Feminism advocates for equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender, challenging societal norms that have historically marginalized women. It explores various dimensions including social, political, and economic equality, aiming to dismantle systemic barriers. Discover how feminism continues to shape conversations about gender equality and impacts your daily life by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
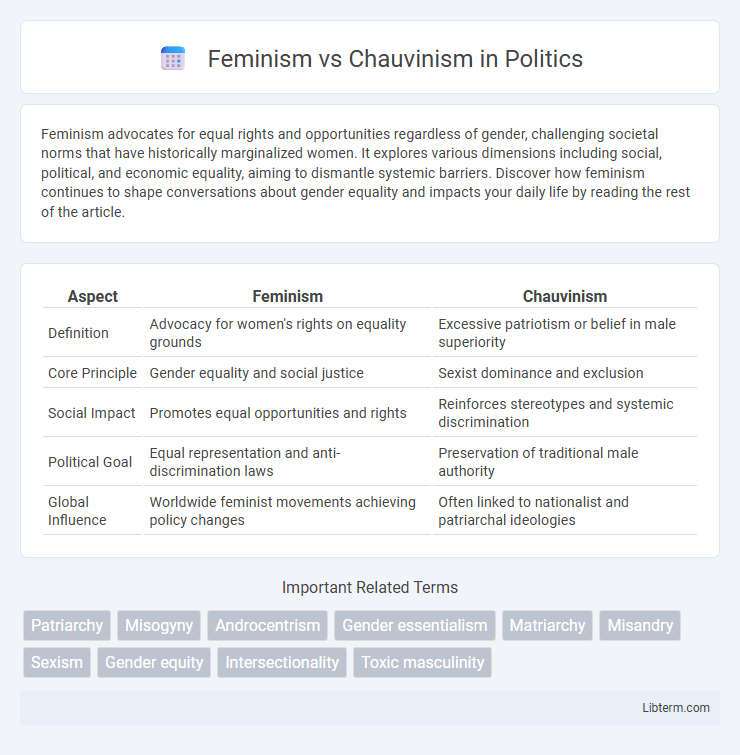
| Aspect | Feminism | Chauvinism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Advocacy for women's rights on equality grounds | Excessive patriotism or belief in male superiority |
| Core Principle | Gender equality and social justice | Sexist dominance and exclusion |
| Social Impact | Promotes equal opportunities and rights | Reinforces stereotypes and systemic discrimination |
| Political Goal | Equal representation and anti-discrimination laws | Preservation of traditional male authority |
| Global Influence | Worldwide feminist movements achieving policy changes | Often linked to nationalist and patriarchal ideologies |
Understanding Feminism: Core Principles and Goals
Feminism advocates for gender equality by challenging societal norms that perpetuate discrimination against women and marginalized genders. Core principles include the pursuit of equal rights, opportunities, and representation in political, economic, and social spheres. The movement seeks to dismantle patriarchal structures and promote intersectionality to address diverse experiences of oppression.
Defining Chauvinism: Origins and Modern Manifestations
Chauvinism originates from the excessive and aggressive patriotism associated with Nicolas Chauvin, a fervent supporter of Napoleon Bonaparte, evolving into a broader term for biased and prejudiced attitudes favoring one's own group. Modern manifestations of chauvinism include male chauvinism, characterized by the belief in male superiority and dominance, which manifests in workplace discrimination, social norms, and cultural stereotypes. Understanding chauvinism's historical roots and its contemporary expressions is essential to addressing gender inequalities and countering its influence in societal structures.
Historical Context: Feminism vs Chauvinism Through Time
Feminism, emerging prominently in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, sought gender equality and women's suffrage, challenging patriarchal norms entrenched in societies worldwide. Chauvinism, rooted in exaggerated male chauvinist attitudes, has historically perpetuated gender discrimination by promoting male dominance and undermining women's rights. The ongoing struggle between these ideologies reflects evolving social, cultural, and political shifts influencing gender roles from the Victorian era to modern feminist movements.
Key Differences Between Feminist and Chauvinist Ideologies
Feminism advocates for gender equality, promoting equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender, whereas chauvinism emphasizes the superiority of one gender over others, often leading to discrimination and bias. Feminist ideology challenges traditional power structures to empower marginalized genders, while chauvinist beliefs reinforce patriarchal dominance and social hierarchies. Understanding these key differences highlights the social and political implications of each stance on gender relations and human rights.
Gender Roles and Stereotypes in Society
Feminism challenges rigid gender roles and stereotypes that confine individuals based on their sex, advocating for equality and dismantling societal norms that promote female subordination. Chauvinism reinforces traditional masculine dominance and perpetuates stereotypes that limit women's opportunities and agency in various domains such as employment, politics, and family life. Addressing these contrasting perspectives is essential to promoting inclusive social structures that respect individual identity beyond prescribed gender expectations.
The Impact of Chauvinism on Social Progress
Chauvinism perpetuates social inequalities by reinforcing gender stereotypes and limiting opportunities for marginalized groups, thereby hindering social progress. The prevalence of chauvinistic attitudes in workplaces and institutions contributes to wage gaps, underrepresentation, and systemic discrimination. Overcoming chauvinism is essential for achieving gender equality and fostering inclusive social development.
How Feminism Challenges Traditional Power Structures
Feminism challenges traditional power structures by advocating for gender equality and dismantling patriarchal norms that have historically concentrated power in male hands. It promotes equal rights, opportunities, and representation for women in social, political, and economic spheres, thereby disrupting entrenched systems of male dominance. By questioning gender roles and power imbalances, feminism drives systemic change toward inclusivity and justice.
Contemporary Debates: Misconceptions and Myths
Contemporary debates on feminism vs chauvinism often reveal misconceptions that conflate gender equality advocacy with male dominance. Feminism seeks to dismantle systemic inequalities and promote equal rights, whereas chauvinism upholds patriarchal supremacy and gender bias. Addressing myths about feminism being anti-male is crucial for advancing informed discussions and fostering mutual understanding.
Promoting Equality: Strategies for Bridging Divides
Promoting equality between feminism and chauvinism requires implementing educational programs that emphasize mutual respect and gender equity while challenging stereotypes and biases. Engaging in open dialogues that encourage empathy and understanding can dismantle adversarial views, fostering collaboration towards shared societal goals. Policy reforms that enforce equal rights and opportunities further bridge divides by institutionalizing fairness across gender lines.
The Future of Gender Relations: Towards Mutual Respect
The future of gender relations hinges on transcending feminism and chauvinism by fostering mutual respect and equality between all genders. Emphasizing inclusive dialogue and equitable policies can dismantle systemic biases and promote shared empowerment. Sustainable progress depends on recognizing diverse perspectives and cultivating environments where respect and collaboration replace dominance and inequality.
Feminism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com