A coalition government forms when multiple political parties cooperate to establish a majority, combining their seats in the legislature. This arrangement often requires negotiation and compromise to maintain stability and implement policies effectively. Explore the rest of the article to understand how coalition governments impact political decision-making and governance.
Table of Comparison
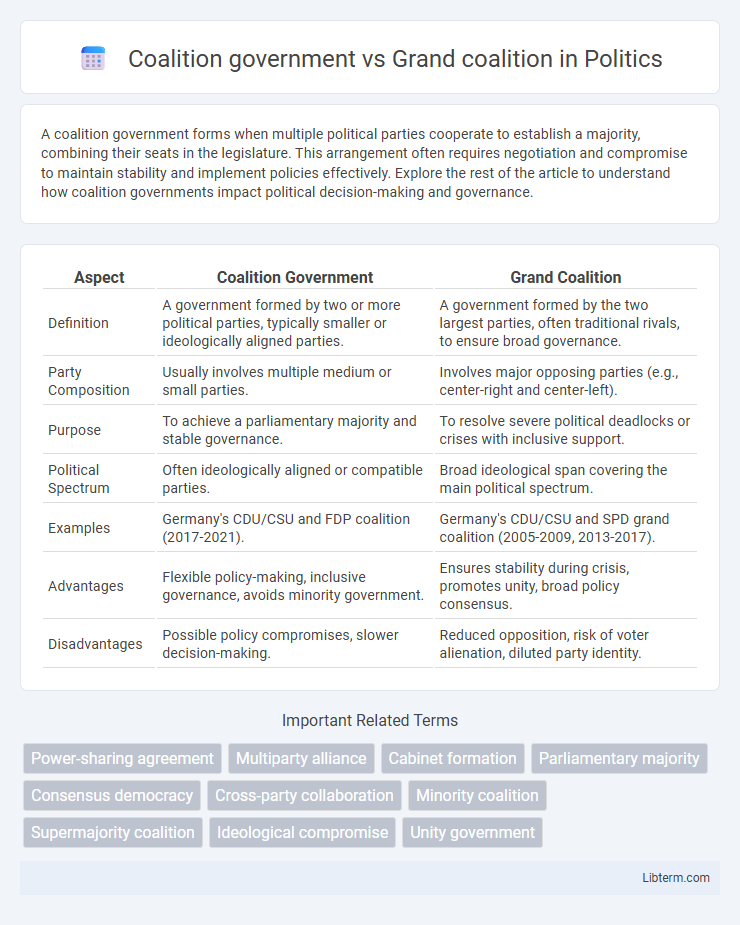
| Aspect | Coalition Government | Grand Coalition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A government formed by two or more political parties, typically smaller or ideologically aligned parties. | A government formed by the two largest parties, often traditional rivals, to ensure broad governance. |
| Party Composition | Usually involves multiple medium or small parties. | Involves major opposing parties (e.g., center-right and center-left). |
| Purpose | To achieve a parliamentary majority and stable governance. | To resolve severe political deadlocks or crises with inclusive support. |
| Political Spectrum | Often ideologically aligned or compatible parties. | Broad ideological span covering the main political spectrum. |
| Examples | Germany's CDU/CSU and FDP coalition (2017-2021). | Germany's CDU/CSU and SPD grand coalition (2005-2009, 2013-2017). |
| Advantages | Flexible policy-making, inclusive governance, avoids minority government. | Ensures stability during crisis, promotes unity, broad policy consensus. |
| Disadvantages | Possible policy compromises, slower decision-making. | Reduced opposition, risk of voter alienation, diluted party identity. |
Introduction to Coalition Governments
Coalition governments form when multiple political parties collaborate to achieve a parliamentary majority, often driving policy compromises and shared governance. A grand coalition involves major political parties, typically from opposite ends of the political spectrum, joining forces to manage national crises or significant legislative agendas. Understanding these distinctions highlights how coalition governments balance political diversity while grand coalitions emphasize stability during critical periods.
Defining Grand Coalitions
Grand coalitions are political alliances formed between the major parties, often the largest and second-largest, to create an overwhelming majority government. Unlike typical coalition governments that may comprise several smaller or ideologically similar parties, grand coalitions bridge significant ideological divides to ensure stable governance during periods of crisis or national importance. This arrangement often leads to shared power across the political spectrum, prioritizing consensus and national unity over partisan competition.
Key Differences Between Coalition and Grand Coalition
Coalition governments typically consist of multiple political parties collaborating to form a majority, often including smaller parties that align on key policy areas, while grand coalitions involve major opposing parties joining forces, usually the largest left- and right-leaning parties, to ensure stability during crises or politically fragmented parliaments. Coalition governments emphasize ideological compatibility and policy compromise among diverse parties, whereas grand coalitions prioritize consensus and broad-based governance despite significant ideological differences. The scale and political context of grand coalitions distinguish them from ordinary coalitions, which are more common in parliamentary systems with proportional representation.
Historical Examples of Coalition Governments
The 1945 United Kingdom coalition government between Winston Churchill's Conservatives and Clement Attlee's Labour Party exemplifies a successful coalition formed during wartime to unify diverse political forces. Germany's post-World War II Grand Coalition, especially under Chancellor Angela Merkel from 2013 to 2021, involved the two largest parties--the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) and the Social Democratic Party (SPD)--collaborating to stabilize governance. Historical coalition governments often arise during crises or fragmented political landscapes, whereas grand coalitions specifically refer to alliances between major parties usually positioned as rivals in a parliamentary system.
Notable Grand Coalition Case Studies
Notable grand coalition case studies include Germany's CDU-SPD alliances, which formed in 2005, 2013, and 2018 to ensure political stability during times of economic or social challenges. Italy's 2013 grand coalition between the Democratic Party and the People of Freedom party demonstrated a cross-ideological partnership to address governmental deadlock. These cases highlight how grand coalitions, involving major parties across the political spectrum, differ from typical coalition governments by seeking broad consensus during national crises.
Advantages of Coalition Governments
Coalition governments enhance political stability by uniting multiple parties, promoting diverse representation and inclusive decision-making processes that reflect broader public interests. These governments often improve policy innovation through collaboration and negotiation among various political groups, reducing the likelihood of extreme policy swings. Shared power in coalition governments helps maintain democratic balance and accountability, minimizing domination by a single party and encouraging compromise-driven governance.
Challenges Facing Grand Coalitions
Grand coalitions, often formed between major political parties to ensure stable governance, face challenges such as policy gridlock due to ideological differences and power-sharing conflicts. The necessity to balance diverse party agendas can result in diluted policy decisions, reducing government effectiveness and public trust. Managing internal dissent while maintaining a unified front often strains coalition cohesion, complicating legislative processes and long-term planning.
Political Stability and Power Sharing
Coalition governments involve multiple political parties collaborating to form a majority, ensuring political stability through negotiated power sharing and policy compromise, which often leads to more representative governance. Grand coalitions unite the two largest parties, typically from opposite sides of the political spectrum, stabilizing the political environment during crises by concentrating power and reducing partisan conflict. Both models enhance stability but differ in their approach to power distribution, with coalitions promoting broader inclusivity and grand coalitions focusing on unified leadership.
Policy Outcomes: Coalition vs Grand Coalition
Coalition governments often produce more diverse policy outcomes by balancing the interests of multiple smaller parties, leading to compromises that reflect a broader spectrum of voter preferences. Grand coalitions, formed by major opposing parties, typically result in more centrist and stable policy decisions, emphasizing consensus over innovation. This can limit radical reforms but ensures continuity and reduces political polarization in policy implementation.
Future Trends in Multi-Party Governance
Coalition governments, typically formed by two or more parties to achieve a parliamentary majority, are evolving with increasing complexity as multi-party systems expand globally; future trends indicate a rise in issue-based alliances rather than strict ideological coalitions. Grand coalitions, involving major parties across the political spectrum, may decrease in frequency due to voter polarization and the demand for clearer policy alternatives, despite their role in stabilizing governance during crises. Advancements in digital platforms and data analytics are expected to enhance coalition negotiations and governance transparency, promoting more dynamic and responsive multi-party collaborations.
Coalition government Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com