A partisan voter consistently supports a specific political party, prioritizing party loyalty over individual candidate policies or issues. This steadfast allegiance can influence election outcomes and shape political landscapes by reinforcing party dominance. Discover how partisan voting impacts democracy and your role in informed decision-making throughout the rest of this article.
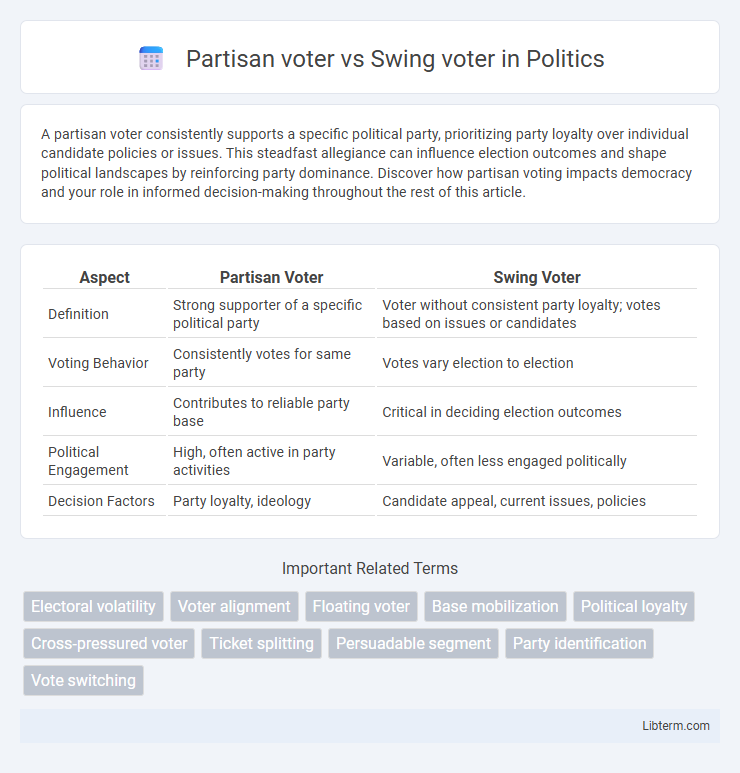
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Partisan Voter | Swing Voter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strong supporter of a specific political party | Voter without consistent party loyalty; votes based on issues or candidates |
| Voting Behavior | Consistently votes for same party | Votes vary election to election |
| Influence | Contributes to reliable party base | Critical in deciding election outcomes |
| Political Engagement | High, often active in party activities | Variable, often less engaged politically |
| Decision Factors | Party loyalty, ideology | Candidate appeal, current issues, policies |
Introduction to Voter Types
Partisan voters demonstrate consistent loyalty to a specific political party, often influenced by ideology, family tradition, or long-term identification. Swing voters lack firm allegiance and evaluate candidates or issues independently, making their vote unpredictable and highly sought after in competitive elections. Understanding these voter types is crucial for campaigns aiming to tailor strategies and effectively mobilize support.
Defining Partisan Voters
Partisan voters consistently support a single political party across multiple election cycles, exhibiting strong loyalty and ideological alignment that influences their voting behavior. These voters tend to prioritize party platforms, values, and candidates, often disregarding individual candidate characteristics or specific election issues. Understanding Partisan voters is crucial for political strategists, as their predictable voting patterns contrast sharply with the more variable and issue-driven preferences of swing voters.
Who Are Swing Voters?
Swing voters are individuals who do not consistently align with a single political party and can be persuaded to vote for different candidates in various elections. These voters represent a critical demographic that often decides the outcome of closely contested races due to their fluctuating political preferences. Understanding swing voters' concerns, values, and key issues is essential for targeted campaign strategies aiming to influence their decision-making process.
Demographics of Partisan and Swing Voters
Partisan voters typically exhibit strong affiliations with a political party, often aligning with consistent ideological beliefs found in older, more educated, and higher-income demographics. Swing voters, characterized by less predictable voting patterns, tend to be younger, more diverse in ethnicity, and encompass a broader range of socioeconomic backgrounds. Understanding these demographic distinctions helps political campaigns target messaging and outreach more effectively.
Voting Behavior Patterns
Partisan voters exhibit consistent loyalty to a single political party, driven by ideological alignment and long-term affiliation, resulting in predictable voting patterns. Swing voters display fluctuating preferences, influenced by candidate appeal, current issues, and campaign effectiveness, making their behavior less predictable and crucial in tight elections. Understanding these distinct voting behavior patterns enables political strategists to tailor their outreach and policy messaging effectively.
Impact on Election Outcomes
Partisan voters consistently support a single political party, creating a reliable voter base that stabilizes election outcomes and shapes party strategies. Swing voters, who shift their support between parties based on current issues or candidate appeal, play a pivotal role in determining election results, especially in closely contested districts or states. Their decisions can tip the balance in tight races, making them the primary target for campaign efforts and policy promises during election cycles.
Campaign Strategies for Each Group
Partisan voters, who consistently support a single party, respond well to campaign strategies emphasizing party loyalty, reinforcing core values, and mobilizing through targeted messaging on key policy issues. Swing voters, characterized by their tendency to change preferences between elections, require campaigns to focus on persuasive communication, emphasizing moderate positions and addressing immediate concerns such as the economy and healthcare. Micro-targeting techniques and tailored advertising optimize outreach to each group's unique motivations, maximizing voter turnout and influence.
Media Influence on Voter Allegiance
Partisan voters tend to consume media that reinforces their existing political beliefs, resulting in stronger allegiances due to confirmation bias and selective exposure. Swing voters remain more susceptible to varied media narratives and persuasive messaging, making them key targets for political campaigns aiming to shift voter preferences. Media influence on swing voters is often amplified through targeted advertising and framing techniques that highlight candidate strengths or opponent weaknesses.
Historical Trends in Voter Loyalty
Historical trends reveal that partisan voters consistently support their chosen political party, reflecting strong ideological commitment and contributing to electoral stability. Swing voters exhibit fluctuating preferences influenced by contemporary issues, candidate appeal, and economic conditions, often determining the outcome in closely contested elections. Data from past decades show increasing polarization, yet swing voters remain crucial in tipping the balance during pivotal elections such as U.S. presidential races.
The Future of Partisan and Swing Voting
The future of partisan and swing voting is shaped by increasing political polarization and the rise of data-driven campaign strategies targeting voter behavior. Partisan voters remain highly loyal to their political parties, while swing voters continue to play a crucial role in closely contested elections by determining the balance of power. Advances in voter analytics and micro-targeting are expected to refine how campaigns engage swing voters, potentially diminishing their proportion as political identities solidify.
Partisan voter Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com