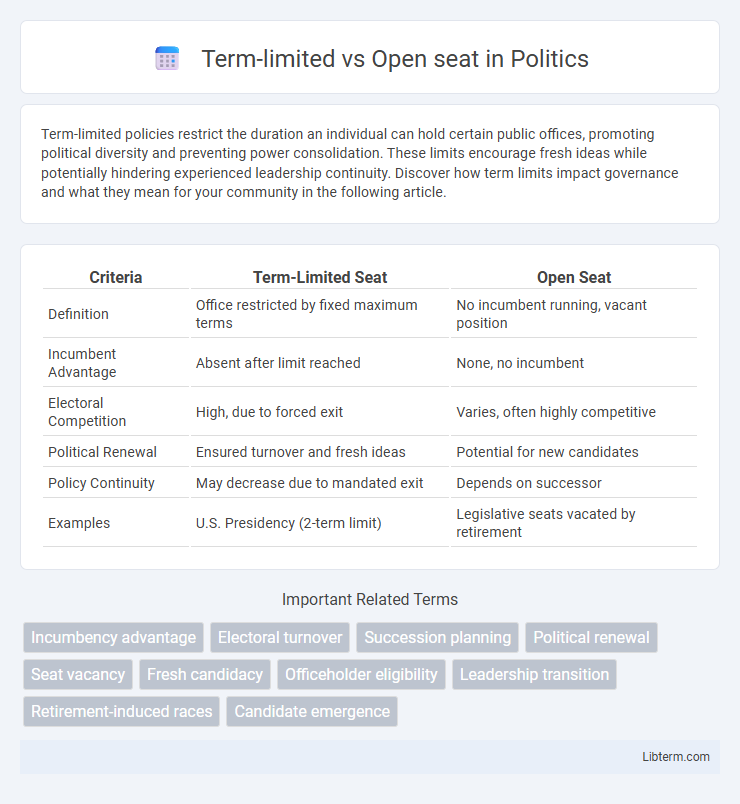
| Criteria | Term-Limited Seat | Open Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Office restricted by fixed maximum terms | No incumbent running, vacant position |
| Incumbent Advantage | Absent after limit reached | None, no incumbent |
| Electoral Competition | High, due to forced exit | Varies, often highly competitive |
| Political Renewal | Ensured turnover and fresh ideas | Potential for new candidates |
| Policy Continuity | May decrease due to mandated exit | Depends on successor |
| Examples | U.S. Presidency (2-term limit) | Legislative seats vacated by retirement |
Introduction to Term-Limited and Open Seats
Term-limited seats restrict elected officials to a fixed number of terms, promoting turnover and limiting incumbency advantages in legislative bodies. Open seats occur when no incumbent is running, often leading to more competitive elections and increased opportunities for new candidates to gain office. Understanding the differences between term-limited and open seats is essential for analyzing electoral dynamics and candidate strategies in political contests.
Defining Term-Limited Seats
Term-limited seats refer to political positions where elected officials can serve only a fixed number of consecutive terms, after which they must leave office. This restriction aims to promote political diversity and prevent incumbency entrenchment by ensuring regular turnover. In contrast, open seats arise when no incumbent is running, often creating competitive elections that attract multiple candidates.
Understanding Open Seats in Elections
The informal sector often lacks legal protections, social security, and minimum wage guarantees, exposing workers to exploitation and poor working conditions. In contrast, the formal sector provides regulated employment with enforced labor laws, social benefits, and access to healthcare and pensions, promoting worker stability and well-being. The disparity significantly impacts social equity, as informal workers face higher vulnerability without formal rights or institutional support.
Key Differences between Term-Limited and Open Seats
Term-limited seats restrict incumbents from running again after serving a specified number of terms, ensuring regular turnover and new candidate opportunities. Open seats occur when no incumbent is running, often resulting in more competitive elections and increased candidate diversity. The primary difference lies in incumbent eligibility: term limits enforce mandatory vacancies, while open seats arise from retirements, resignations, or incumbents seeking other offices.
Historical Overview of Term Limits in Politics
Term limits have shaped political dynamics since ancient Greece, with modern implementations influenced by U.S. presidential limits established in the 22nd Amendment of 1951. Historically, term-limited seats prevent incumbents from indefinite reelection, promoting political renewal and reducing entrenched power. Open seats, emerging when incumbents reach term limits or voluntarily exit, often generate competitive elections and opportunities for diverse candidates to enter the political arena.
Impact of Term-Limited Seats on Political Strategy
Term-limited seats significantly influence political strategy by creating frequent opportunities for new candidates to enter the race, reducing incumbency advantage and increasing electoral competitiveness. Political parties often allocate more resources and strategic efforts to open term-limited seats, anticipating higher voter volatility and the potential for shifting party control. This dynamic forces candidates to prioritize early campaigning, coalition-building, and voter outreach to capitalize on the unique electoral environment presented by term-limited positions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Open Seats
Open seats offer significant advantages, such as increased electoral competitiveness and greater opportunities for new candidates to enter the political arena without facing incumbents' advantages. However, disadvantages include potential voter uncertainty and the possibility of decreased accountability since no incumbent is held responsible for past performance. Open seats can also lead to fragmented party support, making election outcomes less predictable and sometimes less stable.
Effects on Voter Engagement and Turnout
Term-limited elections often increase voter engagement by creating predictable opportunities for new candidates, leading to higher turnout as voters anticipate fresh choices. Open seat races typically generate more competition and media coverage, which energizes the electorate and boosts participation rates. Both conditions disrupt incumbent advantage, fostering a dynamic political environment that encourages voter involvement.
Case Studies: Notable Term-Limited and Open Seat Races
The 2010 California gubernatorial race exemplifies a notable term-limited contest, where incumbent Arnold Schwarzenegger was ineligible to run, leading to a highly competitive open field won by Jerry Brown. In contrast, the 2018 Florida Senate race, an open seat following Marco Rubio's Senate bid for the presidency, showcased intense partisan mobilization resulting in Rick Scott's narrow victory. These case studies highlight how term limits create predictable vacancy-driven battles, whereas open seats often trigger dynamic electoral realignments and heightened voter engagement.
Future Trends in Term Limits and Open Seat Dynamics
Future trends in term limits reveal increasing legislative proposals aimed at balancing political renewal with experience retention, signaling shifting dynamics in governance structures. Open seat elections are expected to become more competitive as demographic changes and redistricting efforts reshape voter bases, intensifying candidate diversity and campaign strategies. Emerging data suggests that states adopting stricter term limits may experience higher turnover rates, influencing legislative effectiveness and party power distribution in the coming electoral cycles.
Term-limited Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com