A straw poll is an informal survey used to gauge opinions or preferences quickly among a group. It helps identify popular choices without the rigor of official voting procedures. Explore the rest of the article to understand how straw polls influence decision-making and their practical applications.
Table of Comparison
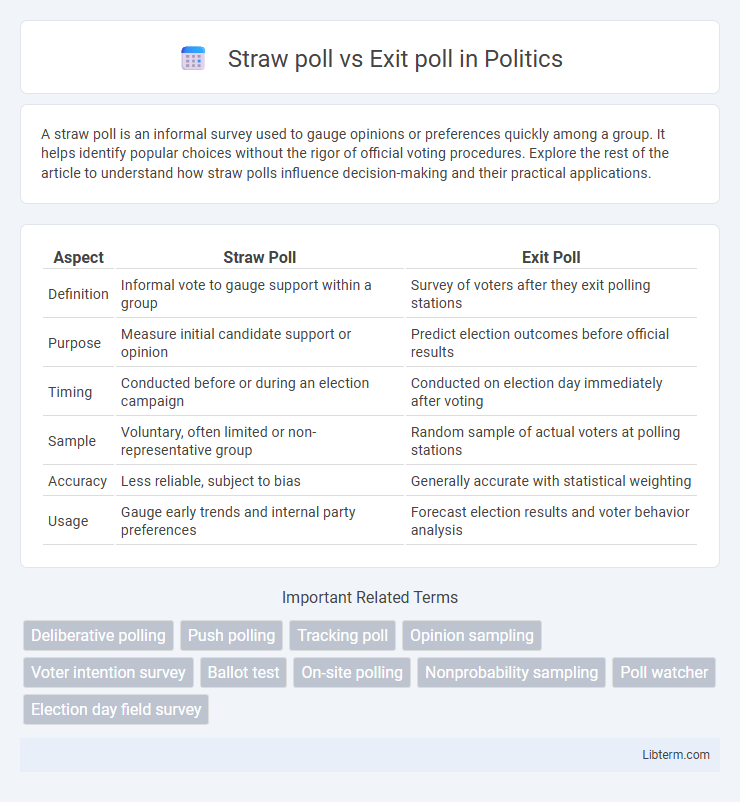
| Aspect | Straw Poll | Exit Poll |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Informal vote to gauge support within a group | Survey of voters after they exit polling stations |
| Purpose | Measure initial candidate support or opinion | Predict election outcomes before official results |
| Timing | Conducted before or during an election campaign | Conducted on election day immediately after voting |
| Sample | Voluntary, often limited or non-representative group | Random sample of actual voters at polling stations |
| Accuracy | Less reliable, subject to bias | Generally accurate with statistical weighting |
| Usage | Gauge early trends and internal party preferences | Forecast election results and voter behavior analysis |
Understanding Straw Polls
Straw polls are informal, non-scientific surveys conducted to gauge the general opinion of a specific group, often within a political context, without strict sampling methods. Unlike exit polls that collect data from voters immediately after they cast ballots to predict election outcomes, straw polls mainly measure preliminary support or opinions before official voting occurs. These polls serve as quick indicators of trends but lack the accuracy and reliability of scientifically designed polling techniques.
What Are Exit Polls?
Exit polls are surveys conducted immediately after voters leave polling stations, designed to predict election outcomes by collecting data on voter choices and demographics. These polls provide real-time insights into voting behavior and help validate official results by comparing anticipated trends with actual votes. Their accuracy depends on sample size, polling methodology, and voter honesty, making them crucial tools in modern electoral analysis.
Key Differences Between Straw Polls and Exit Polls
Straw polls gauge general public opinion before an election by sampling volunteer respondents, while exit polls collect data from voters immediately after they have cast their ballots at polling stations. Straw polls lack scientific rigor and often involve self-selected participants, making them less reliable, whereas exit polls use structured sampling techniques to predict election outcomes with higher accuracy. Exit polls provide real-time insights into voting patterns and demographics, whereas straw polls primarily measure preliminary candidate popularity.
Purpose and Objectives of Straw Polls
Straw polls serve as informal surveys aimed at gauging public opinion or preferences within a specific group, often used to predict outcomes or test reactions before formal decisions or elections. Their objective is to quickly capture voter sentiment or participant views in scenarios such as political caucuses, conventions, or local gatherings without official weighting or statistical rigor. Unlike exit polls conducted on election day to forecast results, straw polls primarily focus on identifying trends and measuring enthusiasm among a smaller, self-selected population.
How Exit Polls Are Conducted
Exit polls are conducted by interviewing voters immediately after they have cast their ballots at polling stations, using a representative sampling method to capture demographic and geographic diversity. Trained pollsters approach voters leaving the polling place, asking standardized questions about their vote choice and demographic information while ensuring anonymity. Statistical weighting and data modeling are applied to adjust for sampling biases and to produce projections of election outcomes before official results are announced.
Accuracy and Reliability: Straw vs. Exit Polls
Exit polls generally offer higher accuracy and reliability compared to straw polls because they are conducted immediately after voters have cast their ballots at polling stations, capturing actual voter behavior. Straw polls rely on voluntary, non-random participants, which often leads to sampling bias and less representative results. The methodological rigor of exit polls, including structured sampling and timing, enhances their predictive validity in election outcomes.
Real-World Applications of Straw Polls
Straw polls are informal surveys used to gauge preliminary opinions or preferences within a specific group, often applied in political campaigns to test candidate popularity or policy support before official voting. Their real-world applications include predicting election outcomes in party caucuses, shaping campaign strategies by identifying voter priorities, and facilitating quick decision-making in organizational meetings or conventions. Unlike exit polls that collect data from actual voters post-election, straw polls provide early insights which can influence media narratives and campaign momentum.
Impact of Exit Polls on Election Results
Exit polls influence public perception by providing early indications of election outcomes, potentially shaping voter behavior in subsequent regions. They offer detailed demographic data and voting patterns, aiding political analysts in forecasting final results and strategy adjustments. However, inaccuracies or premature projections can lead to misinformation and affect voter turnout or confidence in the electoral process.
Limitations and Challenges of Both Poll Types
Straw polls often face limitations due to non-random, self-selecting participants, which can lead to significant sampling bias and unrepresentative results. Exit polls encounter challenges such as respondents' reluctance to participate or inaccurate answers, impacting data reliability and voter confidentiality. Both methods struggle with timing constraints and the inability to fully capture the diverse demographics of the electorate, affecting the accuracy of their predictive insights.
Choosing the Right Poll for Your Needs
Straw polls offer quick, informal snapshots of public opinion, ideal for initial reactions or gauging interest in specific ideas without the need for complex methodology. Exit polls provide more accurate insights by surveying voters immediately after they leave polling stations, helping predict election outcomes and analyze voter behavior with higher reliability. Choosing the right poll depends on whether the goal is rapid, exploratory feedback or statistically robust data for decision-making and forecasting.
Straw poll Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com